The active development of the plastic card business has led to the fact that the cards become an instrument of banks' competition not only for the depositor, but also for the borrower. Recently, along with consumer express lending, many banks have begun to actively offer credit cards to their customers. According to experts, credit cards will soon dominate the consumer lending market. Thus, according to the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, in 2007 the volume of issue of credit cards in Russia exceeded 200 thousand, while the issue of credit cards over the past year increased by 4.3 times, and the volume of transactions - by 2.3 times.
Not only traditional products based on Classic/Mass or Gold cards with an overdraft account management mode have appeared in circulation, but also a number of new credit products from international payment systems, such as Viza Electronic Instant or MasterCard Electronic, which are aimed at the mass consumer.
It is natural to assume that competition in the plastic card market will become fiercer in the coming years (considering that card transactions can currently be attributed to the most profitable types of banking activities). The implementation of salary schemes allows banks to gain access to additional cheap resources, similar to the settlement accounts of organizations, the balances of which can be predicted quite accurately. The costs of servicing card accounts are quite low due to the high degree of automation. Quite significant for banks are commission deductions for making payments when using plastic cards, as well as acquiring receipts. With the spread of credit cards, banks receive more interest income on loans. And this, in turn, means that banks are interested in the diversified development of the card business no less than card users.
The largest bank in our country is Sberbank of Russia. Its activities serve as an approximate guideline for all other Russian commercial banks.
The share of Sberbank of Russia in the bank card market remains stable and, according to the results of its work, is more than 30% in terms of such key indicators as the number of cards serviced and their turnover. The share of Sberbank of Russia in the total amount of settlements in the Russian merchant acquiring network decreased from 7.4% to 6.7%.
The total number of issued cards increased by 7.6% in the first quarter of 2005 and exceeded 9.8 million. At the same time, Sberbank of Russia ensured the growth of card issuance adequate to the overall growth of the Russian bank card market.
The number of cards of international payment systems increased in 2007 by 0.6 million cards or 52% (in 2006 - 2.15 million cards) and reached 6.3 million cards (Figure 3.1):
Rice. 3.1.
As one of the objectives of the business plan for 2006 on the issuance of cards, the task was to restructure the package of card issuance in territorial banks by increasing the share of international bank cards in the total volume of issue of bank cards from 47.9% to 53.2%, due to reduction in the share of SBERCARD cards and the share of cards of local payment systems. In general, this share in the bank increased over the year by 6.8% to 54.7%.
In 2006, the balances of individuals' funds on bank card accounts of Sberbank of Russia increased, reaching 14.7 billion rubles as of 01.01.2007. and 133.3 million US dollars (as of January 1, 2006, respectively, 8.44 billion rubles and 98.4 million US dollars). Growth for the year amounted to 74% and 35%, respectively, which ensured an increase in the share of funds attracted to bank card accounts in the total volume of funds attracted from individuals from 2.33% to 2.74%.
The distribution of all types of cards was facilitated by the further development of the infrastructure for their service.
In the reporting period, much attention was paid to the problem of creating a universal bank card service network. Thus, the 148% growth in the number of ATMs serving cards of international payment systems is primarily due to the fact that banks actively implemented a software solution for ATMs that allows servicing international payment systems cards and SBERKART microprocessor cards on one device.
The increase in the number of cash points and the installation of ATMs in all major industrial centers of Russia contributed to the growth in the volume of transactions in them with international cards issued by third-party issuers and Sberbank of Russia cards issued in other TBs. The volume of cash withdrawals in other TBs using Sberbank cards amounted to 11.9 billion rubles. (for 2006 - 8.6 billion rubles), including 8.35 billion rubles for SBERCART cards and international cards. and 3.56 billion rubles. respectively. The volume of cash withdrawals on international cards issued by third-party issuers exceeded 4.79 billion rubles in the reporting period (2.3 billion rubles in 2006).
In 2006, the total number of cards issued and serviced by Russian banks increased by 45% and reached 15.4 million cards compared to 10.6 million cards at the beginning of the year (Figure 3.2).

Rice. 3.2.
The growth rate of card issuance for various payment systems during the year was not uniform. Among the main market participants, the number of cards of international systems grew at the maximum rate by 77% (of which: VISA - 98%, MasterCard - 54%), as well as the Accord payment system - 102%. Sberbank of Russia ensured an increase in issuance adequate to market growth - by 44%, while during the specified period the number of local cards was reduced by 230,000 pieces. Excluding local maps. The growth rate of the issue volume of Sberbank of Russia amounted to 57% in 2006 (Fig. 3.3)

Rice. 3.3.
The following qualitative changes characterizing the state of the market can be noted:
International cards already account for 50% of all issued cards in Russia, while their market share increased by 9% during the year. In fact, the growth in the number of cards of the Unioncard payment system has stopped, and the banks continue to reissue these cards to cards of international payment systems. The growth rate of Golden Crown cards decreased to 24% per year, which led to a decrease in their market share from 8.4% to 7.2%. Similarly, both the share and the absolute number of cards issued by banks under their own local programs were declining. As a result, their market share dropped from 14% to 8.5% (Figure 3.4).

Rice. 3.4.
The share of Sberbank of Russia in the Russian market of bank cards remained practically unchanged and is about 30% both in terms of the number of cards issued and in terms of debit turnovers on them. For the MasterCard payment system in Russia, cards serviced by Sberbank of Russia account for 57% (a year ago 51%), for the Viza payment system - 16.3% (a year ago 12.8%).
Analyzing the nature of the use of cards issued by various payment systems, we can draw the following conclusions.
Cards are still in the vast majority of cases used only for cash withdrawals. On the whole in Russia, the share of trade transactions accounted for only 7.0% of the total debit turnover (excluding customs payments). At the same time, for cards of international payment systems, this figure is 11.9%, for cards of Sberbank of Russia, on average for all products - 7.1%.
The total volume of transactions in the trade and service network using cards issued by Russian banks exceeded 50 billion rubles, while Sberbank of Russia cards account for 8.7 billion rubles or 14%. In the context of payment systems, data on turnovers are shown in Fig. 3.5.

Fig.3.5.
The volume of merchant acquiring operations with bank cards in the 1st quarter of 2005 amounted to 4.6 billion rubles, having increased by more than 2.4 times as compared to the same period of 2007.
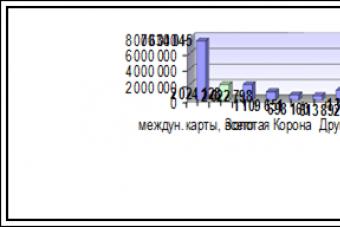
The average amount of one operation for the reporting period did not change and amounted to 1,080 rubles. The main volume of transactions is accounted for by cards of international payment systems - 81% of the total amount of transactions (a decrease in the share over the year by 4%). The average amount of a transaction with an international card was 2,600 rubles. For comparison, the average amount of 1 transaction for Sbercards, Zolotaya Korona and Union cards was 234 rubles, 251 rubles, respectively. and 154 rubles (these cards are intensively used for micropayments and in local settlements). Trade turnover with Russian Standard cards grew rapidly during the year, which allowed this bank to increase its market share to 1.0% with the highest average purchase amount among all payment systems, equal to 10,300 rubles.
A characteristic moment is the fact that in the volume of merchant acquiring operations with international cards, the share of turnover with cards of Russian banks increased significantly - from 39% in 2005 to 57% in 2007. In retail outlets serviced by Sberbank of Russia, the share of transactions with Russian cards was even higher on average for the year - 68% (in December 2007 - 76%). This trend leads to a decrease in the cost of servicing acquiring operations of Sberbank of Russia, since in the total volume the number of operations increases with the bank's own cards, for which no interchange commission is paid (for Sberbank of Russia, the share of ON-US operations in the total acquiring turnover amounted to 15.2 %, an increase of 2.4%) (Fig. 3.6)

Rice. 3.6.
In 2007, the growth of the banking card service infrastructure in the country continued at a high rate. The total number of ATMs has increased. Sberbank of Russia installed 5,194 ATMs (as of 01.01.2007 - 4,816 units, which is 33% higher than in the previous year, 01.01.2008 - 3,202 units), of which:
4884 ATMs accept cards of international payment systems Visa and MasterCard;
3300 ATMs accept SBERCART cards;
4615 ATMs accept American Express cards;
3899 ATMs accept payments for the services of enterprises (cellular operators, satellite television, etc.).
The number of electronic terminals serving cards amounted to 61.1 thousand units (a year ago 41.4 thousand units), the number of trade and service outlets with which contracts for accepting bank cards were concluded reached 49.0 thousand organizations, having increased over the period by 52%.
The branch network of Sberbank consists of 173 institutions: the head office, 17 OSB and 155 branches. The issue of international cards is carried out in 19 of them - the Tomsk head OSB, all branches of the Tomsk region (17 OSB) and f. No. 13/122 in Tomsk. In 2 of them, AS Sbercard is issued - OPERA of Tomsk OSB and Central OSB No. 8607.
The main objective of the bank card development program of the Branch of Sberbank of Russia is a significant increase in the scale of activities in all areas of the card business, improvement of card products in order to meet their quality level with world standards. Work continues on the creation of the Sberbank of Russia payment system, which includes a single set of card products issued by the bank and a single card acceptance network, an integral part of which is the network of Sberbank ATMs and terminals. A significant expansion of the scope of application of bank cards is expected, both for individuals and for legal entities.
Simultaneously with the program for the development of international bank cards, the bank will consistently develop its own program of AS SBERKART microprocessor cards, the use of which does not depend on the infrastructure of communication services existing in various regions.
Sberbank defines the following main directions for the development of the card business:
International cards Viza, Eurocard/MasterCard - Classic and Gold cards are intended for the middle class and wealthy clients. International debit cards Sberbank - Cirrus / Maestro, Sberbank - Visa Electron - are intended for working citizens to pay wages, as well as for pensioners and youth in terms of transferring pensions, social payments, scholarships.
AS SBERKART microprocessor cards - for paying wages, as well as when using Internet banking and in e-commerce.
Providing trade organizations and service enterprises with the possibility of accepting both international bank cards and AS SBERCART as a means of payment.
Provision of services for servicing bank card payments to medium and small commercial banks of a high reliability category (processing), which will contribute to the development of the card business in Russia as a whole.
The attractiveness of bank cards is ensured by the spread of overdraft lending operations on card accounts.
In order to improve the quality of customer service, in 2005 Sberbank implemented the following projects of Sberbank of Russia:
July 2005 Sberbank began dispensing cash using American Express cards at its ATMs.
August 2005 Sberbank provided employees of enterprises (organizations) that have entered into “salary” agreements with Sberbank with the opportunity to receive an overdraft on card accounts.
September 2005 Sberbank, within the framework of a joint project of Aeroflot - Russian Airlines and Sberbank of Russia, offered its customers an international bank card "Visa Aeroflot", the holders of which become participants in the Aeroflot Bonus Program.
October 2005 Sberbank, within the framework of the Sberbank of Russia project, offered its clients - holders of international bank cards to realize the possibility of prompt access to information on bank cards using a mobile phone - “Mobile Bank”.
Sberbank continues to work to increase the issuance of cards of international payment systems in the region and to attract large customers for servicing.
In order to increase the balance of funds on bank card accounts, Sberbank is increasing the efficiency of its work to attract potential holders from among military pensioners for servicing using Sberbank-Maestro Socialnaya cards.
The number of Sberbank-Maestro Social cards for those who receive pension benefits and other social benefits amounted to 606,000.
The share of the balance of funds on the accounts of bank cards of individuals and legal entities in the total balance as of 01.01.07 is shown in fig. 3.7, 3.8.

Rice. 3.7.

Rice. 3.8.
As of January 1, 2005, there were 7.4 thousand cash withdrawal points in the system of the Savings Bank of Russia, of which 6.2 thousand serve operations with cards of international payment systems Visa and MasterCard and 1.2 thousand - with microprocessor cards SBERKART .
In the Tomsk region, in all settlements with a population of over 15,000, Sberbank organized cash points for servicing cards of international payment systems. Sberbank of Russia serves card transactions in 2.6 thousand settlements in 79 constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
A lot of work has been done by the branch of Sberbank of Russia to expand the network of servicing bank card holders using ATMs. According to the latest data, at the beginning of 2005, 42 ATMs were installed in the Tomsk Region.
Thus, the branch of Sberbank of Russia successfully operates in the field of bank cards. The pace of implementation of card projects, as well as the level of development of the acquiring network leave a good impression and open up broad prospects for deeper penetration into the bank card market in the Tomsk region.
Theoretical aspects of the functioning of payment systems based on plastic cards. Legal regulation of the activities of credit organizations in the field of plastic cards. Types of plastic cards and their characteristics. Analysis and development trends of the plastic cards market in the Russian Federation. Analysis of operations with plastic cards in OJSC RGS Bank.
Share work on social networks
If this work does not suit you, there is a list of similar works at the bottom of the page. You can also use the search button
Other related works that may interest you.vshm> |
|||
| 1004. | Analysis of the development of active operations in OJSC "Baltic Bank" | 1.42MB | |
| Economic essence and types of active operations of a commercial bank. Legal regulation of active operations of a commercial bank. Decentralization of cash flows will make it possible to increase the efficiency of meeting the needs of business entities in cash and ensure the uninterrupted functioning of cash circulation, especially in regions where there are no Bank of Russia institutions. | |||
| 18025. | Ways to improve credit operations of Southern Trade Bank OJSC | 88.53KB | |
| General analysis of loans issued to customers of OJSC Southern Trade Bank. Practice of lending by foreign banks. The relevance of this problem in modern economic reality determined the choice of the topic of this thesis and its main goal: to explore the theoretical concepts of credit operations of a commercial bank, analyze the practical implementation of lending schemes and propose measures to improve them. The stated purpose of this work puts before the author the following ... | |||
| 1233. | Development of a proposal to improve the passive operations of JSCB "Absolut Bank" | 1.03MB | |
| Theoretical and methodological foundations of passive operations of a commercial bank. The essence and types of passive operations of a commercial bank. Operations for the formation of own funds of a commercial bank. Bank fundraising and customer service operations. | |||
| 17808. | ORGANIZATION AND ACCOUNTING OF CASH OPERATIONS ON THE EXAMPLE OF "JSC" ASIA-PACIFIC BANK | 34.46KB | |
| Based on the foregoing, banks have a big burden to provide cash services to market entities, since the correct organization of cash circulation plays an important role in the development of the Russian economy. From how well the mechanism for promoting cash from institutions of the Bank of Russia to commercial banks and further these banks to business entities will be debugged, as well as how quickly banks will be able to collect and process cash proceeds, withdraw old banknotes that have become unusable from circulation and replace ... | |||
| 5243. | Study of banking operations and services in "Home Credit and Finance Bank" | 95.44KB | |
| The object of industrial practice is LLC Home Credit and Finance Bank. During the internship, we studied the requirements for a specialist in the field of knowledge of the skills and abilities of the practical activities of banks. During the internship, gain experience in performing work by profession as a bank controller. In accordance with the goal, the tasks of passing the on-the-job training were determined: to study the interface and the procedure for using specialized software for completing and formalizing... | |||
| 19716. | Analysis of the financial condition of JSC ATF Bank | 179.8KB | |
| Theoretical and methodological foundations of commercial bank liability management. The role and importance of the liabilities of a commercial bank. Theoretical foundations of complex management of liabilities and assets of a commercial bank. Funds raised by the bank. | |||
| 1118. | Analysis of the financial condition of Bank CenterCredit JSC | 79.57KB | |
| The main purpose of this work practice is the financial and economic analysis of the activities of a commercial bank and the development on its basis of proposals for improving the activities of the bank. Analyzed indicators: indicators of financial results dynamics and structure of income and expenses of the bank; dynamics of profit indicators; profitability ratios; indicators of the financial condition dynamics of the volume and structure of own funds capital adequacy indicators ... | |||
| 11386. | Analysis of active operations of commercial banks of the Republic of Kazakhstan | 327.18KB | |
| Classification of assets of a commercial bank by degree of liquidity Liquid assets include, in addition to the listed highly liquid assets, all loans issued by a credit institution in tenge and foreign currency with a maturity within the next 30 days, as well as other payments in favor of a credit institution to be transferred within the next 30 days. Long-term liquidity assets include all loans issued by a credit institution in tenge and foreign currency with a remaining maturity of more than a year, as well as 50... | |||
| 13732. | Modeling and analysis of business operations of Beta LLC | 94.1KB | |
| Materials and inventory with a period of use of not more than 1 year are recorded on account 10 "Materials", sub-accounts 10/1 "Raw materials and materials" and 10/9 "Inventory and household supplies" at discount prices. The purchase of materials and equipment is reflected on account 15 "Procurement and acquisition of material assets" | |||
| 19756. | Analysis of the effectiveness of foreign exchange transactions (on the example of Tsesnabank JSC) | 716.69KB | |
| The development of the domestic foreign exchange market of Kazakhstan requires a generalization of the experience of its functioning and capabilities. The use by specialists of the accumulated experience of foreign exchange transactions in the Kazakhstani foreign exchange market gives impetus to the further development of this market. The foreign exchange market is a kind of tool for coordinating the interests of the seller and buyer of currency values. Any action of the seller or buyer in the market is associated with commercial risk. | |||
1. Fominna E., Kazantzev D. Small business in Russia: state and problems. Mode of access: http://smao.ru/ru/tp/analytics/article_1023.html.
2. Kryukov S. Support of small business increases. (OJSC "RBD"). Mode of access: http://www.rosbr.ru.
Reviewers:
ON THE. Sedelnikova, Candidate of Historical Sciences, Branch of the Omsk State Pedagogical University in Tara;
T.V. Zinkevich, Candidate of Economic Sciences, Administration of the Tara Municipal District, Committee for Economics and Management of Municipal Property.
UDC336.717.13
E.V. Ivanova
Omsk branch of the Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation
ANALYSIS OF THE MARKET OF BANKING OPERATIONS WITH PLASTIC CARDS
Plastic cards are a relatively new banking product, but have already managed to take their place among banking services. Working with plastic cards is one of the most promising for banks at the present time. The article analyzes the provision and use of cards, their types are considered and the advantages and disadvantages are identified. The author formulated the problems of development of the bank card market and concluded that in order to intensify the development of the bank card market in the Russian Federation, constant and systematic work with the population and trade enterprises is required to change the stereotypical approach to settlements in the trade network, which must be carried out in close cooperation between credit organizations and authorities. state power and administration.
Key words: bank cards, banks, non-cash payments, international payment system.
In modern conditions of economic development, there is a process of integration of the banking systems of individual states and the development of payment systems, in particular, in the direction of the development of non-cash forms of payment, which, in turn, are widely used in the modern world. One of the instruments of non-cash payments is a plastic card. In economically developed countries, a plastic card is the main attribute of the sphere of trade and services. Carrying out transactions with the help of payment cards shows the degree of integration of the banking system and society. Suffice it to say that non-cash payment for goods and services in industrialized countries reaches 90% in the structure of all monetary transactions.
The payment card market is increasingly becoming a field of competition between Russian banks. Bank card transactions are among the most profitable types of banking activities. On average, the income per unit of cost in the card business is higher than in other types of operations.
If we compare bank cards with deposit accounts as a mechanism for attracting funds from the population, then the former are less effective, because the interest rate on them can be significantly lower than the interest rate on the deposit. But interest in cards remains, since it is due not so much to interest as to other factors: ease of use, automatic provision of a bank loan, the possibility of repayment.
to delay the repayment of the debt, regular receipt of complete information about the operations performed.
The introduction of a settlement system based on bank cards also has advantages for the bank: overcoming spatial restrictions on attracting and serving clients; attraction of new corporate and private clients; increase in working capital; reduction of overhead costs.
The market of bank cards has received rather wide development in Russia. Plastic cards occupy a leading position in Russia among other retail payment instruments. But, despite the rapid development of the Russian card market and the steady growth of all its indicators, cards in Russia still have not become a full-fledged means of payment and more than 90% are used to withdraw cash, and not to pay for goods and services. On fig. 1 shows the share of trade transactions through plastic cards in Russia in 2013 for each federal district (in %).
■ Moscow and Moscow Region
■ SPb iLO
■ Northwestern
■ Ural
■ Siberian
■ Central
■ Privolzhsky Far East
Rice. 1. Share of trading operations (%)
Despite this, various plastic systems are being deployed and gaining momentum in Russia, and experts call the market for bank payment cards among the most promising areas for the development of banking services for the population.
There has been a trend towards the merger of small local payment systems with systems of a national scale, which is associated with the territorial expansion of services and the functionality of card products.
Therefore, a characteristic feature of the domestic plastic card market has become the struggle for customers, resulting in a trend to reduce the cost of cards and charge fees for using them.
The development of the Russian market of payment cards is one of the most important factors in solving the problems of reducing cash payments and developing cashless payments in the field of retail payments. To solve this problem, the Bank of Russia is working to create conditions for the further improvement of modern retail payment instruments that contribute to the development of the card industry in Russia. The development of the card industry ensures an increase in the transparency of financial transactions, an increase in tax revenues, significantly reduces the costs associated with servicing cash circulation, leads to an increase in the volume of funds attracted to the banking sector and, accordingly, the credit capabilities of banks, and also largely contributes to the active development of related areas of activity, such as industrial, social and employment.
The growth in the number of non-cash payments using cards is largely
is associated with an increase in the number of transactions for payment for housing and communal services, mobile communication services, Internet providers, cable TV, etc., made through ATMs and mobile phones.
The share of non-cash transactions with cards in the total volume of retail trade, public catering and paid services to the population increased by 1.2 times in 2013 compared to 2012 and amounted to 2.7%, which also indicates positive trends in the use of the card as cashless payment instrument.
In 2013, Russian banks continued to increase the volume of issued plastic cards, with an annual growth of about 20%. However, despite the huge potential of the card market and the wide geography, the culture of using such financial instruments in Russia has not yet reached the required level.
According to the CBR, more than 65% of banks issue and/or acquire payment cards (655 credit institutions out of 954), the number of bank cards issued by them (data as of April 1, 2013) amounted to 210 million, which is 28% more than in 2012 .
More than 80% of issued bank cards were issued by international payment systems VISA and MasterCard. Russian payment systems (Sberkart, Zolotaya Korona, STB Card, UnionCard) control from 6% to 12% of the market (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. Number of transactions by types of cards in 2013 (%)
The focus of the Russian payment card market on the issuance and maintenance of cards of international payment systems is due to the following reasons. Firstly, a more developed infrastructure for accepting payment cards of international payment systems both in Russia and abroad. In Russia, cards of payment systems VISA Int. and MasterCard Int. almost all ATMs are accepted for service (the share in the total number is about 90%), cash points (almost 90%) and devices (electronic terminals, imprinters and ATMs) used to pay for goods (works and services) (almost 90% ).
Secondly, the development of domestic payment systems is hindered by the lack of compatible software and hardware; difference in transaction processing technology; lack of guarantees for the acceptance by member banks of cards issued within the framework of one system. Competition and technological peculiarities of functioning of the systems existing in Russia hinder their integration in the near future, which in general is a deterrent to the development of cashless payments in the field of retail payments.
In 2013, Russian banks continued to increase the volume of issued plastic cards, but the growth rate slowed down somewhat.
Thus, according to the RBC rating, the largest bank in terms of the number of active plastic cards in circulation as of July 1, 2013 is Sberbank. The clients of this largest bank in Russia have 58.2 million plastic cards in their hands. As of
On July 1, 2012, customers had almost 47.8 million cards, that is, an increase over the year amounted to 21.9%, or slightly less than 10.5 million cards. (table).
No. Bank Number of active cards issued (pieces) as of 07/01/2013 Number of active cards issued (pieces) as of 07/01/2012 Change (pieces)
1 Sberbank 58,262,731 47,792,488 10,470,243
2 VTB 24 12,019,072 10,338,679 1,680,393
3 Uralsib 5,360,071 6,385,571 -1,025,500
4 Rosbank 2,625,578 3,404,527 -778,949
5 SKB-bank 2,146,911 1,360,289 786,622
6 TransCreditBank 1,959,828 2,040,356 -80,528
7 Credit Europe Bank 1,738,474 1,516,545 221,929
8 Moskomprivatbank 1,623,413 1,434,813 188,600
9 Raiffeisenbank 1,504,314 1,245,761 258,553
10 Promsvyazbank 1,430,312 1,218,885 211,427
Sberbank is now actively distributing plastic cards, both settlement and credit, among its many customers. Among all components of the retail portfolio, the bank's credit card segment grew at the fastest pace: in 2013, the portfolio increased 1.7 times to RUB 270 billion. The number of cards issued during the year exceeded 12.1 million, which allowed Sberbank to strengthen its leadership position in this segment, increasing its share in the national market from 19.9% to 23.5%. In August 2013, Sberbank introduced new premium cards under the Premier tariff plan: Visa Platinum PayWave and World MasterCard Black Edition PayPass. During the year, the number of working salary cards increased by 1.9 million - up to 21.1 million. The volume of wage transfers increased by 28% and amounted to almost 6.3 trillion rubles. The number of pensioners receiving a social pension through Sberbank increased to 21.8 million people. At the same time, the share of pensioners receiving pensions through Sberbank in the total number of social pensioners in the Russian Federation increased to 53.2%.
VTB 24 has 4 times fewer active plastic cards in circulation than Sberbank - more than 12 million. During the year, VTB 24 also increased the number of active plastic cards in circulation. In percentage terms, the growth was 16.3%.
In third place in terms of the number of active plastic cards in circulation is Uralsib - as of July 1, 2013, it had almost 5.4 million active plastic cards, which is less than it was in circulation a year ago, namely by 16%. .
In general, out of dozens of banks - leaders in the plastic card market, a decrease in the volume of cards in circulation is observed in three banks: Uralsib, Rosbank and TransCreditBank.
Operations of a commercial bank with credit cards should be considered from the standpoint of their conduct by the bank itself and from the standpoint of their implementation by the client. For banks, the issue of plastic cards is a profitable way of investing financial resources, and therefore, almost every bank issues its own cards or cards of international payment systems.
One of the achievements of Sberbank in the retail sector is the increase in the volume of the card business and other services provided on a commission basis. As a result, the number of transactions carried out has increased and the corresponding income has increased. The large-scale growth in the number of transactions was accompanied by an increase in the share of non-cash transactions.
The combination of these factors, which resulted from massive investment in service quality, resulted in a 28.3% increase in commission income from retail operations; at the same time, commission income from bank card transactions increased
by 56%. Thus, transactions with bank cards have become the main factor in the growth of Sberbank's commission income: over the past two years, receipts from them have more than doubled.
Currently, Sberbank issues cards of the international payment systems Visa, MasterCard, American Express. Types of Sberbank plastic cards include: debit, credit, social, virtual, co-branded.
Sberbank Maestro and Visa Electron are the most affordable cards for servicing. On them, the client can be credited with wages, make purchases with their help, and also withdraw cash.
A Visa Electron or Maestro plastic card has a number of significant limitations. Firstly, their acceptance is limited in some foreign countries (for example, in the USA or Ireland), but this only applies to terminals at retail outlets, ATMs must serve such cards everywhere. Secondly, such cards, as a rule, cannot be paid in an online store. You cannot link them to an account in an electronic payment system (PayPal, YandexMoney or WebMoney).
The Sberbank MaestroMomentum instant issuance card is issued right at the time of contacting the bank - it is enough to present a passport. There is no service fee for such a card, which is “compensated” by the inconvenience in use. Thus, this card is accepted for service only in Russia (entering a PIN code is required for each transaction), and cash is issued / accepted only at Sberbank branches and ATMs. Unlike other cards, the owner can only have one MaestroMomentum.
Classic cards such as VisaClassic or MasterCardStandart are optimal in terms of the combination of features and service cost. Compared to electronic ones, they can provide their owners with discounts when buying goods or paying for services.
A classic Sberbank debit card costs 750 rubles. per year, additional cards can be issued to the main card, their maintenance will cost 450 rubles. Classic category credit cards are offered at an attractive interest rate of 24%. Their maintenance will also cost the client 750 rubles annually.
For participants in payroll projects, Sberbank issues credit cards on special terms (the rates are lower, only a passport and a questionnaire are required from the documents) to individuals - employees of their "salary" clients, owners of Sberbank personal cards, as well as borrowers on mortgage, consumer and car loans.
Premium cards are Visa and MasterCard silver cards, VisaGold or MasterCardGold gold cards, platinum cards, including PlatinumAmericanExpress. The Sberbank Gold Card provides the owner with higher limits for withdrawing cash from ATMs or paying for purchases in stores, more favorable interest rates on a loan or overdraft. The platinum card, in addition, gives access to special offers and discounts that are introduced for cardholders by partners of the payment system. Gold cards also have affiliate programs with discounts and promotions, but there are fewer of them, and interesting offers are not often found.
Debit plastic cards of premium categories will cost customers 3,000 rubles. annually. Gold credit cards will also cost 3,000 rubles. The interest rate on the credit card will be 23%. The grace period for all cards is 50 days.
The platinum card is the most expensive in terms of annual service - 15,000 rubles. in the first year and 10,000 thereafter, but the interest rate on it can be up to 17%. Owners of deposits in the amount of 3 million rubles or more can count on preferential terms for the PlatinumAmericanExpress issue. The size of the credit limit is determined on an individual basis, but for ordinary cards it is lower than for Gold and Platinum cards.
Youth cards are issued both debit and credit. Youth debit cards are issued as part of the Respect from Sberbank program. These cards give the right to discounts from partners, as well as the opportunity to receive a scholarship or salary to the account
such a card. The annual maintenance of the youth card will cost the holder 150 rubles.
The transport card VisaElectron Transport or Maestro Transport combines the functions of a salary card and an unlimited travel ticket in the Moscow metro. The card is issued with an already activated transport application - its owner does not need to contact the cashier in the metro, while there are no restrictions on the number of trips and the time interval for re-passing. A citizen of the Russian Federation aged from
14 years, but it is issued on the terms of an agreement with the organization - the employer of this citizen.
Virtual debit cards VisaVirtual, MasterCardVirtual are issued without issuing a material carrier (i.e. the actual plastic card). Details of such cards are used only to pay for goods and services on the Internet; when a card is issued in the name of a client, the latter is informed of the 16-digit card number and its validity period, which are displayed in the client's Personal Account in Sberbank Online. In addition, an SMS with the CVV2 or CVC2 code (used when performing a virtual card transaction) is sent to the client's mobile phone.
It is important to note that, unlike other cards, to which mobile and Internet banking may not be linked, a virtual card is issued exclusively on the terms of linking to these services - and only for existing Sberbank customers. As for replenishing the account of such a card, it is carried out only non-cash (by transferring funds from the account of the main debit card through Sberbank Online or a Sberbank self-service device).
A Sberbank gift card is a kind of "cash gift" for up to
15 thousand rubles This is an unnamed debit card of instant issue, while Sberbank does not conclude an agreement on its issue and maintenance - a person who purchases this card to present to another person simply buys it as a product and replenishes it with the amount that he intends to present.
A plastic "gift" gives the recipient the right to receive goods or services for the amount indicated on the card, while the holder is identified by signature (on the card and in the passport, which must be presented when paying with this card). You can also pay with such a card on the Internet: on the back of it is a 3-digit CVV2 code, which the holder will need to conduct transactions on the Web.
Social cards are issued in two categories - student and social. Scholarships are accrued on the first, pensions and social benefits on the second. A Sberbank social category bank card can be issued to people aged 14 years and over (residents and non-residents) on the basis of an application or from 10 years old - provided that the child is closely related to the main cardholder or is under his care. A student card is issued from the age of 14 to students and students.
The social card is serviced free of charge, but if the client decides to issue an additional card to the account, each additional card will cost 150 rubles. annually. Maintenance of a student card costs 150 rubles. in year. Issue of additional cards to the client's card account is not provided.
Co-branded cards are issued as part of joint programs of Sberbank and its partners. Sberbank has 3 bonus programs: two co-branded ones (Visa Aeroflot and MasterCard MTS) and a charitable one (Visa Give Life). All three cards can be credit or debit, regular or gold.
Subscribers of a mobile operator and the largest air carrier in Russia - holders of MasterCard and Visa cards, respectively, can accumulate bonus points and miles as part of the MTS-Bonus and Aeroflot-Bonus partner programs, and Visa holders "Give Life" - participate in a charity program ( 50% of the fee for the first year of servicing the card and 0.3% of the amount of purchases made on it are credited by Sberbank to the Fund of the same name).
For each spent 1 dollar / euro or 30 rubles. 1 mile is credited (VisaClassic) or
1.5 miles (VisaGold) under the Aeroflot-Bonus program or 1 point - under the MTS-Bonus program. In addition, when opening an account, welcome points/miles are awarded.
Let's analyze the offer of bank cards of banks competing with Sberbank - Russian Standard and VTB-24.
In Russian Standard Bank, in addition to classic, "gold" and "platinum" cards, there are a number of offers with additional benefits for the owner. For example, the RSB World MasterCard Cash Back Card card provides for a refund to the account after each purchase made by the owner (up to 3% of their value).
The Blue American Express transparent plastic card is connected to a worldwide accident insurance program. In addition, if money was stolen from such a card, Russian Standard undertakes to pay compensation to its owner in the amount of 10,000 US dollars.
The annual fee for servicing credit cards in this bank is from 600 rubles. (classic version) up to 3000 rubles. (premium cards). Minimum monthly payment: 5-10% of the balance due, depending on the type of card. The grace period for all credit offers is 55 days. But the annual interest rate depends on the type of card and varies from 28% to 36% per annum.
Another feature of Russian Standard credit cards is that its owner automatically becomes a member of the Discount Club. The club has more than a thousand shops, beauty salons, restaurants and entertainment centers. Paying in these networks with a credit card from Russian Standard, you can get discounts on goods and services up to 30%.
The main conditions of VTB 24 credit cards include: the size of the credit limit (set based on the solvency of the applicant), interest rate (from 17%), grace period (from 50 days), minimum one-time payment (5% of the amount of debt), card validity period (2 years), credit term is not limited.
VTB-24 offers similar plastic cards:
Visa Classical and multicurrency (a distinctive feature of this program is the ability to have three accounts in different currencies at the same time: in euros, dollars and rubles), debit and credit cards. The service fee is 750 rubles. in year. The limit amount per day is 300 thousand, but per month it should not exceed a million. The validity period of the VTB-24 debit card is 2 years. When withdrawing cash through other ATMs, the commission is 1%.
Salary card VTB-24.
Plastic cards Gold VTB-24.
Visa Platinum and Premium credit and debit cards. A distinctive feature of this loan program is the ability to return part of the money spent. It is possible to choose one of the most frequently used categories of services and goods (restaurants, gas stations, cosmetics, pharmacies), making purchases in this area, 5% of the amount paid will be returned back to the account.
Affiliate program for providing discounts for flights - co-branding card of VTB-24 and Transaero.
Bonus program "My conditions" MasterCard Standard. The main advantage is the ability to return to the card 5% of the purchase price provided for by the regulated list. When purchasing goods that are not included in the list, VTB-24 Bank will return an amount of 1% of the costs to the account.
Thus, leading banks offer similar card products. Each bank has affiliate programs for both debit and credit cards. Products are offered for the premium and classic segment.
It can be seen that the conditions for providing a credit card by one or another bank differ slightly from each other. Each of the three banks provides for individual
new approach to the client. The interest rate on the loan will depend on the type of credit card, the income of the borrower and the amount of the loan. The banks discussed above use two types of payment systems - Visa and Master Card. When using Visa and Master Card credit cards within the Russian Federation, there are no differences between them. These differences show up when going abroad. The fact is that currency conversion in the Visa system occurs through the US dollar, and in the MasterCard system - through the euro. Therefore, for people who frequently visit European countries, the MasterCard credit card will be the most suitable, and for all other countries, a Visa credit card. In all other cases, everyone can choose the system that he likes best.
Based on the analysis, we highlight the main problems for the plastic card market in general:
To date, a full-fledged state policy regarding the plastic card market has not been developed, which would provide for the regulation of the entire range of relations between market participants. So, in March 2014, after the United States imposed sanctions against Russia in connection with the annexation of Crimea to Russia, the international payment systems Visa and Master Card for the second time in history stopped servicing cards of several Russian banks at retail outlets and ATMs of the international network, the creation of a national system of payment cards in the country, independent of the state of international relations, has again become relevant. The preparation of amendments to the Federal Law “On the National Payment System” was started with the aim of infrastructurally and informationally closing the process of making money transfers within Russia, that is, operational centers and payment clearing centers must be located on the territory of Russia. The bill also provides for prohibiting the transfer (provision) of access to foreign states to information about domestic payment transactions.
By the end of March 2014, the society began to seriously discuss the creation of a national system of payment cards. On March 27, 2014, President of the Russian Federation Vladimir Putin approved the creation of a national payment system in Russia and ordered that it be developed and implemented as soon as possible.
Insufficient investment in the development of regional networks.
Distrust of the population in the banking system and plastic cards in particular.
Low financial literacy of the population, caused by the lack of training in working with cards and expressed in misunderstanding, fear and subsequent unwillingness to use a bank card as a payment instrument.
Lack of financial incentives for the use of cards by both consumers and suppliers of goods and services.
It is these moments that are the reason that many customers do not want to issue credit cards. Consumers simply don't know that there are many benefits to be gained when using a card wisely.
"Plastic" business in Russia at the moment - one of the main directions of development of banking services. Cards are in demand as a financial service as a means of payment for corporate clients and individuals, as well as the most convenient way to get a loan.
The main problems in the development of the plastic card market are the lack of infrastructure and the low level of financial literacy of the population. In addition, a certain role in slowing down the development of the market is played by the low level of income of the population.
It is necessary to highlight some features of the development of the plastic card market in Russia:
1. Increase in the interest rate. Most banks have raised the interest for the use of loan funds.
2. Informing the client about the change in the interest rate. Not every bank, unfortunately
leniation, considers it necessary to inform each of its clients about changes in the interest rate. Not all banks send a notice to the cardholder by mail. Expecting to save money, some financial organizations have switched to SMS-informing about changes in card conditions. There are also less client-friendly ways of providing information - publication in the all-Russian press. This was done, in particular, in Home Credit and Finance Bank, placing an ad in the Komsomolskaya Pravda newspaper.
3. Introduction of an additional fee for the option of connecting a credit account or a period of interest-free lending (grace period). These additional charges apply to banks that issue debit/credit or overdraft cards.
4. Rise in the cost of withdrawing money from a credit card at an ATM. Of course, banks are trying to accustom customers to the idea that credit cards exist in order to pay with them in stores, and not just withdraw cash from them. But it often happens that it is at this time that the client - the cardholder - needs cash. Before the crisis, withdrawing money cost an average of 3-7% of the required amount (depending on the bank issuing the card) at your own ATM, and there is also a minimum amount for withdrawing cash, for example, 350 rubles. at the Bank of Moscow. Currently, cash withdrawal fees reach 10% (Alfa-Bank credit card). Previously, some credit organizations did not charge interest at all for cashing cards through their ATM. At the same time, many financial institutions do not personally notify customers of the increase in the cost of the service, limiting themselves to a message on their websites.
5. Cutting the credit limit. For most newly issued credit cards, the limits have been significantly reduced compared to the amounts that banks provided to customers before the crisis. As a result, employees of the same company with the same salary may have significantly different credit limits. So, for an employee who receives 60 thousand rubles a month, on cards issued earlier, the limit was 180 thousand rubles, and on the same cards issued today, only 81 thousand are provided to his colleague. a bank can cut the limit on a valid credit card if the borrower is not careful. However, by the end of 2014, the situation may develop in the opposite direction, that is, a return to large (pre-crisis) limits.
6. Dependence on international payment systems.
Thus, the problems listed above had a negative impact on the plastic card market in Russia, undermining the confidence of potential consumers and disappointing existing bank customers.
The elimination of problematic moments in the use of cards should help strengthen the reputation of banks and restore consumer confidence in modern banking services, and, consequently, expand the number of card users.
In conclusion, I would like to note that plastic cards will not become a line in the reports of payment systems, but a real means of payment only if the holders start them consciously. This will happen when they are not imposed on clients as part of salary projects.
Thus, after analyzing all the problems associated with the circulation of plastic cards in Russia, we can propose the following mechanism for solving them:
Development of a regulatory framework that fixes the specifics of the circulation of plastic cards.
Information and educational work among the population.
Protection of information resources from unauthorized access.
Implementation and development of customer incentive programs.
Expansion and continuous improvement of the range of products and services offered to customers by increasing co-branding cards, for example, offering bonus programs together with Russian Railways.
Expanding the functionality of our own payment terminals - providing
the ability to replenish the card through the terminals of other banks. This is very convenient, since you do not need to spend time traveling to the office or searching for a cash-in terminal / ATM of a particular bank.
Introduction of a universal electronic card. With the help of the card, you can pay taxes and fines, receive a passport and other documents. Also, the card can be used instead of a ticket for travel in public transport, etc.
Implementation of innovative terminals with signature capture and recognition technology. This will speed up the card payment process, providing customers with a high level of service.
Thanks to such innovations, the advantages of non-cash payment technologies in Russian banks will manifest themselves and new opportunities will open up for conquering the plastic card market for steadily growing participants. Further development of events depends on the general macroeconomic situation in the country, the actions of the state and bank management to develop the promising segment of card lending.
Bibliographic list
2. Official Website of Sberbank (OJSC) [Electronic resource]. - Access mode: http://sberbank.ru/.
3. Official site of the Bank "Russian Standard" [Electronic resource]. - Access mode: http://www.rsb.ru/.
4. Official website of VTB Bank 24 [Electronic resource]. - Access mode: http://www.vtb24.ru/.
6. Data on payments on Russian cards will be banned from being transferred abroad [Electronic resource]. - Access mode: http://top.rbc.ru/economics/21/03/2014/912777.shtml.
Omsk branch of the University of Finance under the Government of the Russian Federation ANALYSIS OF THE MARKET OF BANKING OPERATIONS WITH PLASTIC CARDS IN RUSSIA
Plastic cards are a relatively new banking product, but it could take its place among banking services. Work with plastic cards is one of the most promising for banks at present. In the article the analysis of the provision and use maps, discussed their views and the advantages and disadvantages. The author formulates the problem of development of the market of Bank cards and concluded that for the activation of development of the market of banking cards in Russia requires constant and systematic work with the population and commercial enterprises to change the stereotypical approach to the calculation in the trade network, which should be implemented in close cooperation with credit organizations with bodies of state power and administration.
Key words: credit cards, banks, non-cash payments, international payment system.
1. Official website of RBC. rating. Mode of access: http://rating. rbc.ru.
2. Official Site of Sberbank. Mode of access: http://sberbank.ru/.
3. Official site of Russian Standard Bank. Mode of access: http://www.rsb.ru/.
4. Official website of Bank VTB 24. Mode of access: http://www.vtb24.ru/.
5. Official site of the rating Agency "Expert RA". Mode of access: http://www.raexpert.ru.
6. Data on payments for Russian cards from being transmitted abroad. Mode of access: http://top.rbc.ru/economics/21/03/2014/912777.shtml.
Reviewers:
N.P. Rebrova, Doctor of Economics, Professor, Omsk branch of the Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation;
N.V. Puzina, Candidate of Economic Sciences, Associate Professor, Siberian Institute of Business and Information Technologies.
The beginning of the work of the branch of the Savings Bank of the Russian Federation in Tyumen with international cards falls on the end of 2000 - beginning of 2001.
In order to obtain permission to carry out transactions with international plastic cards, controllers of foreign currency deposits underwent special training: they studied the signs of the solvency of plastic cards, the procedure for conducting transactions with them, the procedure for conducting authorization. To do this, a test authorization of each controller was carried out, after which the data of the controllers who passed this authorization were sent to the bank of the Savings Bank of the Russian Federation, and the workplaces of the controllers servicing plastic cards were also checked for their compliance with the cash point (PVN) for plastic cards. PVN - special equipment and certified workplace.
Requirements for MPS: presence of imprinters; availability of a package of application programs for making operations with plastic cards; fax (for voice or data transfer) connected to various telephone network numbers; auxiliary equipment: a magnifying glass with at least five times magnification, a source of ultraviolet light for checking the authenticity of plastic cards.
Therefore, the department carried out the following organizational and technical measures: a fax was installed; purchased a printer; a draft package of applied programs was developed; The PVN was equipped with everything necessary for storing material assets in accordance with Regulation No. 56 of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation “On the Procedure for Conducting Cash Transactions in Credit Institutions on the Territory of the Russian Federation” dated March 25, 1997: it was connected to a private security console and reinforced with physical protection equipment.
Employees with a certificate giving the right to perform operations with plastic cards may be allowed to work with the PVN. The training and certification of controllers was carried out at the Academy of the Savings Bank of the Russian Federation.
After carrying out all the procedures necessary to start working with plastic cards, the branch of Sberbank of the Russian Federation in Tyumen sent the following documents to the branch of the Savings Bank of the Russian Federation: an act of the security service on the readiness to participate in the issuance of cash using plastic cards, with a list of equipment installed in the PVN; lists of employees who have a certificate for performing operations with plastic cards.
The Territorial Bank, in turn, sent the above documents to the Main Processing Center, asking for the date of commencement of work.
Having received a conclusion from the main processing center, the Territorial Bank issued an order on the date of commencement of the work of the PVN of the branch of the Security Council of the Russian Federation.
Currently, Sberbank of Russia is a full member of the international payment systems Visa International and Europay International, issues Eurocard/MasterCard (Mass, Gold, Business) and Visa (Classic, Gold, Business) cards, debit card Sberbank-Cirrus/Maestro (Sberbank- Visa Electron, Sberbank-Maestro Pension, Sberbank-Maestro Student). As of January 1, 2004, more than 1,680 institutions in 61 regional banks and OPERAs of Sberbank of Russia were issuing international cards.
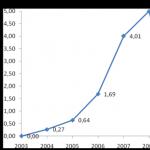
The growth in the number of international cards issued by Sberbank of Russia is developing at a significant pace. The total number of international cards increased by 14.8 times over the year, from 26,318 to 235,392 cards (absolute increase - 209,074 cards), of which: Visa and EU / MS - from 12,230 to 26,761 cards (an increase of 2 .7 times / + 14,531 pieces); Sberbank-Cirrus/Maestro - from 14,088 to 208,631 units (an increase of 12.1 times / + 194,543 units).
In 2000, Sberbank of Russia began issuing international cards linked to a ruble account. Currently, Visa, EU/MS cards with a ruble account account for 35.6%. Sberbank cards - Cirrus / Maestro are issued mainly with a ruble account. In 2003, the development of the infrastructure for accepting international cards continued. In addition, international cards are accepted at 162 ATMs of Sberbank of Russia (in Moscow - 136, in St. Petersburg - 26 (only EU/MS, Cirrus/Maestro)) and in 191 outlets in St. Petersburg. As of January 1, 2003, the balance of funds attracted to the accounts of international cards was: in foreign currency - 18.6 million US dollars, in rubles - 141.2 million rubles.
Table 2.1 Comparative characteristics of plastic cards of Sberbank of Russia and international plastic cards
|
Terms of opening and service |
Card products |
|||||
|
Visa Classic Eurocard/MasterCard |
VisaCold Eurocard/MasterCard |
Cirrus/Maestro Vsa Elertron |
Cirrus/Maestro Molodyednaya |
Cirrus/Maestro Pension/Student |
AS "Sberkart" |
|
|
Time spending |
||||||
|
Service Level |
low level of service (only in the back office) |
Wide service network |
||||
|
Initial payment to the card account |
By discretion. |
By discretion. |
||||
|
Card account annual maintenance fee By main map For each additional card |
|
|
|
6$ or 144 r not issued |
|
|
|
Accrual of % on the balance of funds on the card account In US dollars In Russian rubles |
Quarterly at the rate of demand deposits |
|||||
|
Contribution to the reserve account |
2002 $ or 48000 rubles. |
|||||
|
Overdraft fee on the account within the allowed overdraft amount, % per annum |
In the amount of the lending rate for individuals |
|||||
|
Putting a card on the stop list |
$70 or 1680 rubles |
100% or 2400 rubles. |
for free |
for free |
for free |
|
|
Early card reissue except for: Loss of the card, loss of the PIN code, change of personal data of the cardholder |
For free |
|||||
|
$5 or 120 rubles |
for free |
2$ or 48 rubles. |
||||
|
Card maintenance in trade / service enterprises |
For free |
|||||
|
Fee for loading funds on the card In institutions of Sberbank In institutions of other territorial banks |
For free |
|||||
|
Card expiry date |
At the end of the year, the card account is closed, and the card is subject to destruction |
Extended at the end of the year |
||||
|
Fee for receiving cash through a cash desk or ATM: In the service area of the Ural Bank that issued the card In the service area of another territorial bank In a third-party bank (excluding fees charged by a third-party bank): Through an ATM Through the cashier |
For free For free
|
Free on Tyumen. Region 1% of the amount |
Analysis of the structure of international bank plastic cards is carried out on the basis of quarterly reports. These summaries are compiled at the end of each quarter based on data received in the operations department from controllers servicing plastic cards. The received information is processed by employees of the department for organizing cash operations and servicing individuals, and then transferred to the territorial bank as part of the report.
Table 2.2 The number of open international plastic cards in the branch of the Savings Bank in Tyumen
According to the table, we can conclude that by the end of the 4th quarter of 2003 there was an increase in the opening of accounts with international plastic cards.
As of the end of the fourth quarter of 2003, a total of 89 card accounts were opened in the Kurchatov branch, including 26 Visa cards, 58 Cirrus/Maestro cards and 5 Euro Card/MasterCard cards.
Table 2.4 Information on the issue and balances on the accounts of cards of international payment systems for department No. 8053 for the 1st quarter of 2004
|
information about the issue and balances on the accounts of cards of international payment systems for department No. 8053 for the III quarter of 2004 |
Number of cards (main holders + additional holders) |
Number of cards in use (primary holders only) |
Turnovers per month |
Cash balances at the end of the month |
Overdraft by cards |
||
|
To card accounts |
To other (reserve, etc.) accounts |
||||||
|
Accounts in the currency of the Russian Federation |
|||||||
|
Visa, total |
|||||||
|
Eurocard/MasterCard, total |
|||||||
|
Sberbank - Cirrus/Maestro |
|||||||
|
Sberbank-Visa Electron |
|||||||
|
Sberbank-Ma Estro pension. |
|||||||
|
Sberbank-Ma Estro student |
|||||||
|
Foreign currency accounts |
|||||||
|
Visa, total |
|||||||
|
Eurocard/MasterCard, total |
|||||||
|
Sberbank - Cirrus/Maestro |
|||||||
|
Sberbank-Visa Electron |
|||||||
|
Visa, total |
|||||||
|
Total Eurocard/MasterCard |
|||||||
|
Total Cirrus Maestro |
|||||||
|
Total Visa Electron |

Rice. 2.5
Graphically, the structure of international maps is presented in the diagrams shown in Figure 2.7.
Rice. 2.7 Structure of international plastic cards opened in the branch of Sberbank of the Russian Federation in Tyumen (4th quarter of 2002)


Rice. 2.8
It is important to note that the structure of international cards issued by the branch in the fourth quarters of 2002 and 2003 did not undergo significant changes. Thus, the share of Eurocard/MasterCard cards remained unchanged and amounted to 2.5% of the total number of issued cards. The Visa card increased its share from 26.9% in the fourth quarter of 2002 to 31.6% in the same period of 2003.
Thus, there are several reasons for the insufficient number of international cards in circulation in the Ural region as a whole.
One of the most important factors is economic - the unstable financial situation of enterprises and the lack of sufficient solvency of the population of the Chelyabinsk region.
The stabilization of the economic situation may soon lead to the fact that tariffs will become more affordable for everyone who wants to receive card data. In addition, the lack of connections between the enterprises of our country and foreign partners leads to the fact that corporate cards remain unclaimed.
Another reason for the small number of issued cards in the branch of Sberbank of the Russian Federation in Tyumen is the insufficient advertising activity of the branch, so the bank needs to take a number of promotional activities in order to increase the performance of issued international cards: conduct an advertising campaign in the media (television, radio, newspapers ); release billboards on city streets; place advertisements in branches of the branch, in large supermarkets of the city.
Based on the advantages and disadvantages described above, in order to improve the work of the department with plastic cards, some recommendations can be made: to expand the network of servicing plastic cards of international systems, that is, to organize work in the branches of the department; revise tariffs for some regions of the country; conduct an advertising campaign on international plastic cards.
Thousands of people and numerous organizations own plastic cards of international and domestic payment systems, local cards of various banks and do not want to part with the convenience that "plastic" provides. Plastic cards surprise us more and more with their diversity. Interest in them is growing rapidly. In itself, the possession of a plastic card already means a certain higher social status of the employee and emphasizes the modern business image of the company.
Schematically, the mechanism of payments using plastic cards is shown in Figure 2.1.
Figure 2.1 - Mechanism of settlements using a plastic card in a local payment system
Let's explain this diagram. The cardholder, having come to the service point, presents the card to pay for goods (services) or to receive cash. A service point can be not only a trade and service company, but also a bank branch or an ATM - in the case of issuing cash. An employee of the service point verifies the authenticity of the card and the eligibility of the holder to dispose of it, using the data indicated on the card itself. Then he leads the authorization procedure, requesting the issuer to confirm the authority of the cardholder and his financial capabilities. The result of the authorization procedure is the permission or prohibition to perform the operation. The authorization technology depends on the scheme of the payment system, the type of card and the technical equipment of the service point.
The considered mechanism is classical and underlies the calculations by the majority of used bank plastic cards in the world, which are magnetic. But there are situations when the use of magnetic tape cards is undesirable or simply impossible.
For example, if it is problematic or even impossible to carry out authorization in the “on-line” mode due to the lack of reliable high-speed communication networks, the way out of the situation is to change the authorization technology, namely, instead of authorization in the “ton-line” mode, it is carried out in the mode off-line.
Carrying out this authorization imposes certain requirements on the card, namely: the presence on the card of data on the size of the spending limit; the possibility of a controlled decrease in the value of the balance of the limit as a result of authorization (the operation of debiting the card); the possibility of restoring the limit on the card (card crediting operation). To meet these requirements, the card must, at a minimum, have writable memory. In principle, magnetic stripe cards allow this use. However, the small capacity of the memory, and, most importantly, the weak degree of protection against unauthorized modification of the data recorded on the magnetic strip, makes them unsuitable for off-line service. On the contrary, the smart card meets the necessary requirements to a greater extent.
To carry out "off-line" authorization, a smart card is placed in the reader of the POS-terminal, after which, based on the system data stored in them, information is exchanged and mutual recognition takes place between them. In case of successful completion of this procedure, the holder enters the PIN code using the POS-terminal, and the service point employee enters the purchase amount, after which the purchase amount is automatically compared with the remaining limit on the card.
If the amount does not exceed the balance, the card reduces the balance of the limit by the given purchase amount, and the PQS-terminal records the transaction data. After that, the card is returned to the holder along with a copy of the invoice and the goods (or the provision of services) (Figure 2.2).

Figure 2.2 - The mechanism for carrying out "off-line" authorization using a smart card
Depending on the options for the technical implementation of the process, during the day after the transactions, information about transactions is accumulated either by the PQS terminal itself, or by the computer to which the terminal is connected, or by a special service point smart card placed in the terminal.
In addition to the considered settlement mechanism, in a local payment system, it is necessary to consider the mechanism for using a plastic card in a developed payment system that is larger than the local one.
In such a payment system, the mechanism of settlement transactions is complicated by delimiting the functions of the issuer and acquirer, as well as adding a settlement bank and a processing company to the list of participants (Figure 2.3).
The most important thing for the cardholder is the conditions under which his card account is serviced, that is, what is called a payment (settlement) scheme in banks. And since this very payment scheme is decisive for the client, then for banks, the competent construction of an attractive payment scheme is the most important factor in the effectiveness of the card program.

Figure 2.3 - Scheme of organizing cashless payments using a plastic card in a developed payment system
Some Western experts divide the whole variety of payment schemes into three large groups - credit, settlement, debit or debit.
The credit scheme provides for a zero initial balance on the card account. All transactions with the card are recorded on credit, which the cardholder must repay under certain conditions.
The essence of a debit card is that the operation carried out on it is debited (debited) from the client's bank account on the same day. If the transaction amount exceeds the account balance, the transaction is not performed. Naturally, debit cards require authorization for each transaction. But the risk of an unauthorized loan is minimized.
Bank plastic cards rightfully occupy the position of an intermediate payment instrument, in the calculations, which can be used both debit and credit transfers.
Credit transfers take place in the local settlement system (where the bank simultaneously acts as an issuer and acquirer) with magnetic stripe cards that perform the technology of one message - an authorization request with a simultaneous indication of debiting funds from the card account (Figure 2.4).

Figure 2.4 - Settlement scheme and local system using magnetic stripe cards
1. Payment for the purchase (insertion of the card into the reader).
Inquiry about the client's solvency.
Solvency confirmation.
4-5. Transfer of funds from the cardholder's account to the account of a trade or service enterprise.
If you do not take into account the finality of the payment, then settlements in this system are possible with any payment scheme that is the basis, both by debit cards and credit cards (in this case, after the period specified in the contract, the 6th operation will be carried out - repayment of the cardholder's debt to the issuer on the loan).
Credit transfers also take place when paying with prepaid cards, the implementation of which is possible only on smart cards (cards with an integrated microcircuit). In smart cards that implement the concepts of "electronic wallet", the balance of available funds is stored in the microprocessor. Before the operation is completed, it is compared with the amount of the purchase of goods, services, the requested cash advance and, in case of a positive result of the check, is reduced by the amount of the operation.
A feature of the "electronic wallet" is that when the amount is written to the card, it is automatically debited from the card account to a special consolidated account that reflects the total balance of the "electronic wallets". Information about the transactions performed is stored in the electronic terminal and transferred to the card accounting system as the sum of all transactions, which is subsequently debited from this consolidated account, and in favor of the recipient of funds (Figure 2.5).
The concept of "electronic wallets" as a financial product implies a certain limit on the amount of funds stored in the wallet and its use for relatively small payments, therefore, as a rule, entering a PIN code is not required before making a transaction.

Figure 2.5 - Scheme of payments using cards - "electronic wallets"
The technological scheme for supporting transactions with prepaid cards should allow the transfer of settlement information from the acquirer to the issuer in a truncated or aggregated form, as payment systems seek to reduce the cost of supporting transactions with insignificant amounts. Settlement information, containing the minimum required part of transactions, allows the issuer to simply write off from his account, which reflects the total balance of "electronic wallets", the amounts received from acquirers.
Since the card contains information about the state of the owner's account, the operation for non-authorized amounts is performed off-line, i.e. without communication with the authorization center. The card is inserted into a special reader (POS-terminal), the cardholder enters his PIN-kid on the terminal's keyboard, and the seller enters the purchase amount. The terminal checks the authenticity and purchasing power of the card, and if there are enough funds on the account, the card balance is reduced by the amount of the transaction. Funds are transferred to the seller's account after a communication session with the bank. The scheme of payments by a card with a built-in microcircuit is shown in Figure 2.6.

Figure 2.6 - Scheme of payments using a card with an integrated microcircuit
1. Entering the PIN code and the amount of the purchase.
Identification and verification of card solvency.
Write off the purchase amount from the card.
Information about the performed operations.
Blacklist update.
Transaction register.
Settlements between banks.
Settlements of the servicing bank with the enterprise of trade, service.
Settlements of the cardholder with the issuing bank.
Payments using cards with an integrated microchip significantly speed up and simplify the process of making payments, do not require the constant use of telecommunication lines. Smart cards have more security levels than magnetic cards, so they are more secure to use. The technical aspect of the definition of plastic cards considered in the paper encourages the author to further consider their economic essence.
The main feature of a bank plastic card as a type of plastic card system is that, not being money and regardless of the degree of technical perfection, it stores a certain set of information or provides access to databases, which allows it to serve as one of the progressive means of organizing cashless payments in sphere of monetary circulation, contributing to the complication and strengthening of the dynamism of financial services.
Using a bank card to pay for a purchase (getting cash) becomes possible only after obtaining the permission of the issuer (authorization of the card). The purchase of goods in a distribution network using a bank card is carried out as follows (Figure 2.7).
The most widespread are cards with a magnetic stripe, on which three tracks are allocated. One of them is designed to overwrite data during each card transaction, and the other two are used for identification purposes. Before issuing such a card to a client, some identification characteristics are embossed on its surface: last name, first name, patronymic of the client, his account number, signature sample, validity period, etc. The same information is entered on the first and second tracks.

Figure 2.7 - Purchase of goods in a distribution network using a bank card
1. the bank card holder provides it to the cashier for placement in the electronic terminal and dials his PIN code;
2. the terminal reads the data from the card, the cashier types from the keyboard the amount paid by the holder;
The issuing bank confirms the transaction;
The terminal debits the purchase amount from the bank card and draws up a slip (it is signed by the cardholder). At the same time, the cardholder receives the purchased goods, a copy of the slip and the card is returned to him;
At the end of each working day, the trading enterprise transfers the slips issued for the day to the bank serving it. They document the operations carried out;
The acquiring bank checks all slips and transfers their total amount to the settlement account of the trading company;
The acquirer sends to the processing center information about transactions using bank cards, the issuer of which is not the acquirer;
The processing center processes the provided information and passes it to the attention of the participants for their mutual settlements;
The settlement bank repays the mutual obligations of the participating banks by debiting the corresponding amount from the correspondent account of the issuing bank maintained by it and crediting it to the correspondent account of the acquiring bank;
The issuer debits the purchase amount, including fees, from its client's account.
Thus, a magnetic stripe card is used only for identification purposes and does not carry information about the current state of the card account and the restrictions applied. Its technical characteristics are such that it cannot carry a large amount of information and has a low degree of protection against unauthorized access. Similar shortcomings are overcome when using the next generation of cards - smart cards.
The smart card stores in memory information about the state of the card account and about the last few transactions with the card. Such a card is multifunctional, has high protection against unauthorized access and allows authorization in off-line mode. In this case, direct connection of the outlet with the processing center is not required. The card exchanges information with the electronic terminal, and “recognition” takes place, then the balance of funds on the card is reduced by the amount of the purchase. As a result, the time to obtain authorization is reduced several times. During the day, the trading company submits information about the transactions performed to the processing center. It forms a register of payments for card transactions and brings it to the attention of all participants. Typically, funds are credited to the account of the merchant by the acquirer on the same day.
“Internet-banking” can be considered a kind of using the “bank-client” technology, which means, first of all, managing clients with their bank accounts without leaving their home (office). This technology in some cases allows you to work in a multi-currency mode, i.e. carry out operations in several currencies (not counting, of course, operations in the national currency).
The settlement and payment technologies used on the Internet (the so-called digital money) form a new segment of the money market. They can be conditionally divided into 5 types, the first 3 of which require the client to have a bank credit card, and the seller to have an agreement with the bank on accepting cards for payment (Figure 2.8).
Figure 2.8 - Technology of settlements and payments on the Internet
Clear text exchange. This is the easiest way to pay online - with a credit card (as when ordering by phone), with the transfer of all necessary information (card number, name and address of the owner) over the Internet without any special precautions. The disadvantages are obvious: information can easily be intercepted and used to the detriment of the cardholder. This method is now practically not used.
Use of information encryption. This is a more secure option for paying with a credit card, with all information transmitted over the Internet using secure session protocols. Although it is almost impossible to intercept information during a transaction, such information is at risk of unauthorized access to it on the merchant's server. There is also the possibility of counterfeiting or substitution of the identification number by both the seller and the buyer.
3. Use of identities. This option of using a credit card on the Internet is much more reliable, since in this case special secure information exchange protocols are used using digital certificates and a digital signature that certify the client and the seller, excluding the refusal to fulfill the terms of the agreement and the substitution of identification codes.
clearing systems. When using clearing within the Internet, the client is not obliged to disclose his personal and banking data to the store. Instead, he only reports his ID or his name in the system, after which the store receives a confirmation or refutation of the payment. In fact, payment to the store is guaranteed, while the client transfers his data once using well-secured protocols (not necessarily over the Internet) to a system where they are also securely protected. Money is deposited in the system in any way available to the client. The system also issues digital certificates identifying the customer and the merchant and uses an electronic digital signature.
Digital cash. A revolutionary type of settlements and payments on the Internet are digital cash - very large numbers (electronic files), which play the role of banknotes and coins. Modern cryptography methods ensure their reliable operation. The operating costs of such a system are minimal. In addition, digital cash can provide complete anonymity, since it does not carry any information about the client who spent it. A variant of digital cash can be a digital check. Digital cash can be physically based both in a personal computer and in a smart card.
Russian banks have become interested in the possibilities of the Internet in recent years. This is due, first of all, to the fact that the technology of providing banking services via the Internet makes it possible to reduce the costs of banking operations by about 10 times.
Bank-client systems are primarily needed by the banks themselves. Not for everyone, of course, but for those who successfully work and expand their client base. At the same time, it is still difficult for banks to assess the financial efficiency of these systems.
From the point of view of customers, the most important advantage of electronic banking services is the ability to obtain any information at any time of the day (along with the use of other features). But in general, for bank customers (both individuals and legal entities), the main factor holding them back from joining the number of users of such systems remains the amount of payment for the system's services.