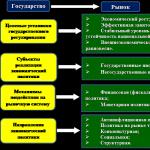
The budget classification of the Russian Federation is a grouping of income, expenses and sources of financing deficits in the budgets of the budget system of the Russian Federation, used for the preparation and execution of budgets, preparation of budget reporting, ensuring comparability of budget indicators of the budget system of the Russian Federation.
The budget classification is unified and is used in the preparation, approval and execution of budgets of all levels and in the preparation of consolidated budgets of all levels.
The value of the budget classification in the budgetary system of the state lies in the fact that with its help it becomes possible to monitor the movement of budgetary resources. Based on the factor analysis of budget items, an analysis of the relevant indicators is carried out, which makes it possible to formulate conclusions and proposals on the formation and use of budget funds. In addition, it greatly simplifies the consolidation of estimates and budgets into common consolidated documents. The existence of a budget classification implies the assignment of a specific code to each institution and organization.
The determination of the principles of appointment, the structure of the codes of the budget classification of the Russian Federation, as well as the assignment of codes to the constituent parts of the budget classification of the Russian Federation, which, in accordance with this Code, are uniform for the budgets of the budgetary system of the Russian Federation, are carried out by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
The budget classification of the Russian Federation includes:
classification of budget revenues;
classification of budget expenditures;
classification of sources of financing budget deficits;
classification of operations of public legal entities (classification of operations of the public administration sector).
The classification of budget revenues of the Russian Federation is a grouping of budget revenues of all levels and is based on the legislative acts of the Russian Federation that determine the sources of formation of budget revenues of all levels. Income groups consist of income items that combine specific types of income according to sources and methods of their receipt.
The functional classification of expenditures of the budgets of the Russian Federation is a grouping of expenditures of budgets of all levels, reflecting the direction of finances for the implementation of the main functions of the state. The first level of this classification are sections consisting of subsections specifying the direction of finance for the implementation of state activities in a certain area and forming its second level.
The classification of sources of financing the budget deficits of the Russian Federation is a grouping of borrowed funds attracted by the Government of the Russian Federation, executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local governments to finance the deficits of the corresponding budgets.
To clarify the role and significance of budget expenditures in the economic life of society, they are classified according to certain criteria.
The basis of the budget classification is such a grouping of indicators that gives an idea of the socio-economic, departmental and territorial aspect of the formation of income and the direction of funds, their composition and structure. Clarity and clarity of groupings is one of the most important requirements for budget classification.
The value of the budget classification lies in the fact that the skillful use of data grouped according to the elements of the budget classification allows you to see the real picture of the movement of budget resources and actively influence the course of economic and social processes. Comparison of planned and reporting data, comparison and analysis of relevant indicators make it possible to draw reasonable conclusions and proposals on the formation and use of budget funds, the concentration of basic financial resources in key areas of economic and social development.
Detailing, grouping incomes and expenses make it easier to check the data included in the budget, compare the estimates of homogeneous departments, institutions of territorial budgets for several years, determine the dynamics of receipts and the share of various incomes and expenses or the degree of satisfaction of any needs.
The classification creates conditions for combining estimates and budgets into general codes, facilitates their consideration and economic analysis, simplifies control over budget execution, over the full and timely accumulation of funds, over their use for their intended purpose. It makes it possible to compare revenues with expenditures according to reports on budget execution, which contributes to the observance of financial discipline, economical spending of funds, and control over the implementation of financial plans.
Given the independence of all parts of the budget system, the classification provides the basis for a unified methodological approach to the preparation and execution of all types of budgets, for comparability of budget indicators in the sectoral and territorial context.
The budget classification is mandatory for all institutions and organizations and is built in accordance with the requirements defined by the budget legislation of the Russian Federation.
Changes that have taken place in budget practice and are associated with changes in the system of state structure and management, with the independence of all types of budgets, the expansion of the rights of state and local governments in the preparation and execution of their budgets, changes in the revenue and expenditure parts of budgets, as well as the decoding of individual articles income and expenditure, required the introduction of a new budget classification.
The most important requirement for the new classification was simplicity, clarity and a clearer reflection of the sources of budget revenues and areas of expenditure. It was necessary to give a more detailed breakdown of the divisions of the classification, especially in terms of spending. An important task of the new classification was to ensure the international comparability of the composition and structure of indicators of the revenue and expenditure parts of the budget, their true content (primarily this applied to indicators of budget expenditures).
In accordance with the Law of the Russian Federation "On the budget classification of the Russian Federation" dated August 15, 1996, the following classifications of budget expenditures are in force in Russia.
Functional classification of expenditures of the budgets of the Russian Federation - a grouping of expenditures of budgets of all levels, reflecting the direction of finances for the implementation of the main functions of the state.
The first level of this classification consists of the following sections:
public administration and local self-government;
judicial branch;
International activity;
national defense;
law enforcement and security;
fundamental research and promotion of scientific and technological progress;
industry, energy and construction industry;
agriculture and fisheries;
protection of the natural environment and natural resources, hydrometeorology, cartography and geodesy, standardization and meteorology;
transport, road facilities, communications and informatics;
development of market infrastructure;
housing and communal services, urban planning;
prevention and liquidation of consequences of emergencies and natural disasters;
education;
culture and art, cinematography;
mass media;
health care and physical culture;
social politics;
service and repayment of public debt;
replenishment of state stocks and reserves;
regional development;
disposal and elimination of weapons, including the implementation of international treaties;
other expenses.
The second level of classification - subsections specifying the direction of budget allocations for the implementation of the activities of state and local authorities in a particular area. For example, the section "Housing and communal services, urban planning" (code 1200) has the following subsections:
housing construction;
housing;
public utilities;
architecture and urban planning;
other structures of public utilities.
Economic classification of budget expenditures of the Russian
Federations - grouping the expenditures of the budgets of all levels according to their economic content.
The classification includes the following sections:
current expenses;
capital expenditures;
granting loans minus repayment.
Sections are divided into subsections:
purchase of goods and payment for services;
payment of interest;
subsidies and current transfers;
capital investments in fixed assets;
creation of state stocks and reserves;
acquisition of land and intangible assets;
capital transfers;
provision of government loans.
In turn, subsections include types of expenses in which cost items are allocated.
The distribution of budget expenditures by economic content into four levels can be illustrated by the example of capital expenditures:
capital expenditures;
capital investment in fixed assets;
capital construction;
housing construction;
. construction of production facilities.
Current budget expenditures are part of the expenditures that ensure the current functioning of public authorities, local governments, budgetary institutions, the provision of state support to other budgets and individual sectors of the economy in the form of grants, subsidies and subventions. These expenditures include expenditures on public consumption (maintenance of economic and social infrastructure, public sectors of the economy, purchases of goods and services of a civil and military nature, current expenses of public institutions), current subsidies to lower authorities, public and private enterprises, transfer payments, interest payments public debt and other expenses. Basically, these costs correspond to the costs reflected in the operating budget.
Capital expenditures of the budget are the monetary costs of the state associated with the financing of innovation and investment activities. They include: expenses intended for investments in existing and newly created legal entities in accordance with the approved investment program, expenses for major repairs, expenses during which state and municipal property is created or increased. Most of these costs are usually reflected in the development budget.
In addition, as an independent direction of spending budget funds within the economic classification, the costs of providing loans are also allocated, minus the funds received for their repayment.
Departmental classification of federal budget expenditures - a grouping of expenditures that reflects the distribution of budget allocations among direct recipients of funds from the federal budget, and within their budgets - by targeted items and types of expenditures.
The first level of this classification is a list of direct recipients of funds from the federal budget. These are ministries, departments, organizations, each of which has its own code.
The second level is the classification of target items of expenditures of the federal budget, reflecting funding for specific areas of activity of direct recipients of funds from the federal budget in certain sections and subsections of the functional classification of expenditures of the budgets of the Russian Federation. For example:
maintenance of deputies of the State Duma and their assistants;
ensuring the activities of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation;
procurement of weapons and military equipment;
conducting statistical surveys and censuses, etc.
The third level is the classification of types of federal expenditures.
budget, detailing the direction of financing by target items.
On the basis of a unified budget classification, the constituent entities of the Russian Federation develop their own budget classifications, which are more detailed and linked to specific types of expenses.
The representative bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation of Local Self-Government approve departmental classifications of the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local budgets - groupings of expenditures of regional and local budgets, reflecting the distribution of budgetary appropriations by direct recipients of funds from the respective budgets in accordance with the organization of the system of executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local self-government.
Budget classification represents a grouping of incomes and expenditures of budgets of all levels, as well as sources of financing their deficits. It provides comparability of indicators of all budgets. With its help, the systematization of information on the formation of budget revenues and the implementation of expenditures is achieved.
The federal law "On the budget classification of the Russian Federation" was adopted by the State Duma of the Russian Federation on June 7, 1996. At present, this law is in force with amendments and additions adopted by federal law No. 115-FZ of August 5, 2000.
The budget classification of the Russian Federation includes:
- classification of budget revenues;
- classification of budget expenditures;
- classification of funding sources;
- classification of operations of public legal entities (hereinafter referred to as the classification of operations of the public administration sector).
- sources of internal financing of budget deficits;
- sources of external financing of the federal budget deficit;
- types of state internal debts of the Russian Federation, subjects of the Russian Federation, municipalities;
- RF types.
Budget classification of income
The classification of budget revenues is a grouping of budget revenues of all levels of the Russian Federation.
Incomes of budgets of all levels are classified into groups, subgroups, articles and sub-articles.
The classification of income provides for the following groups: Further detailing of income is carried out by subgroups, items and sub-items of the budget classification, for example:Such detail allows to take into account receipts to the budgets of all types of income provided for by law. For each of them, an independent code is provided in the budget classification.
Budget classification of expenditures
Cost classification carried out in several ways:
- functional the classification reflects the allocation of budget funds to the implementation of the main functions of the state (management, defense, etc.). (Section → Subsection → Target items → Types of expenses).
- Departmental the classification of budget expenditures is directly related to the management structure, it reflects the grouping of legal entities that receive budgetary funds. (The main managers of budget funds).
- Economic the classification shows the division of state expenditures into current and capital, as well as wages, material costs, and the purchase of goods and services. (Expenditure category → Groups → Subject items → Sub-items)
Functional classification of budget expenditures
It is a grouping of expenditures of budgets of all levels of the budget system of the Russian Federation and reflects the expenditure of funds for the implementation of the main ones.
The functional classification of expenses has four levels: sections; subsections; targeted articles; types of expenses.
In particular, the functional classification provides for the following sections (Code - Name):- 0100 - State administration and local self-government
- 0200 - Judiciary
- 0300 - International activities
- 0400 - National Defense
- 0500 - Law enforcement and state security
- 0600 - Basic research and promotion of scientific and technological progress
- 0700 - Industry, energy and construction
- 0800 - Agriculture and fishing
- 0900 - Protection of the natural environment and natural resources, hydrometeorology, cartography and geodesy
- 1000 - Transport, road facilities, communications and informatics
- 1100 - Development of market infrastructure
- 1200 - Housing and communal services
- 1300 - Prevention and elimination of consequences of emergencies and natural disasters
- 1400 - Education
- 1500 - Culture, art and cinematography
- 1600 - Media
- 1700 - Health and physical culture
- 1800 - Social policy
- 1900 - Servicing the public debt
- 2000 - Replenishment of state stocks and reserves
- 2100 - Financial assistance to budgets of other levels
- 2200 - Utilization and elimination of weapons, including the implementation of international treaties
- 2300 - Mobilization preparation of the economy
- 2400 - Exploration and use of outer space
- 3000 - Other expenses
- 3100 -Target budget funds
Based on the above functional classification, budgets of all levels are built. It is clear that this takes into account the specifics of the budget of a particular level. The full functional classification is used for.
Departmental classification of budget expenditures
Departmental classification budgets is a grouping of expenses by recipients of budgetary funds. The list of recipients of funds from the federal budget is approved by law for the next year.
Departmental classifications of the budgets of the subjects of the Federation and local budgets are approved by the authorities of the subjects of the Federation and local governments, respectively.
An example of a functional classification of expenses by 4 levels:
Economic classification of budget expenditures
Economic classification budget expenditures is a grouping of expenditures of budgets of all levels of the budget system of the Russian Federation according to their economic content. It reflects the types of financial transactions carried out in the performance of state bodies of their tasks. The economic classification includes groups, subgroups, subject items, subitems and cost elements.
The expense groups are:|
Name |
|
|
Current expenses- this is a part of budget expenditures that ensures the current functioning of public authorities, budgetary institutions, etc. The category "Current expenses" includes the following groups: purchases of goods and services; interest payments; subsidies and current transfers; payment for services for the recognition of property rights abroad. |
|
|
Capital expenditure- this is a part of budget expenditures that provides innovation and investment activities. A development budget can be allocated as part of capital expenditures. Capital expenditures have the following groups: capital investments in fixed assets, the creation of state stocks and reserves, the acquisition of land and intangible assets, capital transfers. |
|
|
Providing loans (budget loans) |
The economic classification of expenditures of the budgets of the Russian Federation has been transformed into a classification of public sector operations. It determines the direction of budget revenues and expenditures, depending on the economic content of operations carried out in the public administration sector.
The classification of general government transactions is a grouping of transactions based on their economic content.
Within this classification, operations of the general government sector are divided into current (income and expenses), investment (operations with non-financial assets) and financial (operations with financial assets and liabilities).
The classification of general government transactions consists of the following groups:
- 100 Income;
- 200 Expenses;
- 300 Receipt of non-financial assets;
- 400 Disposal of non-financial assets;
- 500 Receipt of financial assets;
- 600 Disposal of financial assets;
- 700 Increase in liabilities;
- 800 Reducing liabilities.
Groups are detailed by articles and sub-articles. The more detailed analytical codes provided in this document are not general government transaction classification codes, but are intended solely for the purpose of structuring the text of these Guidelines.
Classification of expenditures of the budgets of the Russian Federation for public sector operations (Codes and names of articles and sub-items)Classification of budget expenditures- grouping of expenditures of budgets of all levels, reflecting the direction of budgetary funds for the performance by units of the public administration and local government sector of the main functions and the solution of socio-economic problems.
The classification of expenses consists of the following elements:
1) code of the main manager of budgetary funds;
2) code of the section, subsection, target item and type of expenses;
3) classification code for operations of the general government sector related to budget expenditures.
| chief manager of budgetary funds | chapter | subsection | target article | program | subroutine | type of expenses | OSGU code related to expenses | ||||||||||||
Chief Budget Manager- a body of state power or local self-government that has the right to distribute budgetary funds between subordinate (subordinate) to it managers or recipients.
The classification of budget expenditures contains 11 sections reflecting the direction of funds for the implementation of the main functions of the state. Sections are divided into 95 subsections.
Separate sections:
01 national issues
02 national defense
03 national security and law enforcement
04 national economy
06 environmental protection
07 education
08 culture, cinematography, media
09 health, physical education and sports
10 social policy
11 intergovernmental transfers.
Target article provides a binding of budget expenditures to specific areas of activity within the subsection. Further detailing of expenditures is carried out by programs and subprograms.
The type of expenses deciphers the direction of funds within each target item.
The OSGU code for operations related to expenses consists of a group, an article and a sub-article.
The main expenses of the budgetary organization.
In carrying out the functions assigned to them, budgetary organizations spend the budgetary appropriations allocated to them and the incoming extrabudgetary funds in accordance with the estimates being developed, which, in turn, are compiled in accordance with the current budget classifications.
In accordance with the OSGU Classification, the main expenses of budgetary organizations are mainly included in groups 200, 300.
Group I. 200 Expenses. This group is detailed by articles 210-260, 290, which group operations related to budget expenditures.
Art. 210 Wages and accruals on payroll payments. The article includes sub-articles 211-213.
211 Salary. This sub-item includes labor costs on the basis of agreements (contracts) and in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on state (municipal) service, labor legislation.
212 Other payments. This sub-item includes expenses for paying additional payments and compensations due to the terms of the employment contract, the status of military personnel and persons equated to them, as well as the status of prosecutors, judges, deputies, and other officials in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation (compensation payments, compensation for partial payment utilities, books, daily allowance).
213 Accruals on wage payments. Expenses for paying insurance premiums to state social funds, insurance tariff contributions for compulsory social insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases (payments from extra-budgetary funds)
Art. 220 Acquisition of works, services. This article is detailed in subarticles 221-226.
221 Communication services. Expenses for payment of contracts for the purchase of communication services for state (municipal) needs.
222 Transport services. Expenses for payment of contracts for the purchase of transport services for state (municipal) needs.
223 Utilities.
224 Rent for the use of property.
225 Works, services for the maintenance of property (repair of furniture, premises, overhaul)
226 Other works, services (payment for accommodation on a business trip, laundry, sanitation, software products)
II Group. 300 Receipt of non-financial assets. This group is detailed by articles 310-340, which group operations related to the acquisition, creation of objects of non-financial assets.
Art. 310 Increase in the value of property, plant and equipment. This article includes the costs of paying for contracts for the construction, acquisition (manufacturing) of objects related to fixed assets into state, municipal ownership, as well as for the reconstruction, technical re-equipment, expansion and modernization of fixed assets owned by state, municipal property received in rent or free use.
Art. 320 Increase in the value of intangible assets. This article includes the costs of paying for contracts for the acquisition of exclusive rights to the results of intellectual activity or means of individualization into state, municipal property, including:
Works of science, literature and art;
Scientific developments and inventions, industrial designs and utility models, breeding achievements;
Trademarks and service marks;
Know-how and objects of related rights;
Software and databases for computers;
Other intangible assets.
Art. 330 Increase in the value of non-produced assets. This article includes expenses for increasing the value of non-produced assets in state, municipal ownership that are not products of production (land, resources, subsoil, etc.), the ownership rights to which must be established and legally fixed.
Art. 340 Increase in the cost of inventories. This article includes the costs of paying for contracts for the acquisition (manufacturing) of objects of material reserves that are not related to fixed assets (food rations for military personnel and persons equated to them, building materials, timber materials, spare parts and components for objects of fixed assets) into state, municipal property. funds, returnable and exchangeable containers, books, brochures, catalogs not intended for acquisition of the library fund, other printed materials (except for printed materials and periodicals (newspapers, magazines)).
Planning expenses in a budgetary organization.
The main goal of cost planning in budgetary institutions is financial support for the effective operation of the institution and its structural divisions. To achieve this goal, it is necessary:
Organization of medium-term and annual planning of the institution's activities;
Coordination of the work of various departments of the institution for the provision of services, attraction and use of budgetary and extrabudgetary sources of funding;
Evaluation of the effectiveness of certain types of activities provided by the institution;
Control over the receipt and expenditure of budgetary and extrabudgetary funds by the founder and institution.
Financial planning in budgetary institutions is based on the following principles:
Completeness of reflection of income and expenses;
Target nature of expenses;
Separation of expenses;
Personal responsibility.
The financial planning system includes objects and subjects of planning. Planning objects are cash flows. Planning subjects- the head of the institution, the planning and financial service, the responsibility centers of the institution. Responsibility Center is a subdivision of an institution, a direction of its activity or an individual, for which planning and control are carried out.
Financial planning in a budgetary organization consists of a number of stages:
1) coordination with the founder of activities for the provision of services;
2) assessment of the use of available labor, material and financial resources for the provision of budgetary services and identification of resource reserves that can be directed to the implementation of extrabudgetary activities of the institution;
3) the choice of areas in which the institution is granted the right to carry out activities related to the attraction and expenditure of extrabudgetary funds;
4) compiling a list of paid services that the institution has the right to provide;
5) determination of the list of property that the institution has the right to lease;
6) establishment of control volumes of activities for the provision of budgetary services in kind and in monetary terms;
7) establishment of control volumes of activities related to the attraction and expenditure of extra-budgetary funds in kind and in monetary terms;
8) coordination of plans for budgetary and extrabudgetary activities of the institution.
In the course of financial planning, the following procedures are performed:
– reviewing the milestones of the medium-term plan for the coming year and assessing the possibility of achieving them;
- drawing up an activity plan for the provision of budgetary services;
- drawing up a plan of activities related to the receipt and expenditure of extrabudgetary funds;
- preparation of estimates of extra-budgetary income and expenses;
– consideration and approval of the action plan and estimates of extra-budgetary income and expenses;
– amendments to the medium-term action plan;
– adjustment of the activity plan and estimates in the process of execution;
– control and analysis of the implementation of the activity plan and budget;
- preparation of a medium-term plan for the next planning period.
Financial planning in budget-supported institutions is based on the preparation of various estimates. On the basis of natural indicators (number of persons served, floor space, etc.) and financial norms, budget estimates of expenditures are compiled. Budget estimates can be of several types.
Individual estimates compiled for a particular institution or for a particular event.
General estimates compiled for a group of similar institutions or activities.
Cost estimates for centralized activities are developed by departments for financing and activities carried out in a centralized manner (purchase of equipment, construction, repair, etc.).
Summary estimates combine individual estimates and estimates for centralized activities, i.e. These are estimates for the department as a whole.
The estimate is compiled by the institution in the form developed and approved by the main manager of the budget funds, containing the following mandatory details:
1) approval stamp containing the signature (and its transcript) of the head authorized to approve the estimate of the institution, and the date of approval;
2) the name of the form of the document;
3) the financial year for which the information contained in the document is provided;
4) the name of the institution that compiled the document and its code according to the All-Russian Classifier of Enterprises and Organizations (OKPO), the name of the main manager of the budget funds that compiled the document (a set of estimates of institutions);
5) code according to the Consolidated Register of the main administrators, administrators and recipients of federal budget funds for the main administrator of federal budget funds (SRRPBS code) (for federal institutions);
6) the name of the units of measurement of indicators included in the estimate, and their code according to the All-Russian Classifier of Units of Measurement (OKEI);
The estimate is compiled by the institution on the basis of the calculated indicators developed and established by the main manager (manager) of the budget funds for the financial year, characterizing the activities of the institution and the adjusted volumes of limits of budget obligations.
Substantiations (calculations) of the planned estimated indicators used in the formation of the estimate are attached to the estimate submitted for approval. The approved estimates of budgetary institutions are their financial plans for a certain period of time.
With the preparation of estimates of budgetary institutions, the following tasks are solved:
– provision of budgetary institutions with state financing;
– analysis of proposed expenditure projects and reports on the use of funds;
- control over the efficient and economical use of funds.
The main methods of planning budget expenditures are program-target and normative.
Program-target method budget planning consists in systematic planning of the allocation of budgetary funds in accordance with the approved target programs drawn up for the implementation of economic and social tasks. This method of planning financial resources contributes to the observance of a unified approach to the formation and rational distribution of funds of financial resources for specific programs and projects, their concentration and intended use, and improvement of control. In turn, all this increases the level of efficiency of absorption of funds.
Planning of funds to finance budget activities, budgeting of budgetary institutions are largely based on the use of normative method planning expenses and payments. Norms are established by legislative or by-laws. Such norms are either the monetary expression of in-kind indicators of meeting social needs (for example, the norms of spending on food for the population in budgetary institutions, providing them with medicines, soft equipment, etc.), or the norms of individual payments (for example, the wage rate, the amount of benefits, scholarships and etc.), or norms based on the average statistical values of expenses for a number of years, as well as the material and financial capabilities of society in a particular period (for example, norms for the maintenance of premises, educational expenses, etc.).
14. Budget rationing as the basis for planning budget expenditures.
Budget rationing- setting the amount (norms) of expenditures of budgetary institutions for certain types of costs: such, for example, are the norms for spending on teaching aids at school; for medicines, underwear, food for patients in medical institutions; for office expenses, heating, lighting of institutions, etc.
Normative cost planning method and payments is used mainly in planning funds for financing budgetary measures and budgeting budgetary institutions. Norms are established by legislative or by-laws. These rules may be:
- monetary expression of natural indicators of satisfaction of social needs (for example, the norms of expenses for food of the population in budgetary institutions, providing them with medicines, soft equipment, etc.);
- individual payment rates (for example, salary rate, allowances, scholarships, etc.);
- norms based on the average statistical values of expenses for a number of years, as well as the material and financial capabilities of society in a particular period (for example, norms for the maintenance of premises, educational expenses, etc.).
Norms can be obligatory(established by the government or territorial authorities) or optional(established by departments).
Budget rules can be simple(for certain types of expenses) and enlarged(for the total cost or for the institution as a whole).
Consumption rates of medical institutions for medicines and food for patients are set for one patient, and according to the contingent (number) of patients, the amount of allocations to the hospital for these expenses is determined. Expenses for food in kindergartens are determined on the basis of the norm (ration) of nutrition established for one child. Consumption rate of institutions for stationery is set based on the need for them by one employee, for heating with wood - per stove or per cubic meter of the building, for lighting - per square meter of area, etc.
The basis for calculating budget expenditures are material norms: a set of linen for one place in kindergarten, for a bed in a hospital; diet (composition and quantity of products) per child or per patient per day; the amount of firewood per 1 cubic meter m during the heating season, etc. The material norm, expressed in money (at state prices), is called financial norm. Expenses in the estimates of budgetary institutions for individual needs are determined according to financial norms.