Keywords
DEPOSIT POLICY/ DEPOSIT POLICY / RATING SYSTEM/ESTIMATE RATING SYSTEM/ COEFFICIENT ANALYSIS/ RATIO ANALYSIS / FINANCIAL INDICATORS/FINANCIAL INDICATORS/ POINT-WEIGHT ASSESSMENT METHOD / POINT RATING AND WEIGHTS EVALUATION METHODannotation scientific article on economics and business, author of scientific work - Mitrokhin V.V., Gribanov A.V., Vilkova M.V.
Item. One of the pressing problems in the field of banking analysis is the lack of effective tools to assess the effectiveness of deposit policy credit organizations. The methods used are focused on the analysis of the economic situation of banking institutions, which does not make it possible to evaluate the effectiveness of measures taken within the framework of certain areas of banking activity, including deposit policy credit organizations. Goals. Development of an assessment methodology deposit policy commercial bank, analysis of existing methods, justification taking into account the identified limitations of the author's approach; approbation of the author's methodology on the example of a credit institution. Methodology. A systematic approach, analysis and synthesis, comparison and comparison method, as well as economic and statistical methods are used. Results. A methodology for assessing deposit policy jar. Application area. When evaluating deposit policy banking institutions. Conclusions. Grade deposit policy is one of the key tasks in the activities of a credit institution. Current methods either do not allow evaluating the effectiveness deposit policy bank segregated from a comprehensive assessment of the effectiveness of its activities as a whole, or focused on certain key aspects of this process. The authors proposed a methodology for evaluating the effectiveness of deposit policy, built on the analysis of three groups of indicators and allowing to study the latter in the context of its impact on the stability of a credit institution.
Related Topics scientific papers on economics and business, author of scientific work - Mitrokhin V.V., Gribanov A.V., Vilkova M.V.
-
Accounting and analytical support of the bank's business processes: deposit operations
2017 / Baeva Elena Alexandrovna, Cheremisina Natalia Valentinovna -
Features of assessing the investment potential of a commercial bank
2018 / Chugunov Victor Ivanovich, Loginov Dmitry Valerievich - 2016 / Litvinova A.V., Parfenova M.V., Litvinov E.O.
-
Clustering of regions of the Russian Federation by the level of deposit risk
2018 / Lunyakova Natalya Avtandilovna, Lavrushin Oleg Ivanovich, Lunyakov Oleg Vladimirovich -
Improving the deposit policy on the example of VTB24 bank (PJSC)
2017 / Kharlamova E.S. -
Methodology for constructing a deposit matrix of a commercial bank
2014 / Balabanova Natalya Vladimirovna, Valinurova Anna Aleksandrovna, Goryunova Yulia Leonidovna -
A comprehensive methodology for building a balanced interest rate policy of a commercial bank in the field of credit relations
2014 / Smulov A.M., Abdyukova E.I. -
Analysis of financial results of credit institutions in the Republic of Mordovia
2015 / Kolesnik N.F., Golovanova V.S. -
The influence of deposit policy on the financial stability of a commercial bank
2016 / Zhilan Oksana Dmitrievna, Danilova Maria Romanovna -
Formation of a deposit policy by a commercial bank
2019 / K. O. Kotlyarov
A methodology for assessing the efficiency of the commercial bank""s deposit policy
Importance This paper concentrates on the issues of deposit policy of credit institutions including organization and management of deposit processes. Objectives The paper aims to develop a methodology for deposit policy assessment of a commercial bank. Methods As the methodological base of the study, we used the systems approach, method of comparison, and economic and statistical methods. Results The paper presents a newly developed technique of assessment of the commercial bank's deposit policy . Conclusions and Relevance The proposed methodology for evaluating the effectiveness of the bank's deposit policy is based on three sets of indicators and allows it to be explored in the context of the impact on the sustainability of the credit organization. The results presented can be used to evaluate the deposit policy of banking institutions.
The text of the scientific work on the topic "Methodology for assessing the effectiveness of the deposit policy of a commercial bank"
pISSN 2071-4688 Banking
METHODOLOGY FOR ASSESSING THE EFFICIENCY OF THE DEPOSIT POLICY OF A COMMERCIAL BANK
Vladimir Vladimirovich MITROKHINA% Alexey Vladimirovich GRIBANOV, Maria Viktorovna VILKOVAs
a Candidate of Economic Sciences, Professor of the Department of Finance and Credit, National Research Mordovian State University. N.P. Ogaryova, Saransk, Russian Federation [email protected]
ь postgraduate student of the Department of Finance and Credit, National Research Mordovian State
university. N.P. Ogaryova, Saransk, Russian Federation
with Economist of the Risk Assessment Department of AKSSB KS BANK (PJSC), Saransk, Russian Federation [email protected]
Article history:
Received 10/04/2017 Received in revised form 11/06/2017 Approved 11/20/2017 Available online 12/22/2017
UDC 336.717.3 JEL: G21
Keywords:
© Publishing house FINANCE and CREDIT, 2017
annotation
Item. One of the pressing problems in the field of analysis of banking activities is the lack of effective tools to assess the effectiveness of the deposit policy of credit institutions. The methods used are focused on the analysis of the economic situation of banking institutions, which does not make it possible to evaluate the effectiveness of measures taken within the framework of certain areas of banking activity, including the deposit policy of credit institutions.
Goals. Development of a methodology for assessing the deposit policy of a commercial bank, analysis of existing methods, justification, taking into account the identified limitations of the author's approach; approbation of the author's methodology on the example of a credit institution.
Methodology. A systematic approach, analysis and synthesis, comparison and comparison method, as well as economic and statistical methods are used. Results. A methodology for evaluating the bank's deposit policy has been developed. Application area. When evaluating the deposit policy of banking institutions. Conclusions. Assessment of the deposit policy is one of the key tasks in the activities of a credit institution. The current methods either do not allow assessing the effectiveness of the bank's deposit policy, segregated from a comprehensive assessment of the effectiveness of its activities as a whole, or are focused on certain key aspects of this process. The authors propose a methodology for evaluating the effectiveness of the deposit policy, which is based on the analysis of three groups of indicators and makes it possible to study the latter in the context of its impact on the stability of a credit institution.
For citation: Mitrokhin V.V., Gribanov A.V., Vilkova M.V. Methodology for evaluating the effectiveness of the deposit policy of a commercial bank // Finance and credit. - 2017. - V. 23, No. 48. - S. 2888 - 2902. https://doi.org/10.24891/fc.23.48.2888
At present, the domestic financial market operates in a highly competitive environment, which makes its development and sustainability a top priority and one of the priorities of the Bank of Russia. Its solution is impossible without
the availability of effective tools for assessing the financial condition of a credit institution, as well as key areas of its activities. One of these areas, the qualitative implementation of which determines the stability of the functioning of credit institutions, is their
deposit policy. This implies a direct need to define the term "deposit policy" in the context of the sustainable development of a commercial bank.
In our opinion, the concept of "sustainable development" in relation to a commercial bank must be defined from the standpoint of a synergistic approach: a steadily developing credit institution should be characterized by the ability to maintain and restore financial stability in the course of its operation, despite the negative impact of external and internal environmental factors, thanks to the developed mechanisms resolution of continuously arising conflicts (contradictions), and in the process of stabilization to move to a new level of self-development; the development of a commercial bank is achieved through a critical analysis of newly received data on factors that bring the system out of balance, updated strategies and tactics of the organization, containing a risk assessment and a system of preventive measures, developed and on an ongoing basis through a critical analysis.
In turn, the concept of "deposit policy" must be disclosed in a broad and narrow sense: in a broad sense, a deposit policy is understood as an integral element of banking policy, which is part of the process of transforming funds attracted by a credit institution into investment resources and providing, through comprehensive strategic planning and a combination of sequentially related actions, methods and methods of management; formation of an effective structure of the resource base, which makes it possible to ensure a given level of profitability and liquidity of a credit institution with uninterrupted deposit financing of its commercial activities; in a narrow sense, the deposit policy is understood directly as the process of raising funds, focused on ensuring the stability of the bank (long money, a variety of attraction tools, an acceptable interest rate policy, etc.).
We believe that if the deposit policy of a commercial bank ensures its sustainable development, it should be recognized as effective. Note that determining the degree of effectiveness of the deposit policy of a particular credit institution is an urgent need in the practice of banking analysis. Taking this into account, let us determine the critical, in our opinion, requirements for the methodology for its assessment.
First, the methodology should provide an opportunity to assess the effectiveness of the deposit policy of a commercial bank segregated from the assessment of its activities as a whole. This is due to the fact that a comprehensive assessment of the activities of a credit institution is extremely complex, and its use reduces the reliability of the results obtained.
Secondly, the evaluation of the effectiveness of the deposit policy of a commercial bank must be carried out in the context of its sustainable development, and therefore for a number of reporting periods. Thus, the methodology should provide the analyst with the possibility of horizontal analysis to identify the main trends in the development of credit institutions. The methodology should also contain elements of a vertical analysis of the credit institution's balance sheet, in particular, the grouping of attracted funds by sources of attraction and by maturity.
Thirdly, the methodology should ensure the objectivity of the results obtained, as a result of which we prefer ratio analysis and an approach based on assigning a rating to credit institutions. This, in turn, will give the analyst the opportunity to compare the effectiveness of the deposit policy of several credit institutions.
Fourthly, the methodology should include the necessary and sufficient system of financial indicators.
Fifthly, the methodology should provide an opportunity to assess the effectiveness of the deposit policy of a commercial bank, both internal and external.
observer, which implies free access to all necessary information.
We have analyzed the currently existing methods for evaluating the effectiveness of the deposit policy of commercial banks. They can be conditionally divided into three groups:
1) methods based on the rating system of assessments of commercial banks. With the help of these methods, an analysis of a certain set of credit institutions is carried out, the choice of which is determined by the purpose and objectives of the relevant study. At the same time, depending on the organization of the assessment procedure, rating methods are divided into methods carried out on the basis of financial statements or on the basis of expert assessments. Accounting valuation methods are based on a rigidly formalized system of financial ratios (which often imposes certain restrictions on the analyst, since not all information about the valuation object can be expressed in numerical representation), while expert assessments are based on a certain amount of subjectivity (professional judgment, experience and qualifications of the specialist conducting the study);
2) methods based on the coefficient analysis of commercial banks. This group of techniques is extremely popular among analysts due to its simplicity. In addition, these methods have a number of other important advantages: firstly, they enable the analyst to operate with relative values and, accordingly, compare banks with different parameters; secondly, knowledge of the normative values (or the range of normative values) allows the analyst to identify inefficient credit institutions; thirdly, they are objective and standardized. However, this group
methods cannot be considered fully perfect. In particular, one of their shortcomings is the difficulty of interpreting the results obtained: a detailed system of financial ratios, on the one hand, allows a comprehensive assessment of the activity of the analyzed commercial bank, but on the other hand, it significantly complicates the systematization and structuring of the information received. In addition, despite the existence of normative values, one should be guided by them with extreme caution, since they significantly depend on the conditions for the credit institution to carry out its commercial activities;
3) methods based on financial analysis of commercial banks. Note that the methods of this particular group are most often used to assess the effectiveness of the deposit policy of commercial banks segregated from the assessment of the effectiveness of their activities as a whole. We also note that absolute indicators, such as revenue or net profit, play a dominant role in financial analysis, which makes it difficult to compare credit institutions whose scale of activity differs significantly from each other. It is important to pay attention to the fact that within the framework of this area, the assessment procedure is carried out in a multi-stage and complex manner, including: a) a horizontal (temporal) analysis, through which information is provided on the dynamics of financial indicators characterizing the efficiency of a commercial bank for a number of reporting periods; b) trend analysis, which is a logical continuation of the horizontal analysis and through which the main trends in the dynamics of the studied financial indicators are determined; c) vertical (structural) analysis, in which the structure of absolute financial indicators characterizing the efficiency of a commercial bank,
is revealed through the specific gravity of the individual elements that make it up; d) ratio analysis, through which the values of financial ratios that characterize the efficiency of a commercial bank are compared with the normative or with the values of financial ratios of compared credit institutions.
It has been established that none of the studied methods fully satisfies the system of requirements previously put forward by us:
1) the vast majority of currently existing methods do not allow evaluating the effectiveness of the deposit policy of a commercial bank segregated from a comprehensive assessment of the effectiveness of its activities as a whole, and therefore does not allow it to be given an exhaustive assessment;
2) the same few works in which the evaluation of the effectiveness of the deposit policy of a commercial bank is carried out segregated from the complex one, are often of a theoretical nature and are not applied in practice. In the same works in which researchers use financial ratios to assess the effectiveness of the deposit policy of a commercial bank, the latter, as a rule, either do not allow assessing the deposit policy in the context of the stability of a credit institution, or their choice is determined by the subjective experience of analysts who form their assessment basis based on own preferences.
That is why we propose the author's methodology for assessing the effectiveness of the deposit policy of commercial banks, segregated from the assessment of its activities as a whole, developed in full accordance with the previously put forward requirements. In order to test the developed methodology, the effectiveness of the deposit policy of AKSSB "KS BANK" (PJSC) was assessed, its effectiveness was correlated with
the regional market as a whole. Note that the completeness of the analysis in this case and in accordance with the requirements for the methodology can be ensured by data obtained from publicly available sources. In particular, these are official reports disclosed by credit institutions on the website of the Bank of Russia (forms No. 0409101, No. 0409102, No. 0409123). In addition, special attention should be paid to the fact that the developed methodology is based on the point-weight method, as well as the method for evaluating the effectiveness of the deposit policy of a commercial bank through the analysis of a system of indicators, which makes it possible to ensure the objectivity of the results obtained, as well as to consider them in dynamics over time. a range of reporting periods. The proposed method is carried out in several stages.
Stage 1. Calculation of coefficients characterizing the effectiveness of the deposit policy. In our opinion, it is necessary to evaluate it through a system-vector analysis of the three main directions of its development. Firstly, this is the formation of the most efficient structure of the resource base of a credit institution; secondly, it is the formation of the most effective active-passive potential of a credit institution; and thirdly, this is the formation of the most stable resource base of a credit institution. Determining the extent to which the individual potential of each of these vectors is realized, we carry out a comprehensive assessment of the effectiveness of the deposit policy. In accordance with the above, for remote evaluation of the effectiveness of the deposit policy of commercial banks, we propose to use a system of financial ratios, which, in turn, consists of three subsystems (Table 1).
In the first subsystem, we propose to include a group of coefficients,
1 The regional banking sector of the Republic of Mordovia is represented by three credit institutions: AKSSB KS BANK (PJSC) (registration number 1752), JSCB AKTIV BANK (PJSC) (registration number 2529), PJSC CB MPSB (registration number 752).
characterizing the structure of the resource base of a commercial bank, which will introduce elements of a vertical analysis of its resource base into the methodology for assessing the effectiveness of the deposit policy of a commercial bank. In particular, this subsystem will include indicator coefficients that make it possible to correlate the share of time deposits (K1), demand deposits and funds on settlement and current accounts (K2), interbank loans (K3) with their standard values.
It is proposed to include in the second subsystem a group of coefficients that characterize the effectiveness of the use by a credit institution of funds raised in its resource base. In this case, we are talking about coefficients-indicators that characterize the degree of consistency of the interest rate policy of a commercial bank on its active and passive operations (otherwise - the net SPRED of a credit institution) (K4), its ability to generate net interest income (otherwise - the interest margin of a credit institution) ( K5), as well as the profit he receives from each ruble of the resource base advanced for the formation of bank assets (in other words, the profitability of the assets of a credit institution) (K6) .
And, finally, in the third subsystem, in our opinion, it is necessary to include coefficients that characterize the stability of the resource base of a credit institution. These include coefficients-indicators that allow us to estimate the average quarterly term of keeping a deposit ruble in deposit accounts of legal entities and individuals (K7 and K8, respectively), the share of the total amount of funds attracted for the quarter to deposit accounts of legal entities and individuals, remaining in resource base of the bank (K9 and K10, respectively), as well as the share of funds attracted to demand accounts and settlement and current accounts, which can be used by the bank as a stable resource (K11 and K12, respectively) .
For AKSSB "KS BANK" (PJSC) and the banking sector of the Republic of Mordovia as a whole were
the data necessary for calculating the coefficients-indicators, as well as the values of the latter as of the first day of each quarter in dynamics from 07/01/2014 to 07/01/2017 were analyzed.
Stage 2. Digitization of the coefficients characterizing the effectiveness of the deposit policy into points. For each of the indicators used, the scales of their values are calibrated into points, which allows, firstly, to monitor the dynamics of changes in the effectiveness of the deposit policy of both a particular credit institution and the banking sector of the region as a whole over the required time interval; second, to compare the effectiveness of the deposit policy of a particular credit institution with the effectiveness of the deposit policy of its closest competitors or, as in our case, with the efficiency of the regional market as a whole; thirdly, to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the effectiveness of the deposit policy of a commercial bank using a system-vector analysis of a set of financial indicators of a different nature, a priori excluding the possibility of their automatic summation. Thus, it is the digitization of indicator coefficients into points that makes it possible to satisfy the previously put forward requirements for the methodology for assessing the effectiveness of the deposit policy.
Note that when digitizing the values of the indicator coefficients into points, their scaling must be done independently of each other. At the same time, preference should be given exclusively to linear scaling, since the range of changes in input variables is obviously determined by analyzing quarterly data using coefficients that characterize the effectiveness of the deposit policy. As criterion points for digitization, we propose to use the minimum value of the input variable, its median and maximum value. Let us note that we
it was the median that was chosen, and not the average value of the input variable, since it has a high rarity (insensitivity to errors and sample heterogeneities) . Thus, the criteria points will set the boundaries for two ranges:
1) in the first range, the value of the variable, measured in points, is in the interval , with the range of values of the input variables [xme;xmax]. Digitization into points in this case is carried out according to the following formula:
v_g 5"(Xi Xme)
The scheme of the transformation mechanism, in accordance with which the values of the coefficients-indicators are digitized into points, is shown in fig. 1.
The values of the coefficients characterizing the effectiveness of the deposit policy of AKSSB "KS BANK" (PJSC) and the banking sector of the region as a whole, digitized into points, are considered.
Stage 3. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the deposit policy. At this stage, we are performing a comprehensive system-vector assessment of the effectiveness of the deposit policy of AKSSB "KS BANK" (PJSC), as well as its comparison with the effectiveness of the deposit policy of credit institutions in the region as a whole, which allows us to most fully demonstrate the capabilities of the developed methodology.
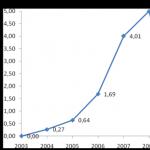
In particular, a horizontal analysis of the effectiveness of the deposit policy in the banking sector of the Republic of Mordovia in
On the whole, it indicates that it cannot be recognized as highly effective in the studied time interval (Fig. 2). For example, as of 07/01/2017, the effectiveness of the deposit policy implemented by credit institutions in the region is estimated at 53.18 points out of 120 possible.
At 13.61 points out of 30 possible, the efficiency of credit institutions in the region is assessed in terms of the formation of the structure of their resource base, which makes it possible to assess this vector of development of their deposit policy as medium effective (Fig. 3).
At 22.47 points out of 30 possible, the effectiveness of credit institutions in the region is assessed in terms of the formation of their active-passive potential, which makes it possible to assess this vector of development of their deposit policy as highly effective (Fig. 4).
At 17.11 points out of 60 possible, the effectiveness of credit institutions in the region is assessed in terms of the formation of a stable resource base, which makes it possible to assess this vector of development of their deposit policy as ineffective (Fig. 5).
A comprehensive analysis of the results obtained indicates that, as of the last reporting date in the analyzed time interval, commercial banks registered in the Republic of Mordovia realized their individual potential to the least degree in terms of forming a stable resource base. At the same time, the dynamics of the development of the deposit policy of AKSSB "KS BANK" (PJSC) in this direction, as a whole, repeats the dynamics of the regional market, a clear evidence of which is the diagram shown in fig. 5. However, noteworthy is the fact that a slight increase in the stability of the resource base, noted for credit institutions of the Republic of Mordovia as a whole, in the period from 01.10.2015 to 01.04.2016 is accompanied by a decrease in the stability of the resource base of AKSSB "KS BANK" (PJSC) particular. This is mainly due
different dynamics of the coefficient-indicator K7, which characterizes the average period of storage of the deposit ruble on the deposit accounts of legal entities for the analyzed period. Indeed, despite the fact that in the case of AKKSB "KS BANK" (PJSC) the average amount of funds in the deposit accounts of legal entities for the quarter increased from 01.10.2015 to 01.04.2016 by 1.25 times, the amount of deposits of legal entities issued during the quarter , increased by 10.87 times. This clearly indicates a sharp decrease in the stability of the bank's resource base, which is all the more negatively assessed, since it runs counter to the trends of the regional market, in which the average amount of funds on deposit accounts of legal entities for the quarter decreased slightly over the same period of time by 1.03 times with a simultaneous decrease in the amount of deposits of legal entities issued during the quarter by 1.63 times. In turn, it should be noted that, as of the last reporting date of the analyzed time interval, KS BANK (PJSC) managed to realize its individual potential to a greater extent in terms of forming a stable resource base than credit institutions in the region as a whole: if As of July 1, 2017, the efficiency of credit institutions in the region in terms of the formation of a stable resource base was assessed as low-efficient, while the effectiveness of KS BANK (PJSC) in terms of the formation of a stable resource base was assessed as medium-efficient. This is mainly due to the fact that in the II quarter. In 2017, AKKSB KS BANK (PJSC) was less subject to the outflow of funds from deposit accounts of legal entities than other commercial banks registered in the Republic of Mordovia. Indeed, if in the regional market the amount of deposits issued for the quarter increased from 04/01/2017 to 07/01/2017 by 1.2 times, then in the case of KS BANK (PJSC) it decreased by 1.23 times, which had a positive effect on the dynamics of the coefficient-indicator K7 in particular and the effectiveness of the deposit
policies regarding the formation of a stable resource base as a whole.
In turn, as of the last reporting date in the analyzed time interval, commercial banks registered in the Republic of Mordovia most successfully implemented their deposit policy in terms of building their active-passive potential. Indeed, the analysis of the diagram shown in fig. 4 indicates that since January 1, 2017, the efficiency of using the funds raised by them has steadily increased. This is primarily due to the growth in the profitability of banking assets, which directly affected the values of the coefficient-indicator K5. Here it is necessary to pay special attention to the fact that although the dynamics of the development of the deposit policy of AKSSB "KS BANK" (PJSC) in the analyzed direction, as a whole, repeats the dynamics of the regional market (a clear evidence of this is the diagram shown in Fig. 4), from 01.01.2017 for this commercial bank, there is a decrease in the efficiency of using the funds attracted by it. This is even more negatively assessed, as it goes against the tendencies of the regional market. In fact, this circumstance is due mainly to a decrease in the profitability of banking assets, which directly affected the values of the indicator coefficient K6. Indeed, if in the IV quarter. 2016 AKKSB "KS BANK" (PJSC) received a net profit of 17 million rubles, then in the II quarter. In 2017, a commercial bank received a net loss of 1 million rubles.
Analysis of the diagram shown in fig. 3 indicates that the dynamics of the development of the deposit policy of AKSSB "KS BANK" in terms of the formation of an effective structure of its resource base is in line with the dynamics of the regional market as a whole. However, against the general background, it becomes obvious that this commercial bank does not fully implement its individual
potential for this vector of deposit policy development. This is mainly due to the fact that starting from 01.04.2016 KS BANK (PJSC) has been actively attracting interbank loans to finance commercial activities, which negatively affects the values of the indicator coefficient K3. Indeed, if as of 01.04.2016 the share of short-term interbank loans in the total amount of funds attracted by KS BANK (PJSC) from other credit institutions was equal to zero, while as of 01.07.2016 it was 0.69% , and as of 07/01/2017 - 91.3%. It should be noted that the short-term nature of interbank lending is an indirect sign of the speculative nature of its deposit operations: funds attracted for a short period are not directed by a credit institution to the real sector of the economy.
In turn, the system-vector analysis of the effectiveness of the deposit policy of AKSSB "KS BANK" (PJSC) allows us to evaluate it as an average effective one during the entire analyzed time period. The dynamics of its development must be recognized as corresponding to the dynamics of the regional market as a whole (Fig. 2). At the same time, it should be especially noted that in the first half of 2017, KS BANK (PJSC) failed to fully realize its potential. Indeed, the effectiveness of the deposit policy pursued by this credit institution was lower than the effectiveness of the deposit policy of the regional banking sector. This indicates that the effectiveness of the deposit policy of AKSSB "KS BANK" (PJSC) can and should be increased. The analysis previously performed using the proposed methodology allows us to single out two directions of its development. First of all, it is necessary to increase the effectiveness of the deposit policy of this commercial bank in terms of the formation of its active-passive potential; secondly, it is necessary to increase the efficiency of the deposit policy of this commercial bank in terms of the formation of an effective structure of its resource base
(From the diagrams shown in Figures 4 and 3, respectively, it follows that according to these vectors of development of a credit institution, there is a trend that unfavorably distinguishes it from the general regional background).
Let's summarize. Comparison of the concepts of "efficiency" and "deposit policy" is carried out by the authors by defining the deposit policy in the context of the sustainable development of a commercial bank. The main requirements for the methodology for evaluating the effectiveness of the deposit policy of a credit institution are determined. Through a comprehensive analysis of currently existing assessment methods, it is established that none of them fully satisfies the system of requirements put forward. The author's methodology for evaluating the effectiveness of the deposit policy is proposed. It is tested on the example of a specific commercial bank (AKKSB "KS BANK" (PJSC), Republic of Mordovia, registration number 1752) in combination with an assessment of the effectiveness of the deposit policy in the banking sector of the Republic of Mordovia as a whole. It is established that the developed methodology is remote (in other words, equally accessible to both internal and external analysts); makes it possible to assess the effectiveness of the deposit policy of a credit institution segregated from the assessment of its activities as a whole in dynamics for a number of reporting periods (horizontal analysis) based on a system-vector analysis of financial ratios (including elements of a vertical analysis of the structure of a credit institution, its active passive potential and stability of its resource base); allows you to get objective and reliable results, determine the place of a particular commercial bank in the regional market; makes it possible to determine the vector of further development of the deposit policy of the analyzed credit institution in order to increase its efficiency. Thus, the goals set for the researchers in this work are recognized as achieved.
Table 1
Coefficients used in the remote assessment method of the deposit policy efficiency of the AKKSB KS BANK (PAO)
Name, designation and description of the coefficient Calculation formula
Group 1. Coefficients characterizing the structure of the resource base of a commercial bank
Coefficient of the structural component of term deposits in the resource base of the bank (K1), reflecting the deviation of their share from the minimum allowable standard value 50% (Average dep. 50%) 50% " jar, %
Coefficient of the structural component of demand deposits and funds on settlement and current accounts in the resource base of the bank (K2), reflecting the deviation of their share from the maximum allowable standard value of 30% 30% " where U.v. - the share of deposits "on demand" and funds on settlement and current accounts in the resource base of a commercial bank,%
The coefficient of the structural component of interbank loans in the resource base of the bank (K3), reflecting the deviation of their share from its maximum allowable standard value 20% Y 1 mbq 20% "where Umbk is the share of interbank loans in the resource base of a commercial bank,%;
Group 2. Coefficients characterizing the effectiveness of the use of borrowed funds by the CB
Net SPREAD (K4), characterizing the level of consistency of the interest rate policy of a commercial bank on its credit and deposit operations, % W.100%---100%, CV SP KV - loans issued for the analyzed period, rub.; PR - interest expenses incurred for the analyzed period, rub.; JV - interbank loans and deposits attracted by the bank for the analyzed period, rub.
Profitability of banking assets (interest margin) (K5), which characterizes the ability of a commercial bank to generate net interest income using income-producing assets, %
Return on assets (ROA) (K6), which characterizes the profitability of the bank's assets and expresses the measure of its profitability in the analyzed period, the profit received by the bank from each ruble advanced for the formation of its assets,% analyzed period, rub.; SVB is the average balance sheet currency of a credit institution for the analyzed period, rub.
Group 3. Coefficients characterizing the degree of stability of the resource base of a commercial bank
Average storage period for the deposit ruble on deposit accounts of legal entities for the analyzed period (K7), days. DYusrT VDYu "where DYuav is the average value of funds in the deposit accounts of legal entities for the analyzed period, rubles; T is the number of days in the analyzed period, days; VDYu is the turnover on issuing deposits of legal entities in the analyzed period, rub.
Average storage period for a deposit ruble in deposit accounts of individuals for the analyzed period (K8), days. DFsr.-t VDF " where DFsr - the average for the analyzed period the amount of funds in the deposit accounts of individuals, rubles; VDF - the turnover on the issuance of deposits of individuals in the analyzed period, rubles.
The level of settling of funds received during the analyzed period on the deposit accounts of legal entities (K9), which makes it possible to assess the share of the total amount of funds attracted to the deposit accounts of legal entities in the analyzed time interval, remaining in deposits, % DUc-DYun PDYu "where DUc is the value funds on deposit accounts of legal entities at the end of the analyzed period, RUB DYUN - the amount of funds on deposit accounts of legal entities at the beginning of the analyzed period, RUB MU - turnover on receipt of deposits of legal entities in the analyzed period, RUB.
The level of settling of funds received during the analyzed period on the deposit accounts of individuals (K10), which allows to estimate the share of the total amount of funds attracted to the deposit accounts of individuals in the analyzed time interval, remaining in deposits, % DFK-DFN PDF "where DFk is the value funds in deposit accounts of individuals at the end of the analyzed period, rubles AFN - the amount of funds in deposit accounts of individuals at the beginning of the analyzed period, rubles PDF - turnover on receipt of deposits of individuals in the analyzed period, rubles.
The degree of stability (minimum balance) of funds on demand deposit accounts (K11), which allows to estimate the share of funds on demand accounts that can be used as a stable resource, % DUdv-100%, PD a.i. " where Dd.v. - the average value of funds for the analyzed period on deposit accounts "on demand", rubles; PDdv. - the turnover on receipt of deposits "on demand" in the analyzed period, rubles.
The degree of stability (minimum balance) of funds on settlement, current accounts of legal entities and individuals, as well as individual entrepreneurs (K12), which allows to evaluate the share of funds on settlement and current accounts that can be used as a stable resource, % DURS-100%, PD r.s. where Dr.s. - the average for the analyzed period the amount of funds on settlement and current accounts, rubles;
In modern conditions, for effective functioning, development and achievement of its goals, each commercial bank must develop its own deposit policy, that is, a practical management strategy. As you know, the attraction of financial resources and their subsequent placement are the main forms of activity of a commercial bank.
A fund of funds formed on a paid basis is used to invest in active instruments. Passive operations, therefore, are primary in relation to most of the banking operations aimed at generating income. In this regard, the attracted funds should be considered as an independent object of policy.
Thus, the management of attracted funds is an important component of the bank's business policy. However, issues related to the study of the theoretical foundations of this field of activity have not been sufficiently developed in the scientific literature. This is especially true of the concept of the deposit policy of a commercial bank as an integral element of the liability management strategy.
The definition of the essence of the bank's deposit policy cannot be approached unambiguously, since it varies depending on its subject. The deposit policy is a strategy and tactics of a commercial bank to attract customer funds on a repayable basis.
The bank's deposit policy should include:
Development of a strategy for the implementation of the bank's activities to raise funds in deposits, based on a comprehensive market research, that is, an analysis of the financial environment, the place and role of the bank in the field of raising funds, diagnostics and forecasting;
Formation of commercial bank tactics for the development, offer and promotion of new bank deposit products for customers (in the field of commodity, pricing, marketing and communication policy);
Implementation of the developed strategy and tactics;
Monitoring the implementation of the policy and its effectiveness;
Monitoring the activities of a commercial bank to raise funds.
The main document regulating in commercial banks the process of attracting temporarily free funds of enterprises, organizations and the population to bank accounts in various kinds of deposits (deposits) is the deposit policy of the bank. This is a document that is developed by each bank independently on the basis of the bank's strategic plan, analysis of the structure, condition and dynamics of the bank's resource base and based on the prospects for its development. In addition, such documents are used that determine the main directions and conditions for the placement of attracted funds, such as the Bank's Credit Policy and the Bank's Investment Policy.
The document "Deposit Policy of the Bank" should define its strategy for raising funds to fulfill the statutory requirements, goals and objectives defined by the memorandums on credit and investment policy, with a focus on maintaining the bank's liquidity and ensuring profitable work. Specifically, the bank provides:
Prospects for the growth of the bank's own funds (capital), and hence the ratio between own and borrowed funds;
The structure of attracted and borrowed funds (deposits, deposits, interbank loans, including loans from the Central Bank of the Russian Federation);
Preferred types of deposits and deposits, terms of their attraction; the ratio between time deposits (deposits) and for the period "on demand";
The main contingent of deposits and deposits, i.e., the category of depositors;
Geography of attraction and borrowing of funds;
Desirable creditor banks for interbank loans, terms for attracting the latter; conditions for attracting deposits (deposits) and interbank loans;
Ways to attract deposits (based on bank account, correspondent account, bank deposit (deposit) agreements, by issuing own certificates, bills of exchange);
The ratio between ruble and foreign currency deposits (deposits);
New forms of attracting funds in deposits;
Special conditions for opening certain types of deposits (deposits);
Measures to comply with the bank's risk standards for borrowed funds.
The deposit policy must first of all meet the following requirements:
Economic expediency;
Competitiveness;
Internal consistency.
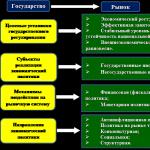
The classification of subjects and objects of the bank's deposit policy is summarized in (Fig. 1).
Figure 1 Composition of subjects and objects of the bank's deposit policy
The formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank is based on both general and specific principles, which is clearly reflected in (Fig. 2).

Figure 2 - Principles of formation of the deposit policy
A number of structural subdivisions of the bank (treasury, financial department, business development department, credit department, securities department), as well as the bank's management bodies are engaged in the development and implementation of the bank's deposit policy in close interconnection with each other: liabilities.

Rice. 3.
Thus, the board of the bank determines and approves the main directions of the deposit policy, approves the procedure and conditions for attracting deposits, and exercises general control over the implementation of the deposit policy.
The Assets and Liabilities Management Committee makes fundamental decisions on the formation of a deposit portfolio, analyzes the structure and dynamics of resources, their contingency in terms and amounts with the bank's assets in order to develop, if necessary, decisions to adjust the bank's deposit policy; exercises current control over the implementation of the deposit policy by individual structural divisions of the bank.
The financial management of the bank, together with the treasury, determines the total need of the bank for deposit funds (for a year, including a breakdown by quarters): sets the interest rates for each type of resource (deposits (deposits), bills, interbank loans); determines the amount of reservation of attracted funds in the Bank of Russia; controls the bank's compliance with the risk ratios for borrowed funds established by the Bank of Russia, etc.
Special departments of the bank are directly involved in attracting deposits in various forms: the department of deposits of citizens, the department of securities (issuing own bills, deposit and savings certificates), the credit department or the department of assets and liabilities (deposits of legal entities) and other departments in accordance with the internal organizational structure each bank.
In order to carry out practical activities to raise funds, banks develop Regulations on deposit (deposit) operations (separately for deposits of individuals and deposits of legal entities), which stipulate:
Rules and conditions for accepting deposits (deposits);
Legal status of subjects of contractual relations;
The procedure for concluding a bank deposit agreement;
Methods of accepting and issuing a deposit (deposit);
The list of documentation required for opening and using a deposit (deposit), and the requirements for them;
The rights of depositors and the obligation of the bank;
Methods of accrual and payment of interest on deposits (deposits).
Intra-bank instructions on the procedure for making specific deposit (deposit) operations, which are developed by the bank in development of the Regulations on deposits (deposits), contain the organization of the work of a branch (subdivision) of the bank with various categories of depositors; the procedure for issuing documents corresponding to the commission of these operations, the scheme of their document flow; reflection in the accounting of operations for the acceptance and issuance of deposits, accrual and payment of interest on them.
The volume of funds attracted by the bank in deposits (deposits) depends on the state of supply and demand for monetary resources, the deficit or excess of funds from the bank, the state of the deposit market.
In order to attract funds from business entities and citizens into their circulation, banks develop and implement a whole range of activities. So, first of all, an important means of competition between banks for attracting resources is the interest rate policy, because the amount of income on invested funds serves as a significant incentive for customers to place their temporarily free funds in deposits (deposits).
The level of interest rates on deposits (deposits) is set by each commercial bank independently with a focus on the refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia and the state of the money market, as well as based on the provisions of its own deposit policy. First of all, the level of interest rate on deposit (deposit) operations of banks depends on the type of deposits (deposits). As a rule, on demand deposits, characterized by the instability of the balance, high mobility and mobility, minimum interest rates are set.
In order to encourage clients to maintain stable, not declining balances on demand accounts, which generally has a significant impact on the profitability of credit operations, banks set increased interest on them or on the amount of the balance not lower than the minimum calculated by the bank and agreed with the client (which is stipulated in the bank account).
When setting the interest rate on time deposits (deposits), the determining factor is the period for which the funds are placed: the longer the period, the higher the interest rate. An equally important factor is the amount of the deposit, and, therefore, the larger the amount of the deposit and the longer the period of its storage, the higher the interest rate on it, as a rule. An essential point is the frequency of payment of income on deposits (deposits). The interest rate on the deposit is inversely related to the frequency of payment of income, i.e. the less often they are made, the higher the level of the interest rate on the deposit (deposit) set by the bank. It should be noted that paying interest to banks at rates significantly higher than the economically justified level is not illegal. In this case, the material benefit received from the difference between the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation and the credit institution's rate on specific deposits should be subject to income tax.
Payment of interest on a deposit (deposit) can be made:
· once a month;
once a quarter;
after the expiration of the contract.
In order to stimulate the attraction of customer funds to time accounts in the bank, the conditions of deposits (deposits) may provide for the capitalization of interest. It is possible if the bank uses the compound interest technique when calculating income.
The traditional type of calculation of income is simple interest, when the actual balance of the deposit is used as the basis for calculation, and, based on the interest rate stipulated by the agreement, the calculation and payment of income on the deposit take place with the established frequency. Another type of income calculation is compound interest (interest on interest). In this case, after the expiration of the settlement period, interest is accrued on the deposit amount, and the resulting amount is added to the deposit amount. Thus, in the next billing period, the interest rate is applied to the new deposit amount, which has increased by the amount of previously accrued income.
To raise funds for deposits, commercial banks have begun to widely use foreign experience, in particular, they carry out:
· Development of various programs to attract funds from the population;
· provision of various types of services to depositor clients, including those of a non-banking nature (for example, elements of medical care; subscription to periodicals of economic literature; subscriptions for excursion services in museums, etc.);
Use of a high interest rate on deposits of an investment nature;
program "Bonus percentage".
In addition to a flexible interest rate policy in order to attract funds, banks must provide depositors with guarantees for the reliability of placing funds in deposits. In order to protect investors and depositors and provide them with guarantees of compensation of funds in the event of their bankruptcy, banks should create special deposit insurance funds both centrally and decentralized.
Along with deposit insurance, it is important for depositors to have access to information about the activities of commercial banks and the guarantees they can provide. When deciding on the placement of available free funds, each creditor must be sufficiently informed about the financial condition of the bank in order to assess the risk of future investments. In this regard, invaluable assistance to depositors and investors can be provided by rating assessments of the activities of banks by special agencies and bureaus.
At the same time, it should be noted that banks must also provide comprehensive information about themselves (on the amount of authorized capital, equity, founders, development prospects, performance results, etc.) to their creditors and depositors. This is especially true for individuals who choose banks to deposit their funds. Therefore, in the premises of a bank (branch, branch, additional office) accepting deposits from citizens, for the information of depositors, the following must be presented:
· a license from the Bank of Russia, which gives a particular bank the right to accept deposits from individuals either in rubles or in rubles and in foreign currency;
· auditor's report on the bank's annual report;
· the bank's balance sheet as of the last reporting date and profit and loss statement according to the forms for publication in print;
· position of the bank on the deposits of individuals;
List of types of deposits accepted by the bank from individuals. persons;
conditions for each type of deposits;
· information about the conditions for providing and guaranteeing deposits by the bank;
Forms of documents required for registration of deposits and transactions with them;
· information of the board of the bank (or other management bodies of the bank) on changes in the interest rate for certain types of deposits (indicating the reasons and terms for making changes to the conditions of deposits).
The work of credit institutions to attract creditors' funds into their circulation is associated with certain risks, which they must take into account in their activities and be able to manage them in order to avoid negative consequences for liquidity and stability.
The Bank of Russia establishes for banks and monitors their compliance with certain restrictions on the amount of funds raised. In accordance with the latest instructions of the Bank of Russia, a procedure is established for determining the balances on demand accounts and term accounts of individuals and legal entities (with the exception of credit institutions) for their inclusion in the calculation (exclusion from the calculation) of the instant (H2), current (H3) and long-term liquidity (N4) of the bank Instruction of the Bank of Russia dated 16.01.2004. No. 110-I.
The approach proposed by the Ordinance implements the method used in international practice for assessing bank liquidity risks, taking into account the so-called "behavioral" adjustments, that is, indicators characterizing the state of assets and liabilities based on accumulated statistical data.
The Ordinance establishes that banks independently determine the appropriateness of using the values of the minimum aggregate balances for calculating liquidity ratios.
It should be noted that not the entire amount of funds attracted by the bank from its customers can act as resources for its active operations. Part of the funds raised in the amount established by the Board of Directors of the Bank of Russia is subject to mandatory deposit on a separate account with the Bank of Russia. Required reserves are deposited with the Bank of Russia in accordance with Bank of Russia Regulation No. 255-P, dated March 20, 200, “On Required Reserves”. The Bank of Russia forms the obligatory reserve fund of the credit and banking system of the state. It can be used to provide credit assistance to commercial banks by the Bank of Russia in various ways, for settlements with depositors and creditors in the event of bankruptcy of a credit institution.
By changing the norms of required reserves, the Bank of Russia influences the credit policy of commercial banks, and, accordingly, the state of the money supply in circulation. For example, a reduction in the mandatory reserve requirements for funds attracted by banks allows them to use the generated resources in their turnover to a greater extent, i.e. increase credit investments in the national economy, and vice versa. Required reserves (reserve requirements) are a mechanism for regulating the overall liquidity of the banking system, used to control monetary aggregates by reducing the money multiplier.
The obligation to fulfill reserve requirements arises for a commercial bank from the moment it receives a license from the Bank of Russia for the right to perform the relevant banking operations.
Required reserve ratios are set by the Bank of Russia for a certain period of time and may be reviewed periodically, but they cannot exceed 20% of a credit institution's liabilities. It should be noted that the norms of required reserves can be differentiated depending on the timing of raising funds, their types (cash of legal entities or individuals), the currency of the deposit (deposit). Usually, the highest reserve ratio is set for demand accounts, since the client can withdraw his funds from them at any time.
The stages of the formation of a savings policy are shown in Figure 4.
Monitoring is a necessary tool for assessing and managing the quality of banking activities in the savings market. It is thanks to monitoring that the commercial bank and supervisory authorities can evaluate the results of the deposit policy pursued by the bank, which is extremely important in the development of monetary policy and other market regulation instruments, as well as to prevent crisis situations in the banking system associated with the loss of customer confidence in financial and commercial institutions.
Next, we consider the stages of formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank. It is very important to study the formation and implementation of the deposit policy mechanism of a commercial bank, since the successful fulfillment of the goals and objectives that are set for the bank in the process of developing and implementing a deposit policy largely depends on the effectiveness of its functioning.

Figure 4 Stages of formation of a savings policy
Based on the analysis of the current practice of behavior of banks in deposit operations, a scheme for the formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank is proposed, which is shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5 Scheme of formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank
Each of the stages of the formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank is closely related to the others and is mandatory for the formation of an optimal deposit policy and the correct organization of the deposit process. In this regard, the following areas of the deposit policy of a commercial bank can be distinguished:
Analysis of the deposit market;
Determination of target markets to minimize deposit risk;
Minimization of costs in the process of raising funds;
Optimization of deposit and loan portfolio management;
Maintaining the liquidity of the bank and increasing its stability.
An analysis of the current practice shows that the formation of the deposit base of any commercial bank, as a complex and time-consuming process, is associated with a large number of problems, both subjective and objective.
Subjective issues include:
1) scale of activity and weak capital base of Russian commercial banks;
2) the lack of interest of the bank's management in attracting funds from customers, especially the population, which is dictated by the tactical and strategic goals and objectives of the bank;
3) insufficient level and quality of top and middle management;
4) the lack of a science-based concept for conducting a deposit policy in most Russian banks;
5) shortcomings in the organization of the deposit process: the absence of an appropriate department in the bank, or a low level of marketing research on the deposit market, a limited range of deposit services offered, etc.
Among the objective factors are the following:
1) direct and indirect impact of the state and state bodies;
2) the impact of macroeconomics, the impact of global financial markets on the state of the Russian money market;
3) interbank competition;
4) the state of the money and financial market in Russia;
The role of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation as a regulatory body over the past few years has been especially pronounced in matters of setting the refinancing rate and reserve requirements for commercial banks. Changes in the refinancing rate do not allow commercial banks to accurately predict and plan their activities in the field of asset and liability management for the long term and make operations with long-term liabilities rather risky.
A negative impact on the structure of the resource base of a commercial bank has a growing dependence on large interbank loans, since an interbank loan does not contribute to the diversification of risks in deposit operations.
To solve existing problems, when developing a deposit policy, a commercial bank must be guided by certain criteria for its optimization. Optimization of the bank's deposit policy is a complex multifactorial task, the solution of which should be based on the consideration of the country's economy as a whole. Obviously, these interests do not always coincide. Therefore, the optimal deposit policy involves first coordinating their interests.
So, the optimization criteria are as follows:
a) the relationship of deposit, credit and other operations of the bank to maintain its stability, reliability and financial stability;
b) diversification of the bank's resources in order to minimize the risk;
c) segmentation of the deposit portfolio (according to clients, products, risks);
d) differentiated approach to different groups of clients;
e) competitiveness of banking products and services;
f) the need for an effective combination of resources, ensuring the optimal combination of stable and "volatile" resources while increasing the share of stable resources in the deposit portfolio of a commercial bank in conditions of increased risks (including deposit operations);
g) taking into account the concept of the life cycle in the process of forming the range of deposits and the deposit portfolio as a whole.
In order to improve the deposit policy of a commercial bank, the following is necessary:
Each commercial bank must have its own deposit policy, developed taking into account the specifics of its activities and the criteria for optimizing this process;
It is necessary to expand the range of deposit accounts of legal entities and individuals with a term “on demand”, which will allow, even in conditions of insignificant financial savings, the field to satisfy the needs of bank customers and increase the interest of investors in placing their funds on bank accounts;
As one of the ways to improve the organization of deposit operations, it is possible to use different types of accounts for all categories of depositors and improve the quality of their service;
Individual approach (the desire of the bank to provide the client with special benefits).
These are some of the possible ways to improve the deposit policy of a commercial bank and increase its role in ensuring its sustainability.
The relationship between the savings and deposit policy of a commercial bank is as follows: on the one hand, the main directions of the deposit policy are elements of the formation of the savings activity of the bank (for example, the range of deposits, interest rate policy, promotion of the product on the market, organization of the work of the relevant departments of the commercial bank). On the other hand, it is impossible to call the deposit policy an integral element of the bank's savings policy. The bank's deposit policy is a broader concept, which includes, in addition to the strategy and tactics of attracting resources on a repayable basis, the organization and management of the deposit process.
In general, each commercial bank develops its own deposit policy. Also, the bank's management independently determines the degree of importance of these areas, the priority of one or another type of bank policy. First of all, it will depend on the area of operation of a particular bank, its specialization and universalization.
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Posted on http://www.allbest.ru/
Introduction
1. Theoretical foundations of the interest rate policy of banks in relation to deposit operations
1.1 Economic aspects of the bank's interest rate policy
1.2 Legal framework for interest rate policy
1.3 Classification and types of interest rate policy of the bank
2. Analysis of the interest rate policy of OJSC Bank Petrocommerce in relation to deposit operations
2.1 General characteristics of OJSC Bank Petrocommerce
2.2 Analysis of the financial performance of JSC Bank Petrocommerce
2.3 Assessment of the interest rate policy of OJSC Bank Petrocommerce in relation to deposit operations
Conclusion
List of sources used
Applications
Introduction
The specificity of a banking institution as one of the types of commercial enterprise is that the vast majority of its resources are formed not at the expense of its own, but at the expense of borrowed funds. The possibilities of banks in raising funds are not unlimited and are regulated by the Central Bank. The main part of the banks' resources is formed by borrowed funds, which cover up to 90% of the total need for funds for active banking operations. A commercial bank has the ability to attract funds from enterprises, organizations, institutions, individuals and other banks in the form of deposits and open appropriate accounts.
In modern conditions, for effective functioning, development and achievement of its goals, each credit institution must develop its own deposit policy, that is, a strategy for the practical management of liabilities. As you know, the attraction of financial resources and their subsequent placement are the main forms of activity of a commercial bank. A fund of funds formed on a paid basis is used to invest in active instruments. Passive operations, therefore, are primary in relation to most of the bank's operations aimed at generating income. In this regard, the attracted funds should be considered as an independent object of banking policy. The management of attracted funds is an important component of the bank's business policy. However, issues related to the study of the theoretical foundations of this field of activity have not been sufficiently developed in the scientific literature. This is especially true of the concept of the interest rate policy of the bank in relation to deposits.
The relevance of the chosen research topic is that the unstable situation in the financial markets in the current crisis, rising inflation, competition, and other factors - all this has a huge impact on a commercial bank. Therefore, a clear and thoughtful deposit policy allows a commercial bank to maintain its position and develop.
The purpose of the final qualifying work is to analyze the interest rate policy of Bank Petrocommerce OJSC in relation to deposit operations and develop proposals for improving the deposit policy of a commercial bank in the system of strengthening its economic stability.
During the study, the following tasks were set:
- consider the theoretical foundations for the formation of the interest rate policy of a commercial bank in relation to deposit operations;
- give a general description of the activities of OJSC Bank Petrocommerce;
- to analyze the financial activity of OJSC Bank Petrocommerce;
- to analyze the deposit policy of a commercial bank on the example of OJSC Bank Petrocommerce.
The object of study of the final qualification work is JSC Bank "Petrocommerce".
The theoretical basis of the study was the legislative acts of the Bank of Russia, educational literature, statistical collections, periodicals, reference and information systems.
The financial statements and internal documents of OJSC Bank Petrocommerce served as the information base of the WRC.
1. Theoretical foundations of the interest rate policy of banks in relation to deposit operations
1.1 Economic Acinterest rate policy of the bank
The main socio-economic function of commercial banks is financial intermediation, the essence of which is to transfer cash flows from entities that have an excess of funds to entities that need them. For the performance of this function, banks receive income in the form of interest, which allows them to develop. In turn, the effectiveness of intermediation is largely determined by the possibility of allocating resources at rates exceeding borrowing rates, which makes the formation of the interest rate policy of commercial banks relevant.
The development of market relations in Russia, on the one hand, created opportunities for the market formation of the interest rate and increased differentiation of interest rates depending on the location of banks, their type, size, duration of operation, the degree of development of regional competition, etc., on the other hand, exacerbated the problems of managing interest rates and their inherent risks.
In the context of increased competition, tougher legislation, a decrease in the overall level of profitability in the banking market, and a decrease in the interest margin between attracted and placed resources, it is possible to maintain the level of profit due to the growth of total turnover and the volume of transactions.
The development by the bank of its interest rate policy, which stipulates general approaches to pricing for the services provided, calculates and fixes interest rates on loans and deposits for a certain period of time, and its implementation in practice allows the bank to have pricing guidelines for today and for some future, coordinate other areas of banking management in terms of income and expense management, profit management, etc., which ultimately ensures the effective operation of the credit institution as a whole.
Interest policy is a set of measures to regulate economic relations through interest rate management.
The interest rate policy of commercial banks is aimed at maximizing net interest income from banking operations, credit risk insurance and liquidity management of the bank's balance sheet. That is, the interest rate policy management process is aimed at solving the following tasks:
- assistance in making a profit at the moment and creating conditions for its receipt in the future;
- regulation of cost pricing (deposit and loan interest rates);
- minimization of interest rate risk;
- maintaining a balance of assets and liabilities in terms of amounts and terms;
- ensuring balance liquidity.
The interest rate policy of the bank is determined by the duration of the gap between the terms of the release of attracted and placed funds and fluctuations in interest rates, the level of interest risk, which is expressed in the risk of losses as a result of the excess of interest rates paid by the bank on attracted funds over the rates on loans.
We can single out the main principles for constructing an interest rate policy:
- close connection with the commercialization of banking activities;
- simultaneous regulation of interest rates on deposit (passive) and loan (active) operations;
- establishment of differentiated interest rates, ensuring the profitability of the bank's operations, and the procedure for their payment on a contractual basis.
The bank's interest rate policy is influenced by external and internal factors.
External factors include:
- state of the financial market;
- inflation rate;
- Demand for banking services;
- the level of banking competition;
- policy of the Bank of Russia and the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation;
- regional specificity;
- the state of the social environment.
Internal factors include:
- range of services rendered by the bank;
- qualifications and experience of personnel;
- composition of the bank's clients.
When forming the interest rate policy, the bank takes into account that different sectors of the financial market are characterized by different interest rates.
The money market rates used in short-term lending operations between financial institutions (including government ones) are the official discount rate, the rate on short-term interbank loans.
The rates of the securities market are mainly the rates of return of various bonds at the time of their issue and subsequently in the secondary market.
Rates on bank transactions with non-bank borrowers and lenders are rates associated with the provision and attraction of funds to specified borrowers and lenders.
The main principle of the interest rate policy pursued by a commercial bank in the field of resource allocation is to ensure maximum income with a balanced asset structure and a minimum level of risk of non-return of the issued resources.
Thus, the interest rate policy of a commercial bank today is aimed at the appropriate management of liquidity and profitability of its balance sheet. An effective interest rate policy should ensure the flexibility of prices for credit and deposit resources, liquidity and profitability of the bank.
1.2 Regulatory rightsNew fundamentals of interest rate policy
Banks are legal entities and are economically independent. They carry out their own interest rate policy in relation to each specific client, the end result of which is making a profit, as the main goal in the conditions of market relations. Economic and legal responsibility for the bank's work with clients lies with the founders and shareholders of the bank.
Prior to the formation of a loan portfolio, a commercial bank needs to form an interest rate policy in relation to credit and deposit operations in such a way as to maximize profits. Accordingly, the interest rate on deposit transactions is at a lower level than on credit transactions. Interest rates on various deposit instruments have their own peculiarities of formation. The rates on deposits of individuals are usually lower than the rates on deposits of legal entities due to the smaller volume of deposits and the high costs of forming a resource base. At the same time, the deposits of individuals are well managed, and by increasing the interest on deposits, a rapid inflow of resources can be ensured.
The main regulatory documents regulating the interest rate policy of commercial banks is the Regulation of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 39-P "On the procedure for calculating interest on operations related to the attraction and placement of funds by banks" . It defines the procedure for calculating interest on active and passive operations of the bank related to the attraction and placement of funds of the bank's customers - individuals and legal entities, both in the national currency of the Russian Federation and in foreign currencies, as well as for the use of funds held on bank accounts.
Banks can charge interest in one of four ways: using simple interest, compound interest, using a fixed or floating interest rate in accordance with the terms of the agreement. If the agreement does not specify the method of calculating interest, then interest is calculated according to the simple interest formula using a fixed interest rate. When calculating the amount of interest on attracted and placed funds, the interest rate (in percent per annum) and the actual number of calendar days for which funds are attracted or placed are taken into account.
Interest can be calculated in one of four ways: using simple interest, compound interest, using a fixed or floating interest rate in accordance with the terms of the agreement. If the agreement does not specify the method of calculating interest, then interest is calculated according to the simple interest formula using a fixed interest rate. When calculating the amount of interest on attracted and placed funds, the interest rate in percent per annum and the actual number of calendar days for which funds are attracted or placed are taken into account.
For participants in credit transactions, the influence on the level of interest rates of market forces and government regulation is of great importance. The state adjusts the level of the interest rate primarily in order to ensure the priority development of certain sectors of the economy. Another goal of regulating interest rates is to create equal conditions for participants in the national credit system.
An important factor determining the cost of resources attracted and placed on the credit market is the interest rate policy of the Central Bank. Most Central Banks conduct their monetary policy on the basis of interest rate regulation, i.e. determines the price of money in the economy. The Central Bank influences the level of interest rates of commercial banks by using methods of direct (directive) and indirect regulation.
Direct regulation methods include:
Limiting the upper level of interest rates;
Establishing the difference between loan and deposit interest.
Direct setting of the limit of interest rates by the Central Bank on active and passive operations of commercial banks can lead to increased competition in the market of credit resources, limiting the possibility of attracting them, the need to increase the authorized capital, reducing lending by reducing risky loans, and increasing interest rates on loans. prime borrowers.
The most effective instruments of indirect influence on the level of interest rates include:
The value of the minimum reserve requirements of the Central Bank;
Volume, conditions and market price of loans provided to commercial banks;
Liquidity ratios;
The mechanism of taxation of commercial banks.
Changes in tax rates directly affect the level of interest rates, i.e. the higher the tax rates, the higher the interest rates for the loan, and vice versa. An increase in the required reserves of the Central Bank also leads to an increase in interest rates for loans.
The rate of payment for resources set by the Central Bank, along with the required reserve ratio and the conditions for the issuance and circulation of government securities, is an effective means of managing commercial banks. Without resorting to direct regulation of the interest rate policy of the latter, the Central Bank determines the unity of the interest rate policy across the economy, stimulating an increase or decrease in interest rates. In most countries, the official rates by which the money and credit markets in the country are regulated include the discount rate or the refinancing rate.
The discount rate is the official rate of lending to commercial banks by the Central Bank. The discount rate is one of the main instruments by which the Central Bank regulates the amount of money in circulation, inflation rates, the state of the balance of payments and the exchange rate. A decrease in the official interest rate leads to a reduction in the cost of credit resources and an increase in supply on the market; on the contrary, its increase leads to a contraction of the money supply, a slowdown in inflation, but at the same time, to a reduction in investment. A change in the refinancing rate signals changes in the monetary policy of the Central Bank, depending on the level of inflation. The policy of influencing the money supply by regulating these rates is called the accounting policy. The main object, which is affected by the interest rate policy of the Central Bank, in all developed countries are short-term loans. However, by regulating the discount rate, the Central Bank affects not only the state of the money market, but also the financial market. Thus, an increase in the discount rate entails an increase in rates on loans and deposits in the money market, which in turn affects a decrease in demand for securities and an increase in their supply.
In the course of the evolution of the monetary system, the refinancing rate began to have more indicative indicators that give the economy a certain benchmark in relation to the value of the national currency in the medium term. By carrying out operations in the financial market and approving interest rates on monetary policy instruments, the bank, thereby, forms a corridor of interest rate fluctuations. The influence of interest rates of the Central Bank on the financial market is also manifested during the implementation by the bank of actions to streamline the current liquidity of the banking system.
Thus, due to strict adherence to the above principles, both in monetary regulation, and in the liquidity support policy and interest rate policy, an incentive is created for the entire banking system to effectively redistribute funds and form a resource base without the participation of bank resources.
1.3 Classification and types of interestbank policy
Based on the main goals and objectives of the interest rate policy of a commercial bank, we can distinguish the following types:
Interest rate policy on active operations;
Interest rate policy on passive operations.
Active operations - operations through which banks place the resources at their disposal. These include:
Short-term and long-term lending for production, social, investment and scientific activities of enterprises;
Provision of consumer loans to the population;
Acquisition of securities;
Factoring;
Innovative financing and lending;
Equity participation of the bank's funds in the economic activities of enterprises;
Loans to other banks.
Management of the interest rate policy for active operations consists in using a set of measures aimed at establishing optimal loan interest rates in order to ensure the bank's cost-effective operation in the implementation of credit operations and to minimize the risks associated with changes in prices for credit services.
When setting interest rates on active operations, the bank takes into account the following factors:
The official discount rate of the Central Bank;
market conditions;
Fundraising costs;
Project risk level;
The financial condition of the borrower, the degree of reliability, solvency.
The upper limit of bank interest for a loan is determined by market conditions. The lower limit is formed taking into account the costs of the bank to raise funds and ensure the functioning of the credit institution. When calculating the rate of interest in each specific transaction, a commercial bank takes into account the level of the base (determined based on the estimated cost of credit investments) and the pledged level of profitability of loans.
When determining the rate of interest in each specific transaction, a commercial bank takes into account:
Base interest rate level;
Risk premium.
The base interest rate is determined on the basis of the planned cost of loan capital and the pledged level of profitability of lending operations for the coming period.
The base bank rate is the minimum rate set by each bank for loans. Banks provide loans by adding some margin, i.e. premium on the base rate for most retail loans. The base rate includes the bank's operating and administrative expenses and profit. Set independently by each bank.
Factors that are taken into account when forming an interest rate policy on active operations also include:
The cost of raising funds (the level of the average interest rate on deposits);
The degree of risk inherent in the loan (including the condition of the collateral);
Loan repayment period;
Expenses for the formation of a loan and control over its repayment;
Competitive bank rates;
The nature of the relationship between banks and borrowers (including income from funds in the borrower's deposit account and expenses for providing services to him - paying his bills and others);
The rate of return that can be earned by investing funds and other assets.
Passive operations are operations through which banks form their resources for lending and other active operations.
These include:
Attraction to settlement and current accounts of legal entities and individuals;
Opening urgent accounts of citizens, enterprises, organizations;
Issue of securities;
Loans received from other banks.
Banks use the interest rate on deposits as the main lever in the competition for free funds of individuals and legal entities. An increase in the rate offered by the bank allows attracting additional resources. Conversely, a bank oversaturated with resources, but limited by a few profitable areas for their placement, maintains or even reduces deposit rates. Banks set differentiated rates depending on the type of deposit account, the period of placement of funds on deposit and the amount of the deposit. Pricing for the bank's deposit liabilities is based on an analysis of the relationship between the deposit rate, which reflects the market value of raising funds, and the bank's costs associated with servicing each type of deposit accounts. If the bank's operating costs for the account are significant, for example, for customer settlement accounts, then the rate will be low, or no interest will be paid at all. Sometimes the bank transfers the cost of servicing the deposit to the client by charging a fixed commission fee or setting the cost of each transaction on the account and at the same time pays interest on the balance of the client's account.
In order to interest a depositor in placing money in a bank and force him to abandon other options, borrowers must compensate him for the average level of profitability in the economy of a given country as a whole. This level is almost equal to the real rate of economic growth over a certain period of time. In this way, the initial, or principal, cost of the loan is determined, which reflects true growth, as opposed to inflationary increases in the prices of goods and services, and is therefore known as the real interest rate.
The main factors that influence the level of the base deposit rate are:
The real rate of economic growth in the country;
Expected inflation rate over the investment period;
The risk of non-return of funds that is associated with a particular banking institution.
The interest paid on deposits performs the function of redistribution, it can regulate the structure of deposits and the inflow of funds into certain forms of investments for various purposes in accordance with the demand for credit resources.
Thus, the interest rate policy is one of the most important and at the same time quite complex tools for regulating banking activity. The basic principles for constructing an interest rate scale should be based on the state of supply and demand for credit resources, retention periods, deposits, inflation rates, etc. Also, in almost all countries interest rate policy is regulated by the state.
An effective interest rate policy in relation to deposit operations is one of the most important components of the successful operation of a commercial bank. Deposit operations constitute the main group of its passive operations. On their basis, most of the bank's resources are used for the purpose of short-term and long-term lending to business entities and the population. The bank's ability to attract deposits is the main criterion for its recognition by other market participants.
2. Analysis of the interest rate policy of OJSC Bank Petrocommerce in relation to deposit operations
2.1 General characteractingOJSC Bank Petrocommerce
Bank Petrocommerce (hereinafter - the Bank) is one of the strategic assets of the IFD Kapital Group, established in 2003 as a group of financial companies and currently representing one of the largest diversified holdings, whose assets are represented in the oil and gas industry, banking and financial services, construction, chemical industry, mass media and high technologies.
In October 2013, the Bank announced the integration of the Bank into the structure of the Otkritie financial corporation through the acquisition of 79.4% of its shares.
The bank was founded in 1992, is a universal financial institution that provides a wide range of services to corporate clients, small and medium businesses, private clients, VIP clients, including investment banking services.
The Bank is one of the largest banks in the Russian Federation, has an extensive regional network, represented in 29 constituent entities of the Russian Federation and as of April 1, 2014, numbering 18 branches, 1,501 ATMs, 7,618 POS-terminals. The Banking Group also includes PJSC "Bank Petrocommerce-Ukraine" - a universal financial institution that provides a wide range of banking services. One of the main activities of PJSC Bank Petrocommerce-Ukraine is servicing Russian companies operating in the Ukrainian market and Ukrainian companies with Russian investments.
The Bank's shareholders are: Company RESERVE INVEST HOLDING (CYPRUS) LIMITED with a share of ownership of 86.03%; Company CONFERN LIMITED with a share of 10.47% and minority shareholders with a total share of 3.49%.
|
Chairman of the Board of Directors |
||
|
Fedun Leonid Arnoldovich |
Chairman of the Board of Directors of Closed Joint Stock Company "IFD Kapital" |
|
|
Members of the Board of Directors |
||
|
Alekseeva Elizaveta Ivanovna |
Director of the Department of Internal Control and Audit of the Group, Closed Joint-Stock Company "IFD Kapital" |
|
|
Zhirkov Alexander Nikolaevich |
||
|
Matytsyn Alexander Kuzmich |
Senior Vice President for Finance of OAO LUKOIL |
|
|
Mikhailov Sergey Anatolievich |
Member of the Board of Directors of Closed Joint Stock Company "IFD Kapital" |
|
|
Nikitenko Vladimir Nikolaevich |
Member of the Board of Directors of OJSC Bank Petrocommerce |
|
|
Nikitin Stanislav Georgievich |
Vice President-Treasurer of OAO LUKOIL |
|
|
Plaksina Olga Vladimirovna |
Chairman of the Board of the Closed Joint Stock Company "IFD Kapital" |
|
|
Ilyinskaya Elena Fedorovna |
First Deputy Chairman of the Board of the Closed Joint Stock Company "IFD Kapital" |
The Bank is included in the register of banks participating in the mandatory deposit insurance system, is a full member of leading professional organizations and associations, including:
Association of Russian Banks;
Association of Bill Market Participants;
National Fund Association (self-regulatory non-profit organization);
Non-profit organization "Association of Regional Banks of Russia";
Self-regulatory (non-profit) organization "National Association of Stock Market Participants";
Association "VISA";
Russian National SWIFT Association;
Moscow International Monetary Association;
National Monetary Association;
Association of MasterCard Members (non-profit organization);
Association of Factoring Companies;
Non-commercial partnership "National Payment Council";
Non-profit organization Charitable Foundation LUKOIL.
The financial reliability and stability of the Bank is confirmed by the high credit ratings of the leading international and national rating agencies.
Standard & Poor's
The Bank pays special attention to maintaining the high quality of assets, effective risk and cost management. The Bank's risk control system was certified by the independent rating agency "Expert RA", following which, on October 7, 2013, the Bank's risk control system was assigned the highest rating "A.rm". The risk management system makes it possible to take them into account both at the stage of making managerial decisions and in the course of banking activities. This system is based on the timely identification of possible risks, their identification and classification, analysis, measurement and evaluation of risk positions, as well as on the application of specific banking risk management methods. Risk assessment procedures and risk management are integrated into the processes of current operations. When building the risk management system in the Bank, the recommendations of the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision and Regulation are taken into account.
The main types of risk that the Bank identifies for management include:
Credit risk - the management mechanism is the limits that are set by the authorized bodies and Committees of the Bank on the basis of the principle of risk sharing by credit positions, which ensures the possibility of effective distribution of limits, as well as operational control over their use;
Market risk - the procedure of daily revaluation of positions and the system of volume and stop limits for positions that carry market risk are used. To establish and revise volume and stop limits, as well as to calculate discounts, the Value at Risk (VAR) method is used;
Risk of loss of liquidity - the risk of current liquidity and structural liquidity is managed separately;
Operational and legal risks - identification and collection of data on internal and external losses, their analysis and assessment. All employees of the Bank, as well as management bodies, when taking actions and making decisions, take into account the impact of operational and legal risks;
Reputational risk - measures are taken to reduce potential losses, preserve and maintain the Bank's business reputation with customers and counterparties, founders (participants), financial market participants, state authorities and local governments, banking unions (associations), self-regulatory organizations whose members is the Bank;
Country and regional risk - when determining the network development strategy, the Bank considers the situation in the regions from the point of view of political and economic stability, as well as from the point of view of the reliability of the most interesting potential counterparties. To predict the occurrence of crises, a model based on the use of econometric methods is used;
Strategic risk - the Bank uses the following methods: SWOT analysis and other methods, on the basis of which the necessary strategic measures (programs, projects) are formed to ensure the effective use of the Bank's potential, to maximize the use of synergy between different businesses.
2.2 Analysis of financial activityOJSC Bank Petrocommerce
In 2013, OJSC Bank Petrocommerce demonstrated sustainable development in all target business areas in accordance with the Bank's development strategy. However, according to the results of 2013, the Bank received a loss in the amount of 7.1 billion rubles.
An assessment of the observance of the mandatory ratios of OJSC Bank Petrocommerce is given in Table 2.
Table 2 - Evaluation of the implementation of mandatory standards
|
Name indicators |
Standard value |
Actual values |
||
|
As of the previous reporting date |
At the reporting date |
|||
|
Bank's own funds (capital) adequacy ratio (N1) |
||||
|
Bank instant liquidity ratio (N2) |
||||
|
Bank's current liquidity ratio (N3) |
||||
|
Bank's long-term liquidity ratio (N4) |
||||
|
Maximum risk limit per borrower or group of related borrowers (N6) |
||||
|
Maximum size of large credit risks (N7) |
||||
|
The norm of the maximum amount of loans, bank guarantees and guarantees provided by the bank to its participants (N9.1) |
||||
|
Total risk ratio for bank insiders (N10.1) |
||||
|
Normative use of own funds (capital) of the bank for the acquisition of shares (stakes) of other legal entities (N12) |
The data in Table 2 indicate an increase in the value of the Bank's own funds adequacy ratio at the end of 2013 compared to 2012. It is obvious that the Bank fully complies with capital adequacy requirements. As of January 1, 2014, the equity capital adequacy ratio (N1) was 12.6% according to RAS; from 01.01.2014, the total capital adequacy ratio in accordance with Basel III is 14.2%.
The Bank's liquidity indicators, as before, are at a high level: as of January 1, 2014, the instant liquidity ratio (N2) was 60.1%, current liquidity (N3) - 75.7%, long-term liquidity - 76.7% . The ratio of the loan portfolio to customer funds is 113% as of 01/01/2014 (99% as of 01/01/2013).
The instant liquidity ratio as of 01.01.2013 was 51.4%, as of 01.01.2014 this ratio increased by 8.7% and amounted to 60.1%. Thus, we can say that the value of the bank worked with an increase in current liquidity. This means that the bank will have enough liquidity to, in the event of claims on all demand obligations, repay them, while maintaining its solvency.
The decrease in the current liquidity ratio for term liabilities to 75.7% as of January 1, 2014 compared to 79.2% as of January 1, 2013, indicates a stable state, despite a slight negative trend, since this ratio still exceeds norm of 50%. Thus, the bank has liquid funds to pay off the required share of term liabilities.
As of January 1, 2013, the long-term liquidity ratio was 77.5%; as of January 1, 2014, this ratio decreased and amounted to 76.7%. This means that as of January 1, 2014, 76.7% of the bank's long-term investments were secured by long-term resources, which is significantly below the 120% standard. Thus, the Bank has a low degree of long-term liquidity, its position is stable in terms of other liquidity ratios, hence the risk of unbalanced liquidity may arise.
The maximum risk ratio per one borrower or a group of related borrowers (N6) increased in 2013 and amounted to 24.8%, which is close to the standard maximum value of 25%, which dictates the need for further diversification of the Bank's loan portfolio in order to reduce the value of this ratio.
The ratios for the maximum amount of loans, bank guarantees and guarantees provided by the bank to its participants (N 9.1) and the use of own funds for the purchase of shares in other legal entities (N12) as of 01.01.2014 amounted to 0, which indicates that the Bank has no risks in these areas .
The standard for the maximum size of large credit risks (N7) both in 2012 and 2013 is significantly lower than the norm of 800, which indicates the Bank's balanced approach to diversifying large credit risks and maintaining this ratio at a low level. In 2013, the aggregate risk ratio for the bank's insiders (N10.1) amounted to 1.7%, which is lower than the maximum possible 3% and also indicates the Bank's desire to optimize its risks.
Balance sheet data for 2012 and 2013 indicate that the Bank's business is fairly well balanced. Moderate asset growth in 2013 (by 5%) was due to focused development in priority business segments and the sale of loans worth RUB 21 billion. as part of the Bank's integration into the Otkritie Financial Corporation. The main drivers of asset growth were customer lending and operations with liquidity instruments.
Table 3 - Analysis of the dynamics of the composition of the bank's assets
|
Article name |
Actual values, million rubles |
Deviation,million rubles(Art. 3 - Art. 2) |
Pacegrowth(growth), %(Art. 3/Art. 2-100%) |
||
|
As of the previous reporting date |
At the reporting date |
||||
|
Cash |
|||||
|
In the Central Bank of the Russian Federation |
|||||
|
Net debt |
|||||
|
Other assets |
|||||
|
Total assets |
According to the financial statements, in 2013 assets grew by 5% to RUB 236.5 billion, including due to an increase in the loan portfolio. At the end of the year, the loan portfolio of Bank Petrocommerce amounted to 156.3 billion rubles, which is 5% higher than in 2012:
The Bank's retail loan portfolio grew at a rate significantly outstripping the market average - 56% against 26%, amounting to 29.6 billion rubles at the end of the year. Growth in the retail loan portfolio was driven primarily by the development of mortgages and consumer lending;
The segment of lending to small and medium-sized businesses demonstrated the highest growth dynamics: the portfolio of these loans increased 4.6 times to 9.8 billion rubles. At the same time, the quality of the Bank's loan portfolio is at a very high level: the share of overdue loans is less than 0.05%;
The factoring portfolio of Bank Petrocommerce increased by 12% to RUB 18.9 billion.
As can be seen from Table 4, the structure of the balance sheet is relatively stable and does not undergo significant changes. The main component of assets is the loan portfolio, liabilities are customer funds. Their weight in the balance structure is comparable to the average market indicators. About 80% of the balance is represented by financial instruments denominated in rubles, which allows minimizing currency risks.
Table 4 - Analysis of the dynamics of the structure of the bank's assets
|
Article name |
Actual values, % |
Deviation, (Art. 3 - Art. 2) |
||
|
As of the previous reporting date |
At the reporting date |
|||
|
Cash |
||||
|
Funds in credit institutions |
||||
|
Financial assets at fair value through profit or loss |
||||
|
Net debt |
||||
|
Net investments in securities and other available-for-sale financial assets |
||||
|
Net investment in securities held to maturity |
||||
|
Fixed assets, intangible assets and inventories |
||||
|
Other assets |
||||
|
Total assets |
The above trends contributed to the change in the structure of the loan portfolio in accordance with the plans laid down in the Bank's development strategy. Thus, the share of corporate loans decreased from 71% to 60%, the share of the retail loan portfolio increased from 13% to 19%; the share of SME loans increased from 1.4% to 6%; the share of factoring - from 11% to 12%.
As for liabilities, the main sources of growth in the resource base in 2013 were subordinated loans, bonded loans and borrowings from the Bank of Russia. In 2013, the Bank executed an offer for three bond issues with a nominal value of RUB 11 billion. Successfully placed a 5-year bond issue for 5 billion rubles. with significant oversubscription. At the end of 2013, the Bank did not experience an outflow of depositors: the decrease in funds of private clients at the end of the year was less than 1%. Attracted in Q4 2013 subordinated loans in the equivalent of RUB 10 billion contributed to the strengthening of the capital base.
Table 5 - Analysis of the dynamics of the composition of liabilities, sources of own funds and off-balance sheet liabilities of the bank
|
Article name |
Actual values, million rubles |
Deviation, (Art. 3 - Art. 2) |
Growth rate (growth), % (Art. 3/Art. 2-100%) |
||
|
As of the previous reporting date |
At the reporting date |
||||
|
Funds of credit institutions |
|||||
|
Other liabilities |
|||||
|
Total liabilities |
|||||
|
Sources of own funds |
|||||
|
Share premium |
|||||
|
reserve fund |
|||||
|
Revaluation of fixed assets |
|||||
|
Off-balance sheet liabilities |
|||||
|
Irrevocable obligations of a credit institution |
|||||
|
Guarantees and guarantees issued to a credit institution |
|||||
|
Contingent liabilities of a non-lending nature |
|||||
|
Total off-balance sheet liabilities |
In 2013, the Bank's funding structure, as shown in Table 6, did not undergo significant changes. As before, its basis (64% of liabilities) is customer funds, which decreased by 7% over the year to 139 billion rubles. In 2013, the Bank successfully executed an offer for three bond issues for 11 billion rubles, and also placed a new bond issue for 5 billion rubles with a significant oversubscription.
Table 6 - Analysis of the dynamics of the structure of liabilities and sources of the bank's own funds
|
Article name |
Actual values, million rubles |
Deviation, (Art. 3 - Art. 2) |
||
|
As of the previous reporting date |
At the reporting date |
|||
|
Loans, deposits and other funds of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation |
||||
|
Funds of credit institutions |
||||
|
Due to customers other than credit institutions |
||||
|
Financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss |
||||
|
Issued debt |
||||
|
Other liabilities |
||||
|
Provisions for possible losses on credit related commitments, other possible losses and transactions |
||||
|
Total liabilities |
||||
|
Sources of own funds |
||||
|
Funds of shareholders (participants) |
||||
|
Own shares (shares) redeemed from shareholders (participants) |
||||
|
Share premium |
||||
|
reserve fund |
||||
|
Fair value revaluation of securities available-for-sale |
||||
|
Revaluation of fixed assets |
||||
|
Retained earnings (uncovered losses) of previous years |
||||
|
Unused profit (loss) for the reporting period |
||||
|
Total sources of own funds |
||||
|
Total liabilities and sources of equity |
The statement of financial results for 2013, as is obvious from table 7, shows an increase in marginality and income from core activities. The positive dynamics of these incomes, primarily the increase in income in priority business segments, is a key factor in the growth of gross profit: interest income in 2013 increased by 21%, to RUB 20.0 billion. (16.6 billion rubles in 2012), net interest income - by 31%, to 8.4 billion rubles. (6.4 billion rubles in 2012), net fee and commission income - by 37%, to 2.0 billion rubles. (1.5 billion rubles in 2012). Gross profit for 2013 amounted to 12.3 billion rubles. (+9% compared to 2012). The increase in operating expenses is in line with business development objectives.
Table 7 - Analysis of the dynamics of the bank's financial results
Similar Documents
thesis, added 11/18/2009
Theoretical foundations for the formation and classification of the deposit policy of commercial banks. Analysis of the organization and accounting procedure for deposit operations on the example of JSC "Rosselkhozbank". Features and ways to improve the deposit insurance system in Russia.
thesis, added 02/28/2010
Formation, stages and principles of implementation of the deposit policy of commercial banks, the deposit guarantee and insurance fund as part of it. Analysis of the deposit policy of a commercial bank on the example of JSC "BTA Bank". Improving deposit operations.
thesis, added 06/19/2015
Classification of deposit operations of commercial banks. Analysis of the formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank in the banking resource management system, ways of its optimization. Development of measures aimed at attracting deposit funds.
thesis, added 04/21/2011
Formation of the deposit policy of commercial banks in the banking resource management system. Analysis of the structure of deposits in the Russian Federation. Classification of deposit operations of commercial banks. Proposals for improving the deposit policy of UbrIR OJSC.
term paper, added 10/10/2011
Types of bank deposits. The main trends in the development of the deposit market in the Russian Federation. Influence of the policy of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank. Analysis of the development of deposit operations of commercial banks on the example of CJSC "Transcapitalbank".
thesis, added 01/27/2013
Forms and instruments of the interest rate policy of a commercial bank, its legal regulation. Features of the interest rate policy of a commercial bank (on the example of FCB "Investtorgbank" (OJSC) "Kostromskoy"). Problems and prospects of interest rate policy.
term paper, added 02/23/2014
Theoretical foundations and essence of the deposit policy. Problems and prospects for the development of the resource base of banks in the Russian Federation. Elements of the deposit policy. The main stages of the formation of savings policy. Enlarged standard structure of the bank.
abstract, added 07/07/2014
Methods for analyzing the deposit policy of a commercial bank. The role of borrowed and own funds in the economy of the bank. The structure of borrowed funds. Features of each type of commercial bank liabilities. Fundamental principles of the bank's deposit policy.
term paper, added 11/10/2009
Theoretical foundations for the formation of the deposit policy of commercial banks. Analysis of the state of the deposit services market. Development of proposals to improve the deposit policy of commercial banks. Deposit policy of OAO "Impexbank".
First of all, it should be noted that in Russia, as such, methods for analyzing the bank's deposit policy have not been developed. As a rule, banks themselves develop methods taking into account the specifics of their activities and the characteristics of their operations, based on the methodological operations of the Bank of Russia.
O.D. Zhilan proposes to evaluate the bank's deposit policy in stages. At the first stage, an “Assessment of the organizational aspects of the deposit policy of a commercial bank” is carried out. To do this, we will establish the presence of the following moments in the bank (Table 3):
Table 3. Organizational aspects of the bank's activities
|
Presence of conditions in the bank |
|
|
A document on the deposit policy containing its goals and objectives, the bank's strategy and means of its implementation Availability of internal procedures and regulations accompanying the process of attracting funds to deposit accounts, namely: regulations on deposits of legal entities, Regulations on deposits of individuals, instructions on the procedure for making deposit transactions with legal entities, · Instructions on the procedure for making deposit transactions with individuals. Divisions and management bodies involved in the analysis of the deposit portfolio and management of deposit resources, exercising control An information base on the basis of which the bank's management and managers can evaluate the consequences of decisions made, their adequacy to the needs of the bank and market requirements |
Based on Table 3, we can conclude that all organizational aspects of the Bank's activities in the field of deposit policy are fully observed.
The second stage involves the analysis of the bank's deposit portfolio. Deposit research should start with market segmentation
by individual characteristics of clients, for example: residents and non-residents; legal entities and individuals; legal entities by branches of activity; small, medium, large average balance on the client's account or total monthly turnover on the client's account; by types of currencies and others.
Let us first analyze the deposit portfolio of a conditional bank in terms of the composition and structure of deposits (Table 4).
Table 4. Structure of the deposit portfolio of BALTINVESTBANK
The data in the table show that on average for 2009--2010. the largest share in the structure of demand deposits and in the structure of time deposits is occupied by deposits of legal entities (about 90% and 60%, respectively). During the analyzed period, the structure of deposits as a whole has not undergone significant changes.
To analyze deposits by maturity, it is advisable to calculate the following indicators:
The coefficient of urgency of the structure of deposits (d in D):
d in D \u003d Ds / D \u003d 23 315 / 28186 \u003d 0.83
where Ds is the volume of time deposits; D is the total volume of deposits.
This coefficient characterizes the degree of constancy and stability of the resource base. For our bank, the share of term deposits in the total amount of the bank's deposits is assessed positively, because Term deposits as the most stable component of attracted funds provide the bank's liquidity, which makes it possible to carry out operations to place resources for longer periods. To ensure the stability of the bank, this ratio should be at a level not lower than 30-35% Banking management: textbook / under Lavrushina O.I. - 2nd ed., revised and additional. - M.: KNORUS, 2009 - p.302.
Commitment Structure Ratio (KSO):
Kso \u003d Dvostr. / Ds \u003d 3 862/14 603 \u003d 0.26
It characterizes the stability of the bank's financial resources. The lower the value of the indicator, the lower the relative need of the bank for liquid assets, due to the structure of liabilities.
Table 5
Structure of deposits of BALTINVESTBANK by customer groups
The analysis of this table allows us to conclude that term deposits (82.8%), including term deposits of legal entities (more than 50%), play a decisive role in the formation of the bank's deposit portfolio. Also, deposits of legal entities form the basis of attracted funds in demand deposits. This structure of deposits can be considered optimal, since the share of resources with certain terms of attraction is quite large.
The movement of deposits in 2010 is characterized by the data presented in Table 6.
Table 6. Movement of BALTINVESTBANK deposits
The data in the table show that the volume of attraction in general for the deposit portfolio increased by 118.5%. Term deposits increased with the greatest speed - the growth rate averaged 145%. The current dynamics testifies to the good work of the bank in the field of management, control and monitoring of attracting deposits.
Based on the data in this table, we will determine the average balances of deposits (Table 7).
Table 7. Balances of deposits of BALTINVESTBANK
Table 6 shows that the resource balances during 2010 increased for all types of deposits and for the deposit portfolio as a whole by 18,247.6 million rubles. (68,334.4-50,086.8). The average balance of deposits (Dav) for the year was:
Dav = (ODnach + ODkon) / 2 = 50,086.8 + 68,334.4 = 59,210.6 million rubles.
where ODnach -- balance of deposits as of 01/01/2010;
ODcon -- balance of deposits as of 01.01.2011.
The efficiency of deposit operations is characterized by two indicators of the turnover of deposits: the number of turnovers of the deposit ruble and the duration of one turnover of deposits for the period (the period of storage of the deposit ruble). The number of turnovers (n) that deposits will make will be equal to
n \u003d OVo / Dav \u003d 57 626.4 / 59 210.6 \u003d 0.97
where OVo is the turnover on the issuance of deposits (the amount of deposits issued for the period).
The number of deposits turnover shows how many times the depositors' funds were turned over during the period, and is a direct characteristic of the deposits turnover. The more turnovers deposits make for a certain period, the more efficient their use.
The average term of deposit storage for a year (T) is determined by the formula:
T \u003d Dav / (OS / m) \u003d 59 219.6 / (57 626.4 / 360) \u003d 370,
where T is the deposit term.
This indicator characterizes the average duration (in days or years) of one turnover of deposits and is the inverse characteristic of the rate of circulation of deposits. As you can see, the average term of keeping deposits in BALTINVESTBANK is long, the deposit policy of the bank is being carried out successfully.
Using the data in the table, we will determine the average retention periods by types of deposits and the number of turnovers that they will make during the year (Table 8).
Table 8. Indicators of the Bank's deposit turnover in 2010
The deposit turnover indicators considered in the table are interconnected as follows:
If T \u003d m / n, then n \u003d m / T,
then T \u003d 360 / 0.97 \u003d 370 days
and n = 360/370 = 0.97 turns
The difference between the inflow (Pd) and outflow of deposits (Vd), and
also between the value of the balance of deposits at the end (ODkon) and the beginning of the period (ODnach) is called the sum of the influx of deposits (Csp).
Spr \u003d ODkon - ODnach \u003d Pd - Vd.
This indicator will demonstrate the absolute increase in the resource base and to some extent will characterize the effectiveness of the bank's work in attracting resources. Let's calculate it based on the table data (Table 9)
Table 9
As you can see in the table, our bank experienced a significant influx of funds in term deposits, namely from individuals, this is due to the fact that the bank is following its strategy to provide itself with a stable resource base at the expense of deposits from the population.
However, for a more specific characterization of the efficiency of operations for receiving and issuing deposits, the coefficients of inflow and settling of deposits are still used.
The deposit influx coefficient (CR) is defined as the percentage of the amount of influx of deposits for the reporting period to the balance of deposits at the beginning of the period:
Kpr \u003d Spr / ODnach * 100%.
The settling rate of deposits (Kos) is obtained by comparing the amount of the influx of deposits with the total amount of deposits received for the period and is also expressed as a percentage:
Kos \u003d Spr / By * 100%.
The deposit inflow coefficient shows the increase in the amount of deposits in relation to their value at the beginning of the period, and the settling coefficient - in relation to the amount of deposits received for the period. Using the table data, we will determine these indicators (Table 10).
Table 10
Inflow and settling coefficients of the Bank's deposits in 2010
Table 10 shows that the amount of the influx of deposits for the year amounted to
RUB 18,247.6 million (75874-57626.4).
Let's calculate the coefficients of tide and settling of deposits:
Kpr \u003d (18247.6 / 59 210.6) * 100 \u003d 30.8%;
Kos \u003d (18247.6 / 75874) * 100 \u003d 24%
At the same time, the data in Table 10 show that there was an inflow of deposits of approximately 12% on time deposits. Moreover, the largest increase of 5% occurred in attracting fixed-term deposits from individuals. This trend emerged due to the great attractiveness of interest rates and terms for time depositors.
To analyze the turnover of resources, we will determine the average shelf life and average balances of deposits for the year (Table 11).
Table 11. Holding periods and balances of bank deposits
The table shows a trend towards an increase in the terms of deposit storage. The duration of resource mobilization for the whole deposit portfolio increased by 38 days (370 - 332) under the influence of changes in the structure of deposits, as well as due to differences in terms of deposits. The terms of attraction vary significantly by types of deposits and types of clients, which may be directly related to the goals of depositors and the attractiveness of deposit storage conditions for different clients, the specifics of the deposit policy of a particular commercial bank, changes in the economic situation and other reasons. That is why the bank must know and study these factors and trends, manage them and act as an active participant in the deposit market.
Let us determine the index of the average duration of use of deposits of variable composition:
It \u003d t1 / t0 \u003d 370/332 \u003d 1.114 or 111.4%
Therefore, we can conclude that the terms of using deposits on average for the deposit portfolio increased by 11.4%, or by 38 days (370--332), so the resource base of this bank became more stable.
The analysis carried out in banks must necessarily end with calculations of reserves for economic efficiency growth. For example, using the indicator of the term for attracting deposits, one can determine the economic effect of increasing the terms for attracting resources (Ed). We calculate it as the difference between the terms of attracting deposits in the reporting and base year, multiplied by the amount of the average daily inflow of deposits in the reporting year. As a result, we get:
Ed \u003d (t1 - t0) * SDpr1
Ed \u003d (370--332) * 49.32 \u003d 1874.16 million rubles.
Based on this formula, we can conclude that the economic effect is related to the increase in settling and the increase in the terms of attracting deposits.
The management of deposit resources of a commercial bank, attracted in sufficient amount, is designed to ensure maximum efficiency of use. The effectiveness of the use of deposit resources is calculated in the next stage of assessing the bank's deposit activities. The conditions for its achievement are the maintenance of liquidity at a level acceptable to the bank, the use of the entire set of deposit resources and the achievement of a high level of profitability (profit on invested deposit resources).
Table 12
Calculation of the effectiveness of the use of attracted funds
Based on the data given in the table, we conclude that the funds raised are not fully used. The rest of the attracted funds goes to the formation of required reserves.
Summing up the analysis, we can conclude that the bank pursues a successful deposit policy. The main part of the resource base is term deposits, and this ensures the stable stability of the bank, the share of term resources exceeds the minimum norm of 30-36% (for BALTINVESTBANK this share is 80%). individuals. Every year, the term of deposit storage increases, which also led to an increase in the stability of BALTINVESTBANK's resources.
conducting
Chapter 1. Theoretical foundations for assessing the organization of the deposit policy of a commercial bank
1.1. Deposit policy of a commercial bank: concept, goals, objectives, principles and factors influencing its formation
1.2. The role of deposits in the formation of the resource base of commercial banks
Chapter 2. Evaluation of the organization of the deposit policy of a commercial bank
2.1. Economic and organizational characteristics of the activities of JSC Bank "TKPB"
2.2. Evaluation of the activities of JSC Bank "TKPB" in the market of deposit services
2.3. Analysis of the deposit portfolio of JSC Bank "TKPB"
Chapter 3. Ways to improve the deposit policy of a commercial bank
3.1. Measures to improve the deposit policy of JSC Bank "TKPB"
3.2. Development of the deposit product "Investment in the Future" for JSC Bank "TKPB"
Conclusion
List of sources used
Introduction
The most important component of all banking activities is the policy of forming the resource base. At present, the main part of banking resources, as is known, is formed in the process of conducting deposit operations of a commercial bank, on the efficient and correct organization of which the stability of the functioning of any credit institution as a whole depends. All types of deposit operations can be considered part of the banking portfolio. When managing a deposit portfolio, one should continuously analyze its composition, volume, profitability, riskiness, make forecasts and quantify cash flows. All this is a determining factor in the formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank.
The attracted funds cover up to 90% of the total need of a commercial bank in cash. In this regard, the issues of increasing the resource base and ensuring its stability through the effective management of the deposit policy are becoming particularly acute.
The relevance of the chosen topic in modern conditions is beyond doubt. The amount of attracted funds of the bank, its ability to perform active operations, and, as a result, its profit, completely depends on the degree of development of the deposit policy of a commercial bank and the confidence of depositors in this bank.
Despite the fact that the importance of studying the fundamentals of the deposit policy of a commercial bank is emphasized in the works of many economists, these issues have not been fully developed in the scientific literature. The basics of the formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank are covered in the works of E.J. Dolan, P.S. Rose, O.I. Lavrushina, V.I. Kolesnikova, V.M. Usoskin, L.G. Batrakova and others.
The purpose of the thesis research is to consider theoretical issues of evaluating the organization of deposit operations and the deposit policy of a commercial bank, as well as developing proposals for its improvement.
In accordance with the specified purpose of the study, the following main tasks are set in the thesis work:
– consider the theoretical foundations for evaluating the organization of the deposit policy of a commercial bank;
- to identify the features of the formation and implementation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank.
– to determine the economic efficiency of the proposed measures.
The object of study of the thesis is the activity of a commercial bank.
The subject of the thesis is the organizational and economic relations that arise in the process of formation and implementation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank.
The theoretical basis of the study was the legislative acts of the Bank of Russia, including Federal Law No. 177 of December 23, 2003 “On insurance of deposits of individuals in banks on the territory of the Russian Federation”, educational literature, statistical collections, periodicals, reference and information systems.
The methodological basis of the work is: the method of synthesis, analysis, the method of generalization, the dialectical method.
Chapter 1. Theoretical foundations for assessing the organization of the deposit policy of a commercial bank
1.1. Deposit policy of a commercial bank: concept, goals, functions and factors influencing its formation
Currently, to ensure the normal functioning of commercial banks, the deposit policy is of great importance, since on its basis the bulk of banking resources are formed, which are the main source for active operations. All commercial banks carry out deposit operations. Despite the existing competition between commercial banks for a depositor, each bank independently develops and implements a deposit policy that is effective for a given economic structure of the bank.
The deposit policy is a set of measures that are aimed at mobilizing funds from legal entities and individuals in the form of deposits (deposits) by banks for the purpose of their subsequent mutually beneficial use.
When forming a deposit policy, the bank independently determines the types of deposits, the deadlines for their storage, the basic rules for performing operations and other conditions.
The bank's deposit policy should include:
- development of a strategy for the implementation of the bank's activities to raise funds in deposits, based on a comprehensive market research, that is, an analysis of the financial environment, the place and role of the bank in the field of raising funds, diagnostics and forecasting;
– formation of commercial bank tactics for the development, offer and promotion of new banking deposit products for customers;
– implementation of the developed strategy and tactics;
– monitoring the implementation of the policy and its effectiveness;
- monitoring the activities of a commercial bank to raise funds.
The most important elements of the deposit policy are: determination of the optimal combination of different types of deposits and the deadlines for their storage. Currently, each commercial bank has the right to independently determine which types of deposits are most beneficial for it.
That is why the deposit policy, first of all, must meet the following basic requirements, such as:
- competitiveness - the deposit rate system should be focused on market conditions, that is, the bank that keeps rates at a lower level than competitors close to it in terms of reliability risks losing part of its clientele;
- economic feasibility - the deposit policy is designed to provide creditors with the benefit from the placement of temporarily free cash, while allowing banks to profitably use the resources they hold;
- internal consistency - the structure of deposit rates, and their differentiation by amounts, types of deposits in comparison with other comparable instruments of the same bank, as well as by different categories of clientele.
Considering the essence of the deposit policy of commercial banks, it is necessary to touch upon such issues as: subjects and objects of the deposit policy, as well as the principles of its formation.
The composition of the subjects of the deposit policy of a commercial bank includes the bank's customers, commercial banks and government agencies. The objects of the deposit policy include attracted funds of the bank and additional services of the bank (comprehensive service).
The formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank is based on both general and specific principles.
The general principles of the deposit policy are understood as principles that are the same both for the state monetary policy of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, pursued at the macroeconomic level, and for the policy specific to a particular commercial bank. These include: the principle of an integrated approach, the principle of scientific validity, optimality and efficiency, as well as the unity of all elements of the bank's deposit policy. An integrated approach is expressed both in the development of theoretical foundations, priority areas of the bank's deposit policy in terms of its development strategy, and in determining the most effective and optimal tactics and methods for its implementation for a given stage of bank development. The specific principles of the deposit policy include the principles of ensuring the optimal level of bank costs, security of deposit operations, reliability, since the bank, by accumulating temporarily free funds for the purpose of their subsequent placement, seeks to receive income not at any cost, but taking into account the realities of the market, on in which he carries out his activities.
The main goal of the deposit policy of a commercial bank is to attract as much money as possible at the lowest price. In the process of achieving this goal, it is planned to solve such problems as:
– pursuing a flexible interest rate policy;
– improving the quality of banking services and improving the culture of customer service;
– conducting deposit operations in order to obtain maximum profit in the future;
– maintaining consistency between deposit operations and credit investments;
– finding ways and means to reduce interest costs;
– minimization of banking risks.
In the process of forming a deposit policy, economic relations are being established between commercial banks and legal entities, individuals and the state regarding the attraction of their temporarily free funds, as well as practical measures in this area and ways to implement them. When conducting a deposit policy, the principles of organizing deposit operations and their relationship with the total cash turnover, the ratio of economic and organizational methods in the management of deposit operations, the forms of deposit accounts and their scope, the procedure for opening and closing deposit accounts, the rules for crediting and withdrawing customer funds are taken into account , the procedure and conditions for transferring funds from one deposit account to another, the deadlines for keeping funds in deposit accounts. Only a commercial bank that constantly focuses on expanding the range of services provided to customers, reduces costs, improves the quality of credit and settlement and cash services, provides various benefits, offers various kinds of consultations to customers, and also constantly monitors the service will be able to implement this set of measures. and service culture. It is this set of measures that plays an important role in establishing the ratio between the levels of interest rates on deposit and credit operations of a commercial bank.
It should also be noted that the process of forming a deposit policy is directly related to the interest rate policy pursued by the bank, since the deposit interest is the most effective tool in the field of attracting resources. At present, banks can independently set competitive interest rates on deposits, based on the discount rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, the state of the money market and based on their own deposit policy - for certain types of deposits, the amount of income is determined by the term of the deposit, the amount, the specifics of the operation of the account, the volume and nature related services. The payment of interest on deposits by the bank is the main part of operating expenses, which is why banks, on the one hand, are not interested in a high level of interest rate, and on the other hand, they are forced to maintain such a level of interest rate on deposits that would be attractive to customers. Trying to attract deposits, especially of large size and for a long period, commercial banks offer high interest rates to their customers, despite the growth in interest costs. However, the attraction of funds from the population by banks is not unlimited.
The determining factor in setting the interest rate on deposits is the term for which funds are placed: the longer the term, the higher the interest rate. An essential point is the frequency of payment of income, the less often payments, the higher the level of interest rate. There are also various ways of calculating interest payments.
The classic type of income calculation is simple interest - in this case, the actual balance of the deposit is used as the basis for calculation, and with the established frequency, based on the interest stipulated by the agreement, the deposit is calculated and paid.
Another type of income calculation is compound interest, when interest is charged on interest. After the expiration of the billing period, interest is accrued on the deposit amount, and the resulting value is added to the deposit amount, and in the next billing period, the interest rate is applied to a new base that has increased by the amount of previously accrued income. Also, a progressively increasing interest rate is often applied, which directly depends on the time the funds are actually on the deposit. This procedure for accruing income stimulates an increase in the period of storage of funds and protects the deposit from inflation.
Currently, commercial banks attract huge amounts of financial resources for a variety of periods, so even minimal losses can lead them to the fact that they will not be able to pay off their debts on time. In this case, the public reaction will be an influx of customers into the bank demanding the return of deposits. This can lead to depletion of the bank's resources, and force them to reduce the volume of operations that generate income. Consequently, banks suffer even from occasional market instability, from panic-stricken excessive withdrawal of deposits, which can subsequently lead individual banks to bankruptcy.
To minimize such situations, a fairly effective method has been invented to combat outbreaks of mass withdrawal of deposits and prevent crisis situations in the economy. This mechanism is called state guaranteeing (insurance) of bank deposits of the population.
Law No. 177-FZ “On insurance of deposits of individuals in banks of the Russian Federation” was signed by the President on December 23, 2003 (current edition of 07/13/2015). The objectives of this Federal Law, first of all, are to protect the rights and legitimate interests of depositors of banks in the Russian Federation, to strengthen confidence in the banking system of the Russian Federation and to stimulate the attraction of household savings to the banking system of the Russian Federation.
In accordance with this Law, the Deposit Insurance Agency pays compensation to depositors upon the occurrence of an insured event. The main objective of the system of compulsory insurance of bank deposits is to protect the savings of the population placed in deposits and on accounts in Russian banks in the territory of the Russian Federation.
The deposit insurance system works as follows - in the event of a bank closing and revocation of its banking license, fixed cash payments are immediately made to its depositors. Compensation for deposits in a bank in respect of which an insured event has occurred is paid to the depositor in the amount of 100 percent of the amount of deposits in the bank, but not more than 1,400,000 rubles. In the event that a depositor has several deposits in one bank and whose total amount of liabilities on these deposits exceeds 1,400,000 rubles, compensation is paid for each of the deposits in proportion to their size.
In accordance with the Federal Law, participation in the deposit insurance system in Russia is mandatory for all banks, which is why banks that do not participate in the deposit insurance system do not have the right to obtain a banking license to attract deposits from individuals
Interest policy is also an integral part of the formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank. It is based on a number of principles, the observance of which, in consequence, implies the development of an optimal interest rate policy of the bank. Among them, first of all, it is necessary to name the principle of differentiation of interest depending on the period of storage and the size of savings, the principle of "social" differentiation of interest on deposits, the principle of ensuring the profitability of banking activities and the principle of preserving and protecting the savings of depositors. The combination of all these principles is a necessary condition for the formation of an effective interest and deposit policy of the bank.
The main part of the bank's operating expenses is the payment of interest on deposits, which is why the bank is not interested in a high level of interest rate, but is forced to maintain such a level of interest rate on deposits that would be attractive to customers. Despite the risk, commercial banks are trying to attract deposits, especially large ones and for a long time, offering high interest rates to their customers. However, the attraction of funds from the population by banks is not unlimited.
Currently, the entire volume of existing individual deposit programs can be divided into two classes: term deposits and demand deposits.
Demand deposits guarantee the opportunity not only to keep funds on the account, but also to withdraw part of the amount, to receive the entire amount on hand on demand, or to replenish it at a convenient time. Despite the primary convenience of this class of deposits, due to the existing opportunity to withdraw your funds on any day, banks offer, in most cases, a small rate. Consequently, demand deposits are inconvenient for those who seek to protect their savings from inflation. They are appropriate only in case of sending (receiving) a transfer of funds, as well as for temporary storage of money, which may come in handy quite unexpectedly.
Currently, term deposits are more profitable for bank depositors. From the name of this class it follows that they are opened for a strictly defined period. Generally, the minimum period is three months and the maximum is thirty-six months (3 years). Interest rates range from nine to thirteen percent in rubles and from five to eight percent in euros and dollars. However, in case of premature withdrawal of the deposit, one should not exclude the possibility of receiving the same interest as on demand deposits. This means that free funds should be invested in time deposits, which can be entrusted to the bank for a certain period without damage.
The ability to add additional funds to a deposit allows an individual to open a replenishable term deposit. The amount deposited in the bank one-time will be a non-replenishable term deposit.
In modern conditions, the most popular variations of term deposits are:
– standard;
- with capitalization;
- multi-currency.
The depositor receives interest on standard time deposits at the end of the term of the agreement. Deposits with capitalization involve the receipt of interest by the depositor once every one or three months. In this case, interest is added to the base amount, and the next accrual is made on the amount resulting from such a merger. Multicurrency deposits represent the simultaneous investment of funds in various currencies, and the subsequent possibility of their redistribution at one's own discretion.
Also, term deposits are divided into renewable and non-renewable.
Extended (extended) deposit - a deposit that is considered to be extended automatically for the same period specified in the agreement, and subject to the same conditions that were specified in the primary agreement, if the depositor did not appear within the specified period for his funds.
Non-prolongable (non-renewable) deposit - a deposit, an increase in the term, the validity of which is not automatically provided.
In modern conditions, the most traditional is the grouping of funds on customer accounts by terms, since it allows you to analyze by terms and amounts, which is necessary to manage the profitability and liquidity of the bank:
- funds on demand accounts;
- funds on deposit accounts for up to 1 month;
- funds on deposit accounts for a period of 1 month to 3 months;
- funds on deposit accounts for a period of 3 months to 6 months;
- funds on deposit accounts for a period of 6 months to 1 year;
- funds on deposit accounts for a period of more than 1 year.
This grouping is the most analytical, as it allows you to most clearly track the timing of the possible return of funds to customers and, therefore, predict and regulate the liquidity of the bank's balance sheet.
Control over the deposit policy of a commercial bank and specific banking operations related to attracting resources is carried out within the framework of the general internal control system operating in the Bank. At the same time, the main supervisory bodies include both internal divisions of the Bank (Department for Processing Transactions, Accounting and Reporting Department, Financial Department, Internal Control Service), such external inspection bodies (Audit Commission, Auditing Organization, Tax Authorities, branch of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, supervising the activities of the Bank).
So, we can conclude that the increased competition between banks and other financial institutions for deposits of individuals has now led to the emergence of a huge variety of deposits, their prices and service methods. According to experts, there are currently more than 30 types of bank deposits. At the same time, each of them has its own characteristics, which allows customers to choose the most appropriate and possible form of saving money and paying for goods and services that suits their interests.
1.2. The role of deposits in the formation of the resource base of commercial banks
Banks in order to carry out their commercial activities must have at their disposal a certain amount of money. The specificity of the banks' activities lies in the fact that, on the one hand, they attract temporarily free funds from various sources, and on the other hand, they place them, satisfying the needs of enterprises, organizations, and the population in need of financial resources.
The resource base in the activities of commercial banks determines the scale and direction of active operations and, consequently, the volume and structure of bank income. The composition and structure of the resources of a commercial bank have a significant impact on its liquidity and financial performance in general.
Traditionally, the main volume of resources is formed by banks at the expense of borrowed funds. Most often, their share in the total amount of bank resources is 70–80%, and the attracted funds of the bank are formed mainly through the implementation of deposit operations.
The nature of bank deposit operations and the attainability of the goals set for them largely depend on the quality of the developed deposit policy.
The bank's deposit policy in the field of attracting resources is one of the indicators of the reliability and stability of the bank's resource base.
This policy must meet two criteria:
1) the level of the interest rate on deposits should be sufficiently attractive for existing and potential customers;
2) the level of the interest rate should not sharply increase the lower limit of the interest margin between active and passive operations.
The formation of the deposit base using various tools and sources of raising funds allows maintaining the bank's potential in terms of conducting active operations at an adequate level, as well as responding flexibly to the financial needs of the clientele.
At present, deposits of individuals are the most dynamically developing source of financing the resource base of commercial banks, which is why the funds of the population should occupy a special place in the banking policy of generating funds. A significant characteristic of the deposits of the population is their "dispersion" among many depositors, who differ significantly in terms of income, age, gender and territorial characteristics, social status and professional affiliation, which significantly increases the level of diversification of banking resources. To date, the deposits of the population are quite manageable, by changing the value of interest rates, the bank has the ability to attract resources with specified characteristics of terms.
The main feature of the deposit market of the population at present is the significant influence of interest rate levels on the formation of demand for deposits - that is, the interest rates on deposits set by banks largely determine the growth rate of their resource base. Moreover, for different groups of banks, this influence manifests itself to varying degrees. The heterogeneity of the deposit services market can lead to a significant redistribution of market shares between banks, which may subsequently be accompanied by the emergence of new major players.
Analysis of the cost of banking resources, first of all, indicates that Russian credit institutions are actively using the factor of manipulating interest rates in their deposit policy, thereby ensuring the influx of new depositors. Of course, the level of interest rates is not the only factor that determines fluctuations in the deposit base, but at present the task of determining the impact of the cost of deposits on fluctuations in the client base "ceteris paribus" is very relevant.
Speaking about the Russian market of deposits of citizens, it should be noted that it cannot be considered as homogeneous, which is why control over the dynamics of the share of banks in it is often insufficient for a correct assessment of changes in the competitive position of a bank.
Thus, for example, the structure of the citizens' deposit market in Russia makes it possible to identify three most significant market segments with clearly different stereotypes of depositors' behavior, as well as different factors in the growth dynamics of deposits - pensioners, who account for almost half of the citizens' deposit market in Russian banks, the middle stratum, VIP and non-residents. The first and most extensive category of depositors is rather conservative; consequently, a noticeable increase in the income of pensioners leads to a rapid strengthening of the positions of commercial banks. These deposits are usually denominated in rubles.
The second most important segment of the deposit market is the funds of VIP clients and non-resident citizens, who traditionally prefer to work with commercial, preferably foreign, banks.
However, the bulk of depositors do not belong to the above two categories, although it is they who have the most important influence on the comparative positions of individual commercial banks, since it is they who account for almost half of citizens' funds in banks.
After analyzing the data for the last three years, we can conclude that in 2015 the volume of household funds in banks increased by 2,714.8 billion rubles. (in 2014 - by 2,371.3 billion rubles) - up to 16,957.5 billion rubles, which in relative terms is 19.1% (in 2014 - 20.0%).
In turn, the volume of insured funds of the population in banks participating in the Deposit Insurance System in 2015 increased by 2,591.3 billion rubles. (in 2014 - by 2,150.1 billion rubles). In relative terms, it increased by 18.5% to 16,591.0 billion rubles. (in 2014 - by 18.1%).
An analysis of the dynamics of the daily growth of deposits shows that in 2015 the savings activity of the population was higher than in 2014 – the growth in deposits in January–November 2015 averaged 6.0 billion rubles. per day, which significantly exceeds the same indicator of the previous year (in January-November 2014 - 4.7 billion rubles per day).
Traditional pre-New Year payments brought banks an additional 650 billion rubles. (at the end of 2014 - 750 billion rubles), this indicates that the inflow of funds from the population at the end of 2015 differs slightly from last year's figure.
In the course of analyzing the structure of deposits by size, it can be concluded that during 2015 different groups of deposits grew unevenly. In the first three quarters, deposits increased most actively - from 700 thousand to 1 million rubles. and over 1 million rubles. - by 25.3 and 22.2% in terms of the amount and by 24 and 24.9% in terms of the number of accounts, respectively. Deposits from 400 thousand to 700 thousand rubles. over three quarters they grew by 10.6% and by 9.8%, however, in the fourth quarter the situation changed and deposits within the limits of insurance compensation began to grow most actively - up to 700 thousand rubles. (an average of 11.6% per quarter), while the growth of large deposits has practically stopped. As a result, deposits from 400,000 to 700,000 rubles showed the highest growth rates over the year. and from 700 thousand to 1 million rubles. - by 25.6 and 28.1% in terms of the amount and by 28.5 and 23.5% in terms of the number of accounts, respectively. Deposits over 1 million rubles. dropped to third place - an increase of 23.4% in terms of amount and 20% in terms of the number of accounts.
At the end of 2015, the share of deposits from 400 thousand to 700 thousand rubles. increased from 15.3 to 16.2%, from 700 thousand to 1 million rubles. - from 7.0 to 7.6%, and deposits over 1 million rubles. increased from 38.4% to 40.0% of the total amount of deposits.
As for the average size of balances on accounts and deposits in the range of up to 700 thousand rubles, an increase of 1-1.7% can be observed here; in the range from 700 thousand rubles. up to 1 million rubles the indicator practically did not change compared to the previous year, and for deposits over 1 million rubles. there is an increase of 3.7%. Therefore, we can conclude that the average deposit size throughout the banking system without small and inactive accounts is estimated at about 155 thousand rubles. (fig.2)
Figure 2. Structure of deposits depending on the size of deposits
The ongoing monitoring of interest rates offered by the 100 largest retail banks showed that 86 out of 100 banks reduced their deposit rates in 2015. Rates increased in 3 banks, and remained unchanged in 11 banks.
The average level of rates, weighted by the volume of deposits, as of January 1, 2015, for annual ruble deposits in the amount of 700 thousand rubles. amounted to 7.2%, while the average unweighted interest rates for deposits in the amount of 700 thousand rubles. amounted to 8.8%.
The reduction in deposit rates occurred mainly in the 2nd and 3rd quarters, and in the 4th quarter there was a multidirectional movement of rates among banks - 39 banks reduced, and 23, on the contrary, increased, as a result, the average level of rates in the 4th quarter slightly decreased.
Throughout 2015, positive real returns on ruble deposits persisted. According to experts, the return on deposits in 2016 will also be at a level slightly higher than inflation.
It should also be noted the growth in the reporting year of the share of long-term deposits over 1 year - from 58.9 to 61.8%, however, along with the growth of long-term deposits, there was a decrease in short-term deposits - from 22 to 19.2%. The share of demand deposits decreased, but slightly - from 19.1% to 18.9%. On the whole, the noted trends are caused by the preference for more profitable long-term investments, especially in the context of relatively high interest rates.
At present, due to the revocation of licenses from several banks at the end of the year, there has been some redistribution of the market positions of credit institutions, for example, the share of the 30 largest banks in terms of household deposits in the first three quarters of 2013 gradually decreased from 77.1 to 76, 4%, but increased to 78.6% in the fourth quarter. The market share of Sberbank of Russia behaved similarly: in the first three quarters it decreased from 45.8% to 44.7%, in the fourth quarter it increased to 46.7%.
At the end of the year, the highest growth rates of deposits were observed in network multi-branch banks - 18.1% and in banks of the Moscow region - 16.4%, regional banks grew by 12.8%, and deposits in Sberbank of Russia increased by 21.6%.
Based on statistics, we can conclude that Russians prefer to keep their savings in rubles - they occupy ⅔ of the retail deposit market. Foreign exchange deposits are growing at a slow pace.
Bank deposits today are an effective means of savings, which makes not only a reliable, but also a profitable investment tool.
In general, the development of the situation on the deposit market in 2012-2015 was characterized by the following positive trends:
– the growth of the deposit base in the majority of operating commercial banks continued;
– the growth trend of long-term lending continued;
– the share of deposits of individuals in the total volume of the deposit base increased.
For commercial banks, household deposits are becoming more and more attractive every year, as a result of which competition in the banking services market is significantly intensifying. This situation is, first of all, beneficial for investors who can receive higher returns on their deposits. The statistics of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation shows that preference is given to deposits for a period of either less than 31 days (19% of all deposits) or more than a year (63%), the share of which has been steadily growing over the past years. Long-term deposits (over 1 year) for quite a long time provide the main share in the growth of the resource base of banks at the expense of household deposits.
The forecast for the retail deposit market for 2016 assumes an increase of RUB 2,880–3,220 billion. – up to 19,840–20,180 billion rubles, which corresponds to a relative increase in deposits by 17–19%.
Summing up, we can conclude that customer funds attracted in deposits form the basis of the resource potential of banks. Based on the above analysis, it can be seen that every year the savings activity of the population is growing, and, consequently, the resource base of commercial banks is being strengthened.
The volume and structure of the deposit base largely determine the nature of the active operations of a credit institution, its lending capabilities and role in the economy. And only an adequate deposit policy, taking into account numerous factors that affect the nature of deposit operations, will ensure the mobilization of appropriate resources for subsequent lending to the economy and participation in the investment process.
Thus, for commercial banks, deposits are the main and at the same time the most profitable type of resources. An increase in the share of this element in the resource base makes it possible to place a larger volume of attracted funds, thereby increasing the bank's liquidity. The deposits of the population among the attracted funds of the bank are an important source of resources. Based on the needs of the population in obtaining banking services, each bank independently develops its own deposit policy, determining the types of deposits, their terms and interest on them, the conditions for conducting deposit operations, while relying on the specifics of their activities and taking into account the factor of competition from other banks and inflation processes taking place in the economy.
Having a clear understanding of the main trends in the development of the deposit market and a clear understanding of the strengths and weaknesses of competitors, the development of the main price nuances of the formation of deposit products becomes a necessary guarantee of the bank's successful operation in the private deposit market.
Chapter 2. Assessment of the deposit policy of a commercial bank
2.1. Economic and organizational characteristics of the activities of JSC Bank "TKPB"
JSC Bank "TKPB" in Tambov is a universal regional credit institution that meets the requirements of a rapidly developing banking services market. JSC Bank "TKPB" was established on the basis of the Tambov regional department of Stroybank in 1990. The main task of the bank is to promote the development of the economy of the Tambov region, improve the quality of life of the population. Starting from 2005, Tambovkreditprombank annually confirms the status of a dynamically developing bank. May 30, 2012 JSC Bank "TKPB" became a laureate in the nomination "The best bank in the region" in the category "Silver".
Full official name of the Bank in Russian: Joint Stock Company Bank “Tambovkreditprombank” Abbreviated name in Russian: JSC Bank “TKPB”
Registration number and date of state registration with the Bank of Russia: No. 1312 dated April 27, 1992.
Main state registration number: 1026800000017.
In connection with bringing the provisions of the Charter in accordance with the Federal Law, Federal Law No. 99-FZ dated May 5, 2014 “On Amending Chapter 4 of Part One of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and on Recognizing Certain Provisions of Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation as Invalid”, in including the name of the Bank, the Main Department of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for the Central Federal District of Moscow on December 14, 2015 issued:
– new version of the Bank's Charter;
– general license No. 1312 dated December 04, 2015 for banking operations with a new name of the bank;
The Bank carries out activities to provide banking services in accordance with the Charter, approved by the decision of the general meeting of shareholders (participants ) , and also in accordance with licenses:
– License for banking operations No. 1312 dated July 25, 2008, issued by the Bank of Russia for attracting deposits and placing precious metals;
– license for attraction in deposits and placement of precious metals No. 1312 dated December 04, 2015 with a new name of the bank
– Licenses of a professional participant in the securities market issued by the Federal Commission for the Securities Market:
- for the implementation of brokerage activities No. 168-03481-100000 dated 07.12.2000 (without limitation of validity);
- for the implementation of dealer activities No. 168-03584-010000 dated 07.12.2000 (without limitation of validity);
- for the implementation of activities for the management of securities No. 168-03679-001000 dated 07.12.2000 (without limitation of validity);
– License No. 068-12030-000100 dated February 13, 2009, issued by the Federal Financial Markets Service for depositary activities, as a professional participant in the securities market (without limitation of validity period).
The Bank is a member of the state deposit insurance program, approved by Federal Law No. 117-FZ "On insurance of deposits of individuals in banks of the Russian Federation" dated 23.12.2003. JSCB TKPB (OJSC) was included in the register of banks participating in the deposit insurance system on January 27, 2005 under No. 507.
The authorized capital of JSC Bank "TKPB" was formed in the amount of 117,500,000 rubles, divided into 116,500 units. ordinary registered shares with a par value of 1000 rubles each, 847 pcs. preferred registered shares with an indefinite dividend with a nominal value of 1000 rubles each and 153 pcs. preferred registered shares with a dividend of 120 percent per annum with a par value of 1,000 rubles each. The authorized capital of the bank can be increased or decreased. Capital can be increased by increasing the nominal value of shares or placing additional shares, and reduced by reducing the nominal value of shares or reducing their total number, including through the acquisition and redemption by the bank of a part of the placed shares in the manner prescribed by the Federal Law “On Joint Stock Companies” Bank part of the banking system of the Russian Federation.
Legal address of JSC Bank "TKPB": 392000, Tambov, st. Soviet 118.
The bank's network consists of a head office, 12 additional offices, 2 operational offices and two cash desks outside the cash center. The head office and 7 branches of the bank operate in Tambov, 2 - in Michurinsk, 2 - in Rasskazovo, one each - in Kotovsk, Uvarovo, Kirsanov. Operational offices operate in Moscow and Lipetsk.
The founding document of the Bank is its Charter. The bank is a legal entity. Owns separate property recorded on an independent balance sheet, can exercise and acquire property and personal non-property rights on its own behalf, bear obligations, be a plaintiff and a defendant in court, has a round seal, a stamp and letterheads with its name.
According to the Charter, JSCB "TKPB" (JSC) provides the following banking services:
– opening and closing accounts of legal entities, individual entrepreneurs without forming a legal entity and individuals in rubles and foreign currency. Settlement and cash services;
– acceptance of deposits of legal entities and individuals in the currency of the Russian Federation and foreign currency;
– lending to legal entities and individuals;
- foreign exchange transactions;
– implementation of money transfers through the Western Union international system, provision of money transfer services through the Kontakt network, the Anelik, Migom, Zolotaya Korona systems;
– acceptance of payments through ATMs for cellular services from individuals;
– acceptance of utility payments from individuals;
– provision of private clients with bank cards of international and Russian payment systems, introduction of payroll card projects. For the convenience of customers, the bank has installed eleven ATMs for servicing cards of VISA and MasterCard payment systems in Tambov, Michurinsk, Kotovsk and Rasskazovo.;
– operations with precious metals;
- provision of bank safes (cells) for use to ensure the safety of funds and valuables;
– issuance of a bank guarantee;
- provision of remote banking services: "Bank - Client", "Internet - banking";
– making transfers without opening an account on behalf of individuals;
- operations with securities.
The priority direction of the bank's activity is to attract funds from the population in deposits. Work on accepting funds from individuals in deposits is carried out on the basis of a general license of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 1312. The Bank can accept from individuals on terms of repayment and payment of funds in deposits: on demand, urgent, as well as those deposited on other terms of return.
A demand deposit in JSCB TKPB (OJSC) is a deposit with an unlimited period of storage. Acceptance of additional contributions, as well as the issuance of deposits, is carried out during the entire period of storage in amounts at the discretion of the depositor.
Term deposits are deposits made to a bank for a specified period. The issuance of deposits is made in accordance with the Regulations for certain types of deposits.
Accrual and payment of interest on deposits is made in accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Article 839), Regulations of the Bank of the Russian Federation No. 39-P of June 26, 1998 and Regulations of JSCB "TKPB" (OJSC) for certain types of deposits. Interest is accrued from the day following the day the deposit funds are received by the Bank until the day preceding their return to the depositor.
A deposit account is opened for a client only if the bank has received all the required documents, and the client has been identified in accordance with the Legislation of the Russian Federation.
Deposits are accepted subject to the requirements of the Federal Law "On counteracting the legalization (laundering) of proceeds from crime and the financing of terrorism".
Deposits are insured in accordance with the Federal Law "On insurance of deposits of individuals in banks of the Russian Federation". Payment of compensations on deposits is made by the State Corporation "Deposit Insurance Agency".
Any citizen of the Russian Federation who has reached the age of 14 and has a passport, foreign citizens and stateless persons can be a depositor of JSC Bank TKPB. The amount of attracted funds (deposit) is not limited.
To open a deposit account, individuals-citizens of the Russian Federation provide the bank with the following documents:
- Identification document of an individual;
- Certificate of registration with the tax authority (if any).
Individuals - foreign citizens or stateless persons additionally provide a migration card and (or) a document confirming the right to stay (residence) in the Russian Federation.
When visiting the Bank for the first time, the depositor must familiarize himself with the terms of the offered deposits, select the type of deposit, make a statement about this orally, presenting an identity document and filling out the following documents:
– bank deposit agreement in 2 copies;
- incoming cash order when making a deposit;
The accountant assigns an account number depending on the type of deposit, while using a PC. The following data is entered into the database: last name, first name, patronymic of the depositor, contract number, details of the depositor's identity document, date of opening the account, the amount of the current interest rate, then a personal account is opened with the amount of the down payment and a credit order is printed, which is signed by the depositor.
The agreement must be signed by the depositor and the head of the bank, the signature of the head is certified by the seal of the bank.
The basis for closing a bank account on a deposit is the termination of the bank deposit agreement.
In its activities, the Bank is guided by the Charter, the legislation of the Russian Federation, and the regulations of the Bank of Russia:
- Federal Law No. 395-1 dated December 2, 1990 "On Banks and Banking Activities", which regulates the procedure for registering credit institutions and licensing banking operations;
- Federal Law No. 115-FZ dated August 7, 2001 "On counteracting the legalization (laundering) of proceeds from crime and the financing of terrorism";
- Federal Law "On currency regulation and currency control" of December 10, 2003 N 173-FZ, which regulates the procedure for conducting currency transactions;
- Bank of Russia Instruction No. 28-I of September 14, 2006 “On the Opening and Closing of Bank Accounts and Deposit Accounts”, which regulates the procedure for opening and closing bank accounts;
- Bank of Russia Regulation No. 283-P dated March 20, 2006 “On the Procedure for Forming Loss Reserves by Credit Institutions”;
- Regulation of the Bank of Russia "On the rules for the transfer of funds" dated June 19, 2012 N 383-P
- Other provisions of the Bank of Russia.
As a result, we can say that JSC Bank "TKPB" operates in all segments of the financial market, is a universal regional credit institution and provides a wide range of financial services. However, one of the bank's priorities is to attract funds from individuals. Household deposits are the main source of expansion of the resource base of JSC Bank "TKPB".
2.2. Evaluation of the activities of JSC Bank "TKPB" in the market of deposit services
JSC Bank "TKPB" offers the population a competitive line of deposits with a variety of conditions in order to meet the needs of citizens in saving and increasing their funds. In order to increase the resource base, the bank is focused on attracting funds from various target groups: working citizens, pensioners, parents who care about the future of their children. The types of deposits of Tambovkreditprombank OJSC are presented in table 1.
Table 1. Deposits of JSC Bank "TKPB" for individuals
Deposits of individuals are placed for a period of 30 to 1800 days with monthly and quarterly interest payments, as well as interest payments at the end of the deposit term. The dynamics and changes in the structure of deposits of individuals depending on the period of storage in the period from 01/01/2015 to 01/01/2016 are presented in table 2.
Table 2. Dynamics of deposits of individuals of JSC Bank "TKPB" depending on the period of storage from 01/01/2016 to 01/01/2015
The deposits of individuals as a whole for this period increased by almost 8%. The most popular for the population are deposits for a period of 91 to 180 days, the change is 134,806 thousand rubles, or 93.7%. This indicates that the interest rate policy of JSC Bank "TKPB" for these deposits is the most attractive for individuals.
Currently, the bank is becoming increasingly popular among the population. This fact is confirmed by the dynamics of the number of customers in the branches of JSC Bank "TKPB" and the increase in the volume of attracted deposits from customers. The number of accounts of individuals is increasing at a rapid pace. Data on the dynamics of deposits for 2015 are presented in Appendix 1.
As of 01/01/2016 the bank's client base is 27,365 individual depositor accounts. Compared to last year, the number of customers increased by 3.3%. Compared to 2014 the total amount of deposits increased by 551 thousand rubles. (19.86%). In the structure of attracted resources, the funds of individuals account for 46.8%. Considering the dynamics of deposits of JSC Bank "TKPB", one can note the trend of increasing the resource potential of the bank. A wide range of deposits, additional payment options and convenient working hours could not but cause a rapid increase in the number of customers.
Thus, we can conclude that the deposits of individuals are one of the main sources of the resource base. The Bank annually increases the volume of deposits of the population. For these purposes, the bank carries out promotions, offers favorable conditions for depositors, and introduces new interest rates.
2.3. Analysis of the deposit portfolio of JSCB "TKPB" (OJSC)
Expansion of the resource base by attracting funds from individuals is one of the priorities of the bank.
As of January 1, 2016, the insured deposits of individuals in the whole bank increased by 160.2 million rubles, in relative terms - by 14.3%, and amounted to 1280.1 million rubles (in 2014 - 1119, 9 million rubles). The share of this source in the total liabilities of the bank decreased slightly (from 33.8% as of 01.01.14 to 33.3% as of 01.01.16).
Comparative growth rates of deposits of individuals for 2015 as a whole for credit institutions of the Tambov region and JSC Bank "TKPB" are shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Deposits of individuals by credit institutions of the Tambov region and JSC Bank "TKPB". for 2015, %
From the above data it can be seen that for the 4th quarter of 2015, the growth rate for Tambovkreditprombank outstrips the growth rate for the region by 4.8%. The growth rate of the bank is 116.2% in the Tambov region 111.4%. The Bank constantly monitors deposits of individuals and interest rates on them. Based on the results of monitoring, it was established that for the 4th quarter of 2015, the growth rates for JSC Bank "TKPB" of the proposed interest rates by divisions of banks in other regions located in the Tambov region. Thus, Express Volga Bank offered rates from 8.5 to 11%, Home Credit Bank from 10 to 11%, Vostochny Express Bank, TRUST Bank up to 11%.
The rates of Sberbank, Rosselkhozbank, Promsvyazbank, VTB-24 did not exceed the rates offered by JSC Bank TKPB.
In 2014, the weighted average rates of JSC Bank TKPB did not exceed the average interest rate on deposits in rubles of ten large credit institutions that attract the largest volume of deposits. From the dynamics of changes in the interest rate, it can be seen that this indicator tends to increase.
The volume of deposits of the population and their share in the context of structural units is characterized by the data given in Table 3.
Table 3. The volume and share of deposits of individuals by divisions of JSC Bank "TKPB"
As can be seen from the given data, the share of deposits by bank divisions has changed insignificantly. The main share of deposits of individuals falls on the Head Office - 38.2%.
The balances of deposits of the population by terms of attraction are characterized by the following data (Table 4)
In the structure of deposits attracted from individuals, funds for a period of 181 days to 1 year have the greatest growth. Their volume for the year increased by 1.2 times or 105.9 million rubles. The share for the specified period in the total amount of borrowed funds also increased from 43.6% to 46.6%.
Table 4. Balances of deposits of individuals by terms of attraction
Deposits attracted for a period of 1 to 3 years increased by 15.4%, while their share remained virtually unchanged in the total volume of deposits of individuals - 33.5%.
The share of household deposits for a period of 91 to 180 days decreased and amounted to 11.3%. There is a decrease in the share by 2.2 and the amount of deposits by 21.9 million rubles. for a period of 31 days to 90 days.
As of January 1, 2016, the balances of funds of individuals (account 40817) increased by 14.9 million rubles compared to January 1, 2015. The December inflow of funds from the population on bank cards exceeded the figure of the previous year by 29.8%.
Payroll projects were not opened in 2015.
Offering a wide range of deposits for individuals, JSC Bank "TKPB" pursues a policy of reliability and security of funds entrusted to the bank.
JSC Bank "TKPB" accepts deposits on terms that are as close as possible to the needs of customers:
- deposit "on demand" with the condition of annual capitalization of interest;
– 27 types of term deposits, including:
2 types with the condition of quarterly payment of accrued interest;
6 types with the condition of monthly capitalization of accrued interest;
2 types with the condition of quarterly capitalization of accrued interest;
16 types with the condition of accruing interest upon the expiration of the term of the bank deposit agreement;
– current accounts of individuals in rubles;
– accounts for settlements using bank cards of international payment systems, including within the framework of payroll projects.
In the reporting period, the bank had sufficient credit resources to meet the requirements of the Bank of Russia to assess the economic situation, ensure sustainability in order to recognize it as sufficient for participation in the deposit insurance system, further lending to individuals.
However, in order to avoid an outflow of deposits, the Board of the Bank decided to change the interest rates upward from February 28, 2015, May 22, 2015, June 4, 2015, August 13, 2015, September 7, 201. to the population new types of deposits with a higher interest rate.
According to the results of the year, the amount of the contribution is in the range from 100 to 400 thousand rubles. increased by 6.5% (up to 400.9 thousand rubles), from 400 to 700 thousand rubles. - by 21.5% (up to 293.9 thousand rubles), from 700 to 1 million rubles. - by 14.5% (up to 151.6 thousand rubles), over 1 million rubles. - by 14.9% (up to 301.3 thousand rubles).
The growth of deposits close to the maximum amount of insurance compensation indicates the active impact of the insurance system on the savings behavior of the population. As a result, by the end of the year, the share of deposits ranging from 400 thousand rubles. up to 700 thousand rubles increased from 21.6% to 23.0% of total deposits, over 700 thousand rubles. increased from 35.2% to 35.4%.
Funds of individuals attracted on the basis of bank deposit agreements are defined as deposits subject to insurance and are included in the calculation base of insurance premiums.
As of January 1, 2016, 6,349 term deposit agreements and 21,016 demand agreements were concluded, and as of January 1, 2015, 5,761 term deposit agreements and 20,788 demand agreements were concluded.
From the moment of joining the deposit insurance system, the amount of the transferred insurance premium to the Agency amounted to 23,090.6 thousand rubles, including 1,171.6 thousand rubles transferred. for the 4th quarter of 2015
The business plan of JSC Bank "TKPB" provides for an increase in the loan portfolio, respectively, this will require additional resources, the growth of which is also provided.
As a result, we can say that the main task of the bank in the field of attracting resources is to maintain and increase the volume of services provided by the bank in the customer banking market, the formation of long-term preferences for customers in determining the timing of the placement of funds.
In order to create a resource base for expanding active operations, investing in the real sector of the economy and reducing its own interest rate risks, the bank identifies as the main priorities in the formation of the resource base: lengthening the terms of raising funds, reducing the total cost of resources, optimizing the structure of raising resources.
The bank's tariff policy is focused on a wide range of clients and provides for flexibility in setting fees for borrowed funds, a wide range of interest rates on deposits and placed funds.
Chapter 3Ways to improve the deposit policy of a commercial bank
3.1. Measures to improve the deposit policy of JSC Bank "TKPB"
One of the problems that commercial banks are currently facing is the problem of forming an optimal resource base that will meet the needs of the bank.
The resource base has a direct impact on the liquidity and solvency of a commercial bank. The amount of income that a commercial bank receives depends strictly on the amount of the resources that the bank acquires in the market of various resources and, in particular, deposit ones. Hence there is a competitive struggle between banks for attracting resources.
The formation of a resource base, which includes attracting new clients, is an integral part of the flexible asset and liability management of a commercial bank. Effective liability management involves the implementation of a competent deposit policy. The specificity of this area of activity is that in terms of passive operations, the choice of a bank is usually limited to a certain group of clientele, to which it is attached much more strongly than to borrowers.
Currently, the development of banking competition leads to a close binding to certain customers. If the circle of these clients is narrow, then the bank's dependence on them is very high. Therefore, in order to strengthen the resource base, commercial banks need a balanced deposit policy, balanced in terms of terms, volumes and interest rates.
In order to expand the resource potential and client JSC Bank "TKPB" it is necessary to improve the deposit policy as much as possible. First of all, the deposit policy should be aimed at expanding the list of deposits available to various groups of clients, as well as introducing new types of services for their convenience.
The deposit policy of JSC Bank "TKPB" should take into account the needs of all social and age groups of citizens - working and pensioners, young people and middle-aged people, and should also be designed for both the low-income segments of the population and people with medium and high income levels.
In order to increase the interest of individuals in receiving deposit services, the following instruments can be used in JSC Bank "TKPB":
- expanding the list of deposits targeted at various social groups of the population;
- the possibility of receiving interest in advance;
- introduction of salary projects;
- receiving benefits, bonuses and discounts in case of constant cooperation with the Bank;
- improvement of the advertising policy of JSC Bank "TKPB";
- implementation of the "Deposit Online" program.
In order to increase the deposits of individuals, JSC Bank "TKPB" could offer the opening of a new type of deposit "Hit of the season" on the following conditions: the term of storage is 370 days, the interest rate is 11% per annum, with the right to replenish, the minimum amount of the initial contribution is 10 thousand rubles.
In order to attract the younger generation to the number of depositors, JSC Bank "TKPB" should develop the deposit "Youth", focused specifically on this social group of the population.
It is proposed to introduce the following conditions for this deposit:
– the minimum amount is 2000 rubles;
– deposit term is 5 years;
– annual percentage – 11%;
– age limit from 18 to 23 years.
In order to ensure the influx of depositors to this type of deposit, it is advisable to introduce incentives that will be attractive among the young population. This may be a discount when buying a train ticket, when buying scientific literature in bookstores. These benefits will be valid only if the funds on this deposit have been paid for for services and have lain for at least one full period of storage.
Focusing on the young population, it is possible to introduce the “Student” deposit, the target audience of which will be students of the city of Tambov. For this deposit, the minimum amount is 1,000 rubles, the deposit term is from 181 to 1,095 days. The interest rate will be 7.5 - 8.5% per annum. The attractiveness of this contribution may be that the accrued interest can be transferred to the account of tuition fees at the university.
As part of the improvement of the deposit policy JSC Bank TKPB could offer a range of deposits targeted at high-income clients. For example, the “Premium” deposit, which would feature personal service, the services of a personal manager who solves the financial problems of his client around the clock, this is the opportunity to come to the bank “on call” without standing in line at branches, this is access to various client services support . According to the "Premium" deposit, it is possible to replenish the deposit within 60 days from the date of its opening. "Premium" - a deposit with the highest interest rates among bank deposits, with monthly interest payments and the possibility of their capitalization.
JSCB "TKPB" (OJSC) should also offer deposit products aimed at meeting the needs of depositors in housing, large purchases, education, tourism and recreation. It is advisable to develop the "Professor" deposit - a deposit product designed for teachers of Tambov universities. The interest rate is 6-10%, and a partial withdrawal is also provided - 20% of the amount of additional contributions.
When developing the “Family +” deposit, a group will be involved who have children under the age of 18 at the time of applying to the bank. The interest rate for this type of deposit can vary from 7 to 10% per annum.
Another measure to improve the deposit policy of JSC Bank "TKPB" and increase the interest of customers in deposit services can be offered to pay interest on deposits in advance in order to compensate for inflationary losses. In this case, the investor, when placing funds for a certain period, immediately receives the income due to him. However, in case of early termination of the bank deposit agreement, the bank will recalculate the interest on the deposit and the overpaid amounts will be deducted from the deposit amount.
In order to speed up and make it easier for customers to obtain the necessary information about deposits in JSC Bank TKPB, it is advisable to create a customer service service, with the help of which a potential depositor will be able to receive all information on available deposit products free of charge by phone. The presence of this service will reduce the time for servicing depositors directly at the bank's office, and, as a result, attract new depositors of various social groups.
At the same time, the bank should constantly focus on advertising policy, which will make it an effective tool for building a client base. Each competitive advantage of the bank and each new deposit product must be known and understandable to customers, easily comparable, and also advantageously different from competitors' offers.
Currently, banks are actively offering online deposits. In this they are supported by clients who, saving time on visiting the office, use the opportunity to become depositors remotely.
Another mechanism to improve the deposit policy JSC Bank "TKPB" can serve implementation of the "Deposit Online" program. To do this, it is enough for a future depositor to have an open account and access to Internet banking in JSC Bank "TKPB". With the help of this program, you can open any deposit from the current line of deposits. The advantages of this program for clients are obvious - saving time on visiting the office and the most comfortable opening of deposits - at work, at home or even while on vacation. Despite the remoteness of this service, the deposit opening agreement is stored at the bank branch, and the client can pick it up at the first visit to the office. The only condition for opening a deposit online will be that this service can only be used by customers who have already had a positive experience of opening a deposit with JSC Bank TKPB.
Thus, when developing measures to improve the deposit policy of JSC Bank "TKPB", one should be guided by certain criteria for its optimization, among which the following can be distinguished:
- segmentation of the deposit portfolio (by clients);
- differentiated approach to different customer groups;
- competitiveness of banking products and services.
In conclusion, we can say that each bank develops its own deposit policy, determining the types of deposits, their terms and interest on them, the conditions for conducting deposit operations, while relying on the specifics of its activities and taking into account the factor of competition from other banks and inflationary processes occurring in economy.
3.2. Development of the deposit product "Investment in the Future" for JSC Bank "TKPB"
Currently, in the banking sector there is a huge number of deposits aimed at meeting the needs of the population of absolutely all social groups. However, in Russia today only a few credit organizations issue targeted deposits for children. They can be opened, for example, at Zenit Bank, Alfa-Bank, PJSC SDM - Bank. The conditions offered by credit institutions for children's deposits vary greatly. So, some banks open such deposits only in the name of children under 14 years old, while others - until the child reaches 18 years of age. The term of the deposit can be either one year or five years. The minimum deposit amount in some banks is set at 1,000 rubles, and in others - 100 thousand. The interest rate policy of banks on the market is also ambiguous, the rate on children's deposits varies from 5% to 9% per annum. Deposits of this type are replenishable. The ability to make debit transactions on a deposit offers a minimum number of banks. As a rule, the deposit is automatically extended until the child reaches the age of majority or reaches 14 years of age.
A child deposit is opened by a parent (guardian) or a close relative in favor of the child. The client who opened such a deposit is called the depositor. He has all the rights of the depositor until they are presented to the deposit by the child. A minor can enter into the rights of a depositor upon reaching the age of 14.
Since JSC Bank "TKPB" periodically reviews its deposit policy and, keeping up with competitors, seeks to improve the product line of deposits, thereby changing interest rates, one should consider such a way to attract a client as the introduction of a new, non-standard deposit product "Investment in the Future" .
The main advantages of a deposit for a child will be:
- This product will ensure the beginning of the adult life of the child upon reaching his majority;
- Both one of the parents and the guardian can open a deposit;
- The ability to replenish the deposit;
- The number of replenishment of the child deposit account is not limited;
- Good interest rate;
- Upon reaching the age of majority, the child has the opportunity to manage the accumulated money independently.
There are also disadvantages in children's deposits, namely, that the interest rate on them is usually 0.5-1% lower than on term deposits. However, this is definitely better than keeping your savings without the possibility of increasing them. Due to the use of the child deposit, the child will already have a large enough capital, thanks to which he can get an education or open his own business. In addition, he will learn to manage his money wisely, which will help him properly manage funds in the future.
Deposit benefits:
– Interest capitalization;
– Possibility of replenishment.
In order to develop the most attractive deposit product "Investment in the Future" in JSC Bank "TKPB", we will calculate what the final amount will be if the client deposits 10,000 rubles for 2 years at a maximum rate of 9% in JSC "Rosselkhozbank" and at 9.5% per annum in PJSC Sovcombank.
These calculations should be carried out using the compound interest formula:
SUM=X*(1+%) n (1)
Where SUM – final amount;
X is the initial amount;
% - interest rate per annum / 100;
n is the number of periods, years (months, quarters).
Comparative characteristics of the profitability of the deposit are shown in Table 5.
Table 5. Comparative characteristics of the profitability of the deposit
The offer of these banks is initially focused on a fairly limited segment of consumers. The yield of the offered deposits remains at the level of 20%. Thus, JSC Bank "TKPB" needs to develop a deposit "Contribution to the Future", which will bring the target consumers the highest income than the competitors presented above.
The terms of the proposed term deposit "Investment in the Future" of JSC Bank "TKPB" are presented in table 6.
Table 6. Deposit "Contribution to the Future" JSC Bank "TKPB"
Deposit benefits:
- Interest capitalization;
- Possibility of replenishment;
- Fixed interest rate;
- Automatic extension.
Let's calculate the profitability of the deposit product "Investment in the Future" using similar conditions.
Profit will be equal to:
10000*(1+14.5/100) 2= 13110.25 rub.
13110.25-10000 \u003d 3110.25 rubles.
The yield of the calculated product will be:
3110,25/10000=31,1 %
Making a comparative analysis of these types of deposits, we can conclude that JSC Bank "TKPB" can offer a more efficient and attractive banking product for customers who have minor children.
A distinctive feature of the proposed deposit product will be the possibility of opening a deposit for "the smallest". The term of the deposit is from 1 to 18 years, this will allow the depositor to open a long-term deposit from the first days of a child's life until he comes of age. Initially, the amount invested by parents on a child's deposit will increase by 5-10 times after 18 years.
How profitable the "Investment in the Future" for a period of 18 years in JSC Bank "TKPB" will be, the calculations show:
Option 1. Parents open a deposit for a period of 18 years and immediately deposit 20 thousand rubles into the account. If it is never replenished, then at an average annual rate of 10% at the end of the term, the child will be able to withdraw 111,198 rubles.
Option 2. Under the same starting conditions, parents replenish the deposit by a symbolic 500 rubles. every month. In this case, an adult child will already have 420,346 rubles at his disposal.
It can be seen from the calculations that the "Investment in the Future" will allow the child to receive funds by the age of majority, which are several times higher than the initial contribution.
Currently, few banks have such products in their deposit line and often the term of such deposits is up to 3-5 years, which does not meet the expectations of parents who, by opening a child deposit, expect to accumulate a significant amount by the age of their child.
The attractiveness of "Investment in the Future" can also be the fact that not only parents, but also relatives - grandfathers, grandmothers, brothers, sister, etc. can open deposits for children in JSC Bank "TKPB". To do this, it will be enough to present your passport and the original birth certificate of the child. "Investment in the future" provides for the accumulation of the required amount of funds by a certain date. The uniqueness of this product will lie in the fact that funds can be placed by clients for a long time.
A bonus for opening this deposit will be a free issue of a Visa Electron bank card. In this case, the bank card will serve as a tool for using the deposit replenishment service through ATMs of JSC Bank "TKPB".
A positive point is also that you can open "Investment in the Future" in the name of a child of any age. Until the age of 14, the depositors manage the funds, and with the receipt of a passport, the child can independently manage the savings on the deposit.
"Investment in the future" in JSC Bank "TKPB" could also be attractive for individuals with a second child, if it is possible to invest maternity capital in this contribution. In 2016, the amount of maternity capital, which is due at the birth of a second child, is 453,026 thousand rubles. Families who have used the deposit product "Investment in the Future" can receive a worthy increase in the family budget. If you put this money on the deposit "Contribution to the Future" in JSCB "TKPB" (OJSC) at 10%, for the year the increase will be about 45,000 rubles. The undoubted advantage will be that the account holders will be able to receive monthly dividends on existing investment. This means that families that transfer maternity capital to a deposit account with Tambovkreditprombank will have the opportunity to receive cash, which, according to today's law on maternity capital, can be spent not only on paying for kindergarten, school and subsequent education of the child at the university, improving housing conditions and the formation of the funded part of the parent's labor pension, but also used for everyday expenses for food, rest, treatment and visiting sections by the child.
Maternity capital, currently, is issued immediately after the birth of the baby, but you can use this amount only after three years, during which you will “just look” at the certificate issued by the Pension Fund. That is why the transfer of maternity capital to a deposit in JSCB "TKPB" (OJSC) immediately after the birth of a child and the subsequent withdrawal of interest on the deposit will significantly help families with more than one child solve everyday worries that require additional expenses from the very first days of a baby's life .
Despite the fact that interest in children's deposits has recently become more and more obvious, experts are cautiously predicting the future of this seemingly promising area of banking. The main reason for this is the high riskiness of children's deposits, since, in most cases, they are long-term. Despite the risk such contributions have many advantages.
Firstly, the interest rate will be proportional to the term for which the contract is concluded. When concluding such a long contract, the rate is approved for the entire period. In addition, there are various bonus programs available to depositors who have chosen this type of agreement. Thanks to them, you can increase income on deposits, as well as take advantage of various kinds of services, discounts, and advantageous offers. JSCB "TKPB" (OJSC) offers a "Contribution to the Future", which the depositor can replenish an unlimited number of times.
Secondly, long-term deposits can be developed, including interest capitalization. That is, in this way, you can significantly increase the income on the deposit.
Thirdly, discounts are provided to customers for other banking services.
When developing a long-term deposit product "Investment in the Future", potential customers may be interested in the question of how JSC Bank "TKPB" will provide such a high interest rate on the deposit. There is a simple explanation for this - "Investment in the Future" will be the only product in the entire line of deposits presented, which offers the highest interest rate. Currently, in Russian banks, there is often a discrepancy between deposit rates and inflation, that is, inflation “eats” all savings on deposits in the long term. However, according to the Central Bank of Russia, an inflation forecast was planned until 2026. Inflation in Russia in 2016 is 6.4%, and during the calculated period, this index will fluctuate between 5.3 - 7.3%. Consequently, the interest rate of 10 - 14.5% per annum on the "Investment in the Future" almost doubles the inflation rate for the depositor.
As a result, we can conclude that after analyzing the situation in the bank deposits market, JSC Bank "TKPB" has every opportunity to offer individuals with a child a highly profitable deposit product "Contribution to the Future", which will be able to attract a large number of depositors interested in increase in own funds.
Conclusion
As a result of the study, the following conclusions can be drawn.
Firstly, in the course of writing the thesis, it was found out that the formation of a deposit policy plays an important role in ensuring the stable and reliable functioning of commercial banks.
The study of the theoretical foundations of the deposit policy of a commercial bank made it possible to reveal that for commercial banks, deposits are the main and at the same time the most profitable type of resources. An increase in the share of this element in the resource base makes it possible to place a larger volume of attracted funds, thereby increasing the bank's liquidity.
Secondly, in the course of writing the work, the current situation in the country's deposit market was analyzed, and the activities of a particular subject of the banking system in the field of deposit operations of JSC Bank "TKPB" were studied.
Based on the results of the study conducted in the thesis, we can conclude that the deposit market of the Russian Federation has a stable situation with the attraction of funds from individuals in deposits.
As for the activities of JSCB "TKPB" (OJSC) in the field of attracting deposits from the population, both positive and negative trends can be noted here. The positive aspects of the bank's work include the ever-expanding client base, the growth of equity capital and borrowed funds.
In the thesis, a number of problems faced by commercial banks were identified. These include the problem of forming the resource base of a commercial bank, as well as the insecurity of citizens' deposits in Russian banks.
Thirdly, a study of the deposit policy and an assessment of the current situation in the field of attracting funds from individuals in deposits made it possible to develop a number of proposals for improving the deposit policy of JSC Bank "TKPB".
Thus, in order to strengthen the deposit base and expand the resource potential, the bank is offered:
- expand the list of deposits, focusing on various social groups of the population;
- pay interest in advance;
- introduce a system of benefits, bonuses and discounts in constant cooperation with the Bank;
- improve the advertising policy of JSC Bank "TKPB";
- implement the "Deposit Online" program.
JSC Bank "TKPB" periodically reviews its deposit policy and, keeping up with its competitors, seeks to improve the deposit product line, thereby changing interest rates. In the thesis, such a way to attract a client as the introduction of a new, non-standard deposit product "Investment in the Future" was developed. The profitability of the calculated deposit will be 31.1%, which is significantly higher than that of competing banks. Investment in the Future also has a number of benefits that may be of interest to individuals with children. These include: long-term deposits, work with maternity capital, free issue of a Visa Electron bank card.
Thus, the purpose and objectives of the study have received their logical conclusion in the consideration of theoretical and development of practical recommendations for improving the process of formation and implementation of an effective deposit policy of a commercial bank.
List of sources used
Regulations
1. Federal Law of December 2, 1990 N 395-1 (as amended on April 5, 2016) “On Banks and Banking Activities” // Consultant Plus Legal Reference System: [Electronic resource] / Consultant Plus Company.
2. On the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (Bank of Russia): Federal Law of July 10, 2002 N 86-FZ (with amendments and additions) // Consultant Plus legal reference system: [Electronic resource ] / Company "Consultant Plus".
3. Charter of the joint-stock commercial bank "Tambovkreditprombank". Approved by the Minutes of the General Meeting of Shareholders No. 1 dated April 22, 2008
List of scientific and educational literature
1. Balabanov, I. T. Banks and banking / I. T. Balabanov. - St. Petersburg. : Peter, 2009. - 345 p.
2. Batalov, A.G. Banking competition / A. G. Batalov. - M.: Publishing house "EXAMINATION", 2014. - 215 p.
3. Batrakova, L.G. Analysis of the interest rate policy of a commercial bank / L.G. Batrakov. – M.: Logos, 2012. – 37 p.
4. Beloglazova, G.N. Banking / G. N. Beloglazova. - M.: Finance and statistics, 2009. - 592 p.
5. Belyaev, M. N. Banking: entertaining about the complex / M. N. Belyaev. – M.: Vershina, 2015. – 29 p.
6. Bratko A.G. Central bank in the banking system of Russia / A. G. Bratko. – M.: Spark, 2014. – 335 p.
7. Buylov, M. T. Two big retailers / M. T. Buylov // Kommersant-Money. - 2014. - No. 14. - S. 27.
8. Bukato, V.I. Banks and banking operations in Russia / V.I. Bukato. – M.: Finance and statistics, 2015. – 28 p.
9. Vedenkin, A.A. The volume of private deposits in banks is growing rapidly / A.A. Vedenkin. – M.: Logos, 2014. – 128 p.
10. Velieva, I. Time to collect money / I. Velieva // Expert. - 2009. - No. 11. – P. 8.
11. Vinogradov, A. V. Basic models of building a deposit guarantee system in the world / A. V. Vinogradov // Money and credit. - 2014. - No. 6. - S. 62-67.
12. Vladimirova, M.P. Money, credit, banks / MP Vladimirova. – M.: INFRA-M, 2010. – 195 p.
13. Vyatko, L. D. Banks and their deposits / L. D. Vyatko. – M.: Logos, 2010. – 152 p.
14. Gamidov, G.M. Banking and credit business / G.M. Gamido. - M.: UNITI, 2009. - 240 p.
15. Gattunen, I. K. Loans and deposits / I. K. Gattunen. – M.: EKSMO, 2014. – 10 p.
16. Grozovsky, B. G. Complete mutual unsuitability / B. G. Grozovsky // Company. - 2014. - No. 22. – S. 23.
17. Dovnar, Yu.P. Protection of bank deposits of individuals. Comparative legal aspect / Yu.P. Dovnar. – M.: Amalfeya, 2013. – 38 p.
18. Zhukov, E. F. Banking / E. F. Zhukov. - M.: UNITI-DANA, 2011. - 264 p.
19. Zhukov E.F. Banks and non-banking credit organizations and their operations / E.F. Zhukov. – M.: VZFEI, 2010. – 75 p.
20. Zaslavskaya, O. D. Reliability in exchange for income / O. D. Zaslavskaya // Business Chronicle. - 2014. - No. 30. - P. 12.
21. Zorina, E.E. Overview of the market of deposits of individuals / E.E. Zori-na // Competitor. - 2015. - No. 9. - S. 18.
22. Karpov, M. T. Depositors return to banks / M. T. Karpov // Today. - 2014. - No. 21. - P.4.
23. Kiryan, P. R. Banks will not give back deposits / P. R. Kiryan // Expert. - 2009. - No. 24. – S. 31.
24. Lavrushin, O. I. Banking / O.I. Lavrushin. - M.: Finance and statistics, 2011. - 101 p.
25. Lavrushin, O.I. Money, credit, banks / O.I. Lavrushin. - M .: "Fi-nance and statistics", 2011. - 590 p.
26. Lexis, V.K. Credit and Banks / V. K. Lexis. – M.: Prospect, 2010. – 240 p.
27. Mazin, E. Investors do not waste time / E. Mazin // Business. - 2014. - No. 6. - P. 12.
28. Matovnikov, M. Yu. Strengthening the monopoly of Sberbank caused by a change in the structure of the retail market / M. Yu. Matovnikov // Banking. - 2014. - No. 8. - P.16.
29. Matyukhin, G. Once again about the strategy of banking reform in Russia / G. Matyukhin // Banking. - 2014. - No. 10. - C. 22 - 25.
30. Parfenov, K.G. Bank accounting and operating techniques in commercial banks / K. G. Parfenov. - M.: Intel - synthesis, 2014. - 458 p.
31. Pukhov, A.V. Methodology for the development of banking retail business / A.V. Pukhov. - M .: LLC "Parfenov.ru", 2012. - 56 p.
32. Puchkova, P.K. Bank deposit: from information support to analytical solutions / P.K. Puchkov. – M.: Prospect, 2014. – 132 p.
33. Romanova, M.V. Banking activity: tax aspect / M.V. Romanova. - M.: Bank business center, 2012. - 97 p.
34. Rumas, S. Funds of the population in the resource base of banks / S. Rumas // Bank Bulletin. - 2014. - No. 7. – P.12–19.
35. Semenyuta, O.G. Money, credit, banks in the Russian Federation / O. G. Semenyuta. – M.: Kontur, 2012. – 302 p.
36. Serebryakov, SV Financial ecology: will it be safe to keep money in Russia / SV Serebryakov // Banking. - 2014. - No. 5. - S. 15-20.
37. Solntsev, O.M. Sources of growth of financial resources / O. M. Solntsev // Expert. - 2015. - No. 38. - S. 41.
38. Tavasiev, A.M. Banking: management and technology / A. M. Tavasiev. - M.: UNITI-DANA, 2013. - 46 p.
39. Tomkovich, R.R. Banking operations: legal regulation and customer service practice / R.R. Tomkovich. – M.: Amalfeya, 2012. – 18 p.
40. Chelnokov, V.A. Money, credit, banks / V.A. Chelnokov. – M.: UNI-TI, 2010. – 70 p.
41. Shmyreva, A.I. Money. Credit. Banks. / A. I. Shmyreva. – M.: Novosibirsk, 2011. – 280 p.
42. Analysis of the market of deposits of individuals in 2015 dated February 10, 2016: Deposit Insurance Agency. – URL: http://asv.org.ru/agency/for_press/pr/311771/?sphrase_id=567173 (date of access: 10.02.2016)
43. Analysis of the deposit policy of individuals for 2015: Central Bank of the Russian Federation. – URL: http://www.cbr.ru/statistics/?prtid=macro_sub (date of access: 03/11/2016)
44. Official website of JSCB "TKPB" (OJSC). URL: http: //www.tkpb.ru/
45. Official website of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. URL: www.cbr.ru
Thesis on the topic “Assessment of the organization of deposit operations and the deposit policy of a commercial bank” updated: May 25, 2018 by: Scientific Articles.Ru