GRADUATE WORK
Deposit policy of a commercial bank
(on the example of JSC "Bank" Petrovsky ")
Made by a student of group 23FB-61
distance learning
Kordesova Elena Yurievna
Scientific adviser: Ph.D.,
assistant professor I.G.Zaitseva
_____________________(signature)
Reviewer:
Head of the Vyborg business center
OJSC Bank Petrovsky I.G. Barkovskaya
_____________________(signature)
St. Petersburg 2009
Introduction
Chapter 1 Theoretical foundations for the formation of the deposit policy of commercial banks
1.2 Classification of deposit operations of commercial banks
1.3 Analysis of the Russian market of deposit services
Chapter 2 Deposit policy of a commercial bank (on the example of JSC "Bank" Petrovsky ")
2.1 Place of JSC "Bank" Petrovsky "in the market of banking services
2.2 Types of deposits of Bank Petrovsky OJSC
2.3 Analysis of the deposit portfolio of OJSC Bank Petrovsky
2.4 Organization of the formation and implementation of the deposit policy
Chapter 3 Improving Deposit Policy
3.1 Tools for improving the deposit policy of Bank Petrovsky OJSC
3.2 The deposit insurance system in the Russian Federation and its improvement
Conclusion
Bibliography
Annex 1
Annex 2
Appendix 3
INTRODUCTION
The specificity of a banking institution as one of the types of commercial enterprise is that the vast majority of its resources are formed not at the expense of its own, but at the expense of borrowed funds. The possibilities of banks in raising funds are not unlimited and are regulated by the central bank in any state.
The main part of the banks' resources is formed by borrowed funds, which cover up to 90% of the total need for funds for active banking operations. A commercial bank has the ability to attract funds from enterprises, organizations, institutions, individuals and other banks in the form of deposits (deposits) and open appropriate accounts.
Funds attracted by banks are diverse in composition. Their main types are funds raised by banks in the process of working with clients (deposits), funds accumulated by issuing their own debt obligations (deposit and savings certificates).
The stated topic of the thesis is closely related to the most acute, in my opinion, currently the problem of the Russian banking system - the problem of banking liquidity.
Relevance chosen research topic is that the unstable situation in the financial markets in the current crisis, rising inflation, competition, and other factors - all this has a huge impact on a commercial bank. Therefore, a clear and thoughtful deposit policy allows a commercial bank to maintain its position and develop.
aim graduation research is the development of proposals for improving the deposit policy of a commercial bank in the system of strengthening its economic stability.
Based on this target setting, there were the following tasks :
Consider the theoretical foundations of the formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank.
Analyze the deposit portfolio of Bank Petrovsky OJSC.
Consider the state and dynamics of attracting deposits;
To analyze the deposit policy of a commercial bank on the example of Bank Petrovsky OJSC.
Object of study of this thesis is JSC "Bank" Petrovsky ".
Subject thesis are attracted funds of individuals and legal entities and their placement through deposit operations and deposit policy in OJSC "Bank" Petrovsky "
practical significance This thesis is that it can be used as additional material for a more detailed study of this topic.
Methodological basis works are: the method of synthesis, analysis, the method of generalization, the dialectical method.
theoretical basis the research compiled legislative acts of the Bank of Russia, including Federal Law No. 177 of December 23, 2003 “On insurance of deposits of individuals in banks on the territory of the Russian Federation”, educational literature, statistical collections, periodicals, reference and information systems.
Information base the thesis was the data of quarterly reports and the internal regulations of JSC "Bank" Petrovsky "g. St. Petersburg.
This thesis has the following structure: introduction, three chapters, conclusion, bibliography, applications.
Chapter 1. Theoretical foundations for the formation of the deposit policy of commercial banks
In modern conditions, for effective functioning, development and achievement of its goals, each commercial bank must develop its own deposit policy, that is, a practical management strategy. As you know, the attraction of financial resources and their subsequent placement are the main forms of activity of a commercial bank.
A fund of funds formed on a paid basis is used to invest in active instruments. Passive operations, therefore, are primary in relation to most of the banking operations aimed at generating income. In this regard, the attracted funds should be considered as an independent object of policy.
Thus, the management of attracted funds is an important component of the bank's business policy. However, issues related to the study of the theoretical foundations of this field of activity have not been sufficiently developed in the scientific literature. This is especially true of the concept of the deposit policy of a commercial bank as an integral element of the liability management strategy.
The definition of the essence of the bank's deposit policy cannot be approached unambiguously, since it varies depending on its subject. The deposit policy is a strategy and tactics of a commercial bank to attract customer funds on a repayable basis.
The bank's deposit policy should include:
Development of a strategy for the implementation of the bank's activities to raise funds in deposits, based on a comprehensive market research, that is, an analysis of the financial environment, the place and role of the bank in the field of raising funds, diagnostics and forecasting;
Formation of commercial bank tactics for the development, offer and promotion of new bank deposit products for customers (in the field of commodity, pricing, marketing and communication policy);
Implementation of the developed strategy and tactics;
Monitoring the implementation of the policy and its effectiveness;
Monitoring the activities of a commercial bank to raise funds.
The main document regulating in commercial banks the process of attracting temporarily free funds of enterprises, organizations and the population to bank accounts in various kinds of deposits (deposits) is the deposit policy of the bank. This is a document that is developed by each bank independently on the basis of the bank's strategic plan, analysis of the structure, condition and dynamics of the bank's resource base and based on the prospects for its development. In addition, such documents are used that determine the main directions and conditions for the placement of attracted funds, such as the Bank's Credit Policy and the Bank's Investment Policy.
The document "Deposit policy of the bank" should define its strategy for raising funds to fulfill the statutory requirements, goals and objectives defined by the memorandums on credit and investment policy, with a focus on maintaining the bank's liquidity and ensuring profitable work. Specifically, the bank provides:
Prospects for the growth of the bank's own funds (capital), and hence the ratio between own and borrowed funds;
The structure of attracted and borrowed funds (deposits, deposits, interbank loans, including loans from the Central Bank of the Russian Federation);
Preferred types of deposits and deposits, terms of their attraction; the ratio between time deposits (deposits) and for the period "on demand";
The main contingent of deposits and deposits, i.e., the category of depositors;
Geography of attraction and borrowing of funds;
Desirable creditor banks for interbank loans, terms for attracting the latter; conditions for attracting deposits (deposits) and interbank loans;
Ways to attract deposits (based on bank account, correspondent account, bank deposit (deposit) agreements, by issuing own certificates, bills of exchange);
The ratio between ruble and foreign currency deposits (deposits);
New forms of attracting funds in deposits;
Special conditions for opening certain types of deposits (deposits);
Measures to comply with the bank's risk standards for borrowed funds.
The deposit policy must first of all meet the following requirements:
- economic expediency;
– competitiveness;
– internal consistency.
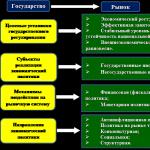
The classification of subjects and objects of the bank's deposit policy is summarized in (Fig. 1).
Figure 1 Composition of subjects and objects of the bank's deposit policy
The formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank is based on both general and specific principles, which is clearly reflected in (Fig. 2).

Figure 2 - Principles of formation of the deposit policy
A number of structural subdivisions of the bank (treasury, financial department, business development department, credit department, securities department), as well as the bank's management bodies are engaged in the development and implementation of the bank's deposit policy in close interconnection with each other: liabilities.

Rice. 3. Enlarged typical bank structure
Thus, the board of the bank determines and approves the main directions of the deposit policy, approves the procedure and conditions for attracting deposits, and exercises general control over the implementation of the deposit policy.
The Assets and Liabilities Management Committee makes fundamental decisions on the formation of a deposit portfolio, analyzes the structure and dynamics of resources, their contingency in terms and amounts with the bank's assets in order to develop, if necessary, decisions to adjust the bank's deposit policy; exercises current control over the implementation of the deposit policy by individual structural divisions of the bank.
The financial management of the bank, together with the treasury, determines the total need of the bank for deposit funds (for a year, including a breakdown by quarters): sets the interest rates for each type of resource (deposits (deposits), bills, interbank loans); determines the amount of reservation of attracted funds in the Bank of Russia; controls the bank's compliance with the risk ratios for borrowed funds established by the Bank of Russia, etc.
Special departments of the bank are directly involved in attracting deposits in various forms: the department of deposits of citizens, the department of securities (issuing own bills, deposit and savings certificates), the credit department or the department of assets and liabilities (deposits of legal entities) and other departments in accordance with the internal organizational structure each bank.
To carry out practical activities to raise funds, banks develop Regulations on deposit (deposit) operations ( separately for deposits of individuals and deposits of legal entities), which stipulate:
Rules and conditions for accepting deposits (deposits);
Legal status of subjects of contractual relations;
The procedure for concluding a bank deposit agreement;
Methods of accepting and issuing a deposit (deposit);
The list of documentation required for opening and using a deposit (deposit), and the requirements for them;
The rights of depositors and the obligation of the bank;
Methods of accrual and payment of interest on deposits (deposits).
Intra-bank instructions on the procedure for making specific deposit (deposit) operations, which are developed by the bank in development of the Regulations on deposits (deposits), contain the organization of the work of a branch (subdivision) of the bank with various categories of depositors; the procedure for issuing documents corresponding to the commission of these operations, the scheme of their document flow; reflection in the accounting of operations for the acceptance and issuance of deposits, accrual and payment of interest on them.
The volume of funds attracted by the bank in deposits (deposits) depends on the state of supply and demand for monetary resources, the deficit or excess of funds from the bank, the state of the deposit market.
In order to attract funds from business entities and citizens into their circulation, banks develop and implement a whole range of activities. So, first of all, an important means of competition between banks for attracting resources is the interest rate policy, because the amount of income on invested funds serves as a significant incentive for customers to place their temporarily free funds in deposits (deposits).
The level of interest rates on deposits (deposits) is set by each commercial bank independently with a focus on the refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia and the state of the money market, as well as based on the provisions of its own deposit policy. First of all, the level of interest rate on deposit (deposit) operations of banks depends on the type of deposits (deposits). As a rule, on demand deposits, characterized by the instability of the balance, high mobility and mobility, minimum interest rates are set.
In order to encourage clients to maintain stable, not declining balances on demand accounts, which generally has a significant impact on the profitability of credit operations, banks set increased interest on them or on the amount of the balance not lower than the minimum calculated by the bank and agreed with the client (which is stipulated in the bank account).
When setting the interest rate on time deposits (deposits), the determining factor is the period for which the funds are placed: the longer the period, the higher the interest rate. An equally important factor is the amount of the deposit, and, therefore, the larger the amount of the deposit and the longer the period of its storage, the higher the interest rate on it, as a rule. An essential point is the frequency of payment of income on deposits (deposits). The interest rate on the deposit is inversely related to the frequency of payment of income, i.e. the less often they are made, the higher the level of the interest rate on the deposit (deposit) set by the bank. It should be noted that paying interest to banks at rates significantly higher than the economically justified level is not illegal. In this case, the material benefit received from the difference between the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation and the credit institution's rate on specific deposits should be subject to income tax.
Payment of interest on a deposit (deposit) can be made:
· once a month;
once a quarter;
after the expiration of the contract.
In order to stimulate the attraction of customer funds to time accounts in the bank, the conditions of deposits (deposits) may provide for the capitalization of interest. It is possible if the bank uses the compound interest technique when calculating income.
The traditional type of calculation of income is simple interest, when the actual balance of the deposit is used as the basis for calculation, and, based on the interest rate stipulated by the agreement, the calculation and payment of income on the deposit take place with the established frequency. Another type of income calculation is compound interest (interest on interest). In this case, after the expiration of the settlement period, interest is accrued on the deposit amount, and the resulting amount is added to the deposit amount. Thus, in the next billing period, the interest rate is applied to the new deposit amount, which has increased by the amount of previously accrued income.
To raise funds for deposits, commercial banks have begun to widely use foreign experience, in particular, they carry out:
· Development of various programs to attract funds from the population;
· provision of various types of services to depositor clients, including those of a non-banking nature (for example, elements of medical care; subscription to periodicals of economic literature; subscriptions for excursion services in museums, etc.);
Use of a high interest rate on deposits of an investment nature;
program "Bonus percentage".
In addition to a flexible interest rate policy in order to attract funds, banks must provide depositors with guarantees for the reliability of placing funds in deposits. In order to protect investors and depositors and provide them with guarantees of compensation of funds in the event of their bankruptcy, banks should create special deposit insurance funds both centrally and decentralized.
Along with deposit insurance, it is important for depositors to have access to information about the activities of commercial banks and the guarantees they can provide. When deciding on the placement of available free funds, each creditor must be sufficiently informed about the financial condition of the bank in order to assess the risk of future investments. In this regard, invaluable assistance to depositors and investors can be provided by rating assessments of the activities of banks by special agencies and bureaus.
At the same time, it should be noted that banks must also provide comprehensive information about themselves (on the amount of authorized capital, equity, founders, development prospects, performance results, etc.) to their creditors and depositors. This is especially true for individuals who choose banks to deposit their funds. Therefore, in the premises of a bank (branch, branch, additional office) accepting deposits from citizens, for the information of depositors, the following must be presented:
· a license from the Bank of Russia, which gives a particular bank the right to accept deposits from individuals either in rubles or in rubles and in foreign currency;
· auditor's report on the bank's annual report;
· the bank's balance sheet as of the last reporting date and profit and loss statement according to the forms for publication in print;
· position of the bank on the deposits of individuals;
List of types of deposits accepted by the bank from individuals. persons;
conditions for each type of deposits;
· information about the conditions for providing and guaranteeing deposits by the bank;
Forms of documents required for registration of deposits and transactions with them;
· information of the board of the bank (or other management bodies of the bank) on changes in the interest rate for certain types of deposits (indicating the reasons and terms for making changes to the conditions of deposits).
The work of credit institutions to attract creditors' funds into their circulation is associated with certain risks, which they must take into account in their activities and be able to manage them in order to avoid negative consequences for liquidity and stability.
The Bank of Russia establishes for banks and monitors their compliance with certain restrictions on the amount of funds raised. In accordance with the latest instructions of the Bank of Russia, a procedure is established for determining the balances on demand accounts and term accounts of individuals and legal entities (with the exception of credit institutions) for their inclusion in the calculation (exclusion from the calculation) of the instant (H2), current (H3) and long-term liquidity (H4) of the bank.
The approach proposed by the Ordinance implements the method used in international practice for assessing bank liquidity risks, taking into account the so-called "behavioral" adjustments, that is, indicators characterizing the state of assets and liabilities based on accumulated statistical data.
The Ordinance establishes that banks independently determine the appropriateness of using the values of the minimum aggregate balances for calculating liquidity ratios.
It should be noted that not the entire amount of funds attracted by the bank from its customers can act as resources for its active operations. Part of the funds raised in the amount established by the Board of Directors of the Bank of Russia is subject to mandatory deposit on a separate account with the Bank of Russia. The Bank of Russia forms the obligatory reserve fund of the credit and banking system of the state. It can be used to provide credit assistance to commercial banks by the Bank of Russia in various ways, for settlements with depositors and creditors in the event of bankruptcy of a credit institution.
By changing the norms of required reserves, the Bank of Russia influences the credit policy of commercial banks, and, accordingly, the state of the money supply in circulation. For example, a reduction in the mandatory reserve requirements for funds attracted by banks allows them to use the generated resources in their turnover to a greater extent, i.e. increase credit investments in the national economy, and vice versa. Required reserves (reserve requirements) are a mechanism for regulating the overall liquidity of the banking system, used to control monetary aggregates by reducing the money multiplier.
The obligation to fulfill reserve requirements arises for a commercial bank from the moment it receives a license from the Bank of Russia for the right to perform the relevant banking operations.
Required reserve ratios are set by the Bank of Russia for a certain period of time and may be reviewed periodically, but they cannot exceed 20% of a credit institution's liabilities. It should be noted that the norms of required reserves can be differentiated depending on the timing of raising funds, their types (cash of legal entities or individuals), the currency of the deposit (deposit). Usually, the highest reserve ratio is set for demand accounts, since the client can withdraw his funds from them at any time.
The stages of the formation of a savings policy are shown in Figure 4.
Monitoring is a necessary tool for assessing and managing the quality of banking activities in the savings market. It is thanks to monitoring that the commercial bank and supervisory authorities can evaluate the results of the deposit policy pursued by the bank, which is extremely important in the development of monetary policy and other market regulation instruments, as well as to prevent crisis situations in the banking system associated with the loss of customer confidence in financial and commercial institutions.
Next, we consider the stages of formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank. It is very important to study the formation and implementation of the deposit policy mechanism of a commercial bank, since the successful fulfillment of the goals and objectives that are set for the bank in the process of developing and implementing a deposit policy largely depends on the effectiveness of its functioning.

Figure 4 Stages of formation of a savings policy
Based on the analysis of the current practice of behavior of banks in deposit operations, a scheme for the formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank is proposed, which is shown in Figure 5.

Figure 5 Scheme of formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank
Each of the stages of the formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank is closely related to the others and is mandatory for the formation of an optimal deposit policy and the correct organization of the deposit process. In this regard, the following areas of the deposit policy of a commercial bank can be distinguished:
Analysis of the deposit market;
Determination of target markets to minimize deposit risk;
Minimization of costs in the process of raising funds;
Optimization of deposit and loan portfolio management;
Maintaining the liquidity of the bank and increasing its stability.
An analysis of the current practice shows that the formation of the deposit base of any commercial bank, as a complex and time-consuming process, is associated with a large number of problems, both subjective and objective.
Subjective issues include:
1) scale of activity and weak capital base of Russian commercial banks;
2) the lack of interest of the bank's management in attracting funds from customers, especially the population, which is dictated by the tactical and strategic goals and objectives of the bank;
3) insufficient level and quality of top and middle management;
4) the lack of a science-based concept for conducting a deposit policy in most Russian banks;
5) shortcomings in the organization of the deposit process: the absence of an appropriate department in the bank, or a low level of marketing research on the deposit market, a limited range of deposit services offered, etc.
Among the objective factors are the following:
1) direct and indirect impact of the state and state bodies;
2) the impact of macroeconomics, the impact of global financial markets on the state of the Russian money market;
3) interbank competition;
4) the state of the money and financial market in Russia;
The role of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation as a regulatory body over the past few years has been especially pronounced in matters of setting the refinancing rate and reserve requirements for commercial banks. Changes in the refinancing rate do not allow commercial banks to accurately predict and plan their activities in the field of asset and liability management for the long term and make operations with long-term liabilities rather risky.
A negative impact on the structure of the resource base of a commercial bank has a growing dependence on large interbank loans, since an interbank loan does not contribute to the diversification of risks in deposit operations.
To solve existing problems, when developing a deposit policy, a commercial bank must be guided by certain criteria for its optimization. Optimization of the bank's deposit policy is a complex multifactorial task, the solution of which should be based on the consideration of the country's economy as a whole. Obviously, these interests do not always coincide. Therefore, the optimal deposit policy involves first coordinating their interests.
So, the optimization criteria are as follows:
a) the relationship of deposit, credit and other operations of the bank to maintain its stability, reliability and financial stability;
b) diversification of the bank's resources in order to minimize the risk;
c) segmentation of the deposit portfolio (according to clients, products, risks);
d) differentiated approach to different groups of clients;
e) competitiveness of banking products and services;
f) the need for an effective combination of resources, ensuring the optimal combination of stable and "volatile" resources while increasing the share of stable resources in the deposit portfolio of a commercial bank in conditions of increased risks (including deposit operations);
g) taking into account the concept of the life cycle in the process of forming the range of deposits and the deposit portfolio as a whole.
In order to improve the deposit policy of a commercial bank, the following is necessary:
Each commercial bank must have its own deposit policy, developed taking into account the specifics of its activities and the criteria for optimizing this process;
It is necessary to expand the range of deposit accounts of legal entities and individuals with a term “on demand”, which will allow, even in conditions of insignificant financial savings, the field to satisfy the needs of bank customers and increase the interest of investors in placing their funds on bank accounts;
As one of the ways to improve the organization of deposit operations, it is possible to use different types of accounts for all categories of depositors and improve the quality of their service;
Individual approach (the desire of the bank to provide the client with special benefits).
These are some of the possible ways to improve the deposit policy of a commercial bank and increase its role in ensuring its sustainability.
The relationship between the savings and deposit policy of a commercial bank is as follows: on the one hand, the main directions of the deposit policy are elements of the formation of the savings activity of the bank (for example, the range of deposits, interest rate policy, promotion of the product on the market, organization of the work of the relevant departments of the commercial bank). On the other hand, it is impossible to call the deposit policy an integral element of the bank's savings policy. The bank's deposit policy is a broader concept, which includes, in addition to the strategy and tactics of attracting resources on a repayable basis, the organization and management of the deposit process.
In general, each commercial bank develops its own deposit policy. Also, the bank's management independently determines the degree of importance of these areas, the priority of one or another type of bank policy. First of all, it will depend on the area of operation of a particular bank, its specialization and universalization.
1.2 Classification of commercial bank deposits
The passive operations of a commercial bank characterize the sources of funds and the nature of the bank's relationships. It is they who largely predetermine the conditions, forms and directions for the use of banking resources, i.e. composition and structure of active operations.
Deposit (deposit) operations of a commercial bank are operations to attract funds from legal entities and individuals in deposits for a certain period or on demand, incl. balances of funds on settlement accounts of clients for their use as credit resources and in investment activities. Contribution ( deposit ) - these are funds (in cash and non-cash form, in national or foreign currency) transferred to the bank by their owner for storage under certain conditions.
Deposit operations are a broad concept, since they include all the bank's activities related to raising funds in deposits. A feature of this group of passive operations is that the bank has relatively weak control over the volume of such operations, since the initiative to place funds in deposits comes from depositors. At the same time, as practice shows, the depositor is interested not only in the interest paid by the bank, but also in the reliability of saving the funds entrusted to the bank.
The organization of deposit operations should be carried out subject to a number of principles:
– receipt by the bank of current profit and creation of conditions for its receipt in the future;
– flexible policy in the management of deposit operations to maintain the operational liquidity of the bank;
– consistency between the deposit policy and the return on assets;
– development of banking services in order to attract customers.
Consider in detail deposit accounts and their characteristics.
Deposit accounts can be very diverse and their classification is based on such criteria as sources of deposits (free cash of organizations, savings of individuals, pensions), their intended purpose (receiving income on time deposits upon expiration of their validity, monthly income in the form of interest on the amount of the deposit), the degree of profitability (depends on the amount, term and additional conditions of the deposit), etc.
However, most often the criterion is the category of the depositor and the form of withdrawal of the deposit. Deposit operations are classified:
– deposits of legal entities (enterprises, organizations);
- deposits of individuals.
- deposits of other banks.
2) By economic content:
- according to the order of use of stored funds. Those. receipt of income in the form of interest on attracted funds to the deposit monthly, quarterly, at the end of the contract.
3) According to the form of withdrawal of funds:
– term deposits;
– demand deposits;
- savings deposits of the population
- conditional deposits subject to withdrawal upon the occurrence of predetermined conditions.
The classification of deposits according to the form of withdrawal can be presented schematically in Figure 6 in more detail.
In the practice of Western banks, deposits, if possible, are divided into the following categories:
- "hot money", which is highly likely to be withdrawn (for example, deposits that are sensitive to changes in interest rates, which are caused by economic instability, inflation, sharp fluctuations in exchange rates). Hot money is money whose owners urgently move it from one bank to another in order to get a higher profit. As a result, there is a migration of capital.
- unreliable, which can be withdrawn within 25-30% of their size. Unreliable deposits include deposits with early repayment;
- stable funds (main deposits), the probability of withdrawal of which is minimal. These include term deposits without early repayment.
However, let us return to Russian banks and consider in more detail the classification of deposits presented in Figure 6.
Figure 6 Classification of deposits (according to O.I. Lavrushin)
Let's start with demand deposits, as they occupy the largest share in the structure of attracted funds of banks - about - 50%.
So, demand deposits are funds that can be claimed at any time without prior notice to the bank by the client. These include funds on current, settlement and correspondent accounts related to settlements or intended use of funds. On such accounts there is a constant movement of funds (credits and write-offs). Due to the high mobility of funds, the balance on demand accounts is not constant, sometimes extremely volatile. However, despite the high mobility of funds on demand accounts, it is possible to determine their minimum, non-decreasing balance and use it as a stable credit resource.
The calculation of the share of funds held on demand accounts that can be transferred to term deposit accounts (in order to increase the income for clients from funds placed in the bank and form a stable lending resource for banks) is made according to the formula:
D \u003d Avg.: K vol. x 100%,
where D is the share of funds held during the year in various current accounts that can be transferred to deposit accounts.
Osr - the average balance of funds on the settlement or current account for the year.
K about. - credit turnover on the settlement or current account for the year.
In order to expand active operations and make a profit for the bank, the best way in terms of managing liabilities is to grow and diversify the main types of deposits, which include demand deposits and term deposits. With the help of demand deposits, the problem of making a profit by the bank is solved, since they are the cheapest resource, and the costs of servicing settlement and current accounts of customers are minimal.
Demand deposits are inherently unstable, which limits their use by commercial banks. For this reason, deposit account holders are paid a low interest rate (on a demand deposit for an individual, currently 0.01%) or it is not paid at all (for example, on settlement and current accounts of legal entities, as well as on a correspondent account of commercial banks) . In the face of increased competition in attracting deposits, commercial banks seek to attract customers and stimulate the growth of demand deposits by providing additional services to account holders, as well as improving the quality of their service.
Interest on demand deposits is credited to the depositor, as a rule, once a year at the beginning of a new calendar year.
Demand deposits are the most liquid. Their owners can at any time use the money on demand accounts. Money is deposited or credited to this account, as well as withdrawn or written off both in parts and completely without restrictions, and it is also allowed to withdraw cash from this account. The advantage of demand deposit accounts for their owners is their high liquidity, and for banks, the establishment of a low interest rate or none at all. The main disadvantages of demand deposits for their owners is the establishment of a low interest rate on the account, and for the bank - the need to have a higher operating reserve. Thus, the features of a demand deposit account can be characterized as follows:
– deposit and withdrawal of money is carried out at any time and in any amount without any restrictions;
– the account holder pays the bank a fee for using the account in the form of a fixed monthly rate (for legal entities);
- the bank pays low interest rates (for individuals) or does not pay at all (for legal entities) for keeping funds on demand accounts, which increases the bank's profit.
Term deposits are generally classified according to their term: deposits with a term of up to 3 months; from 3 to 6 months; 6 to 9 months; from 9 to 12 months; over 12 months.
The advantage of time deposit accounts for the client is the establishment of a higher interest rate compared to a demand deposit, and for the bank - the ability to maintain liquidity with a smaller operating reserve. The disadvantage of term deposit accounts for clients is low liquidity. For the bank, the disadvantage is the need to pay increased interest on deposits and thus reduce profits.
There are two types of term deposits:
– term deposit with a fixed term;
– term deposit with prior notice of withdrawal.
Actually term deposits imply the transfer of funds at the full disposal of the bank for the term and conditions under the agreement, and after this period the term deposit can be withdrawn by the owner at any time. The amount of remuneration paid to the client on a term deposit depends on the term, amount of the deposit and the fulfillment by the depositor of the terms of the agreement. The longer the terms and (or) the larger the amount of the deposit, the larger the amount of remuneration, as a rule. Such a detailed gradation encourages depositors to rationally organize their own funds and place them in deposits, and also creates conditions for banks to manage their liquidity. For example, in JSC "Bank" Petrovsky "frequency of payment of income varies from 1 month to the moment of payment of the amount of the entire deposit as a whole.
Deposits with prior notice of withdrawal of funds means that the client must notify the bank in advance of the withdrawal of the deposit within the period specified by the agreement. Depending on the notice period, the interest rate on deposits is also determined.
If the depositor wishes to change the amount of the deposit - to reduce or increase, then he can terminate the current agreement, withdraw and re-register his deposit on new terms. However, in case of early withdrawal by the depositor of funds on the deposit, he may lose the interest provided for by the agreement in part or in full. As a rule, in these cases, the interest is reduced to the amount of interest paid on demand deposits. The current demand rate is 0.15%. Many commercial banks apply prolongation of deposits up to several times (1-3 or more). When prolonging the current deposit in case of a change in the interest rate, the newly established interest rate is applied.
By attracting time deposits, the problem of ensuring the liquidity of the bank's balance sheet is solved.
The most important instruments of the deposit policy of commercial banks are deposit and savings certificates. In the Russian Federation, the circulation of certificates takes place on a legislative basis.
A certificate is a written obligation of the issuing bank to deposit funds, certifying the right of the depositor or his right of the receiver to receive the amount of the deposit and interest on it after the expiration of the established period. Deposit and savings certificates are a type of income security, therefore they cannot serve as a settlement or payment instrument for goods sold or services rendered. There are also restrictions on transferring them from one owner to another. The form of the nominal certificate must have a place for transfer inscriptions.
The certificates issued by the bank must be printed and meet the requirements for such securities.
Commercial banks have the right to start issuing certificates only after the approval of the conditions for their issuance and circulation by the main territorial departments of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. The conditions must contain the full procedure for issuing and circulation of certificates, a description of the appearance and a sample certificate. The certificate must contain the following mandatory details: name "deposit" (or "savings") certificate; the reason for issuing the certificate (making a deposit or savings deposit); date of deposit, amount (in words and numbers); an unconditional obligation of the bank to return the amount deposited or deposited; date of claiming the amount of the certificate; interest rates and the amount of interest due; name and address of the issuing bank; for a personal certificate - the owner; signatures of two persons authorized to sign such obligations, sealed by the bank.
In addition to dividing certificates into deposit and savings, depending on the category of depositors, certificates can be classified according to other criteria:
1) According to the release method:
- issued on a one-time basis, i.e. a certificate of a certain number and denomination is issued once;
- produced in series, i.e. a batch of certificates is issued, one series and one denomination, but under different numbers
2) According to the design method:
Nominal - by concluding an agreement on the assignment of the right to claim (cession);
- to the bearer - are transferred to the new owner by simple delivery.
Cash settlements for the purchase and sale of certificates of deposit and the payment of amounts on them are carried out only in a non-cash manner.
The certificate is not subject to export to the territory of a state that does not use the ruble as an official currency. The right to claim a certificate of deposit can only be transferred to legal entities registered in the territory of the Russian Federation or another state that uses the ruble as an official currency.
Certificates must be current. If the deadline for receiving a deposit or a deposit under a certificate is overdue, then such a certificate is considered a demand document, according to which the bank is obliged to pay the deposit at the first request of the owner (beneficiary). The Bank may provide for the possibility of early presentation for payment of an urgent certificate. In this case, the bank pays the owner of such a certificate the amount of the certificate and interest at a reduced rate established by the bank when issuing the certificate. Interest on certificates is set upon issuance and is indicated on the forms in percentage and monetary form. At the same time, interest payments due to the owner after the expiration of the certificate do not depend on the time of purchase. You can get a certificate only in the commercial bank in which it was issued or in any of its branches.
The certificate form must contain all the conditions for the issuance, payment and circulation of the certificate (the conditions and procedure for the assignment of rights, the requirement for a certificate. If an operation was performed with a certificate that was not provided for by the conditions contained on its form, such an operation is considered invalid. Production of deposit and Savings certificates, both nominal and bearer, are produced only by printing companies that have a license to issue securities.The Bank independently develops the conditions for issuing and circulation of the certificate.
The conditions for issuing and circulation of certificates, a description of the appearance and a sample of the certificate are approved by the board of the issuing bank and sent in 3 copies for examination to the Main Territorial Directorate of the Central Bank at the location of the correspondent account, which gives an opinion on the observance by the issuing bank of the existing rules for issuing a certificate and in the absence of violations, one copy of the conditions is sent to the Securities Department of the CBR. Certificates, being securities, are not subject to registration and do not require a special decision on their issue by the CRB. At the same time, the territorial administration may prohibit the issuance of certificates, as well as invalidate those issued for the following reasons:
The terms of issue are contrary to the current legislation or the rules of the CBR;
The issuing bank did not timely submit the terms of the issue to the Main Territorial Department of the CBR;
The Bank violates the current legislation and the CBR rules on the process of issuing and circulation of the certificate.
The owner of the certificate may assign the right to claim the certificate to another person. For a bearer certificate, this assignment is carried out by simple delivery, for a nominal one, it is drawn up on the back of the certificate by a bilateral agreement (cession). Upon the expiration of the claim period, the owner of the certificate must submit it to the bank along with an application containing an indication of the method of redeeming the certificate.
In order to account for the sold certificates, commercial banks keep special registration journals or provide for the issuance of a certificate with special sending stubs containing the same registration details.
Certificates are issued for terms from 1 month to 3 years, and for the amount of certificates of deposit - from 5 thousand to 10 million rubles, savings certificates from 1 thousand and more than 1 million rubles. Interest rates depend on the size and term of the deposit, some banks carry out indexation and monthly payment of income.
Consider the features of deposit certificates. A deposit certificate can only be transferred from a legal entity to a legal entity. A certificate of deposit can only be issued to an organization that is a legal entity registered in the territory of the Russian Federation or in the territory of another state that uses the ruble as an official currency. A certificate of deposit has two advantages. First, unlike other deposit policy instruments, it is the subject of an exchange game, and, therefore, its owner can count on extracting additional profit as a result of favorable changes in market conditions. Secondly, if the government implements its intentions to freeze the deposits of enterprises, the purchase of a certificate that is freely circulating on the market will give their owners some freedom of maneuver. In this situation, the certificate becomes an alternative means of payment.
The term of circulation for certificates of deposit (from the date of issue to the date when the owner of the certificate receives the right to demand a deposit or deposit under the certificate) is limited to one year.
In international practice, interest-bearing certificates of deposit, discount, i.e. sold at a price below par and certificates with a "floating" rate. The validity of the last certificate is from 3 to 5 years and the interest rate is determined every 6 months for the next six months. Certificates of deposit can be purchased at any time during their validity period - interest is accrued from the date of purchase.
Some commercial banks issue certificates of deposit that are transferable (or non-transferable) to other owners by endorsement in denominations from 500,000 rubles to 10 million rubles. up to a year, designed for large investors. Transferable certificates of deposit are usually sold to government agencies, pension funds, corporations. They generate income in excess of the interest rate on short-term treasury bills of a shorter term (three months and others) and can be traded on the secondary securities market.
Consider the features of Savings Certificates. A savings certificate can be transferred from an individual to an individual. A savings certificate can only be issued to a citizen of the Russian Federation or another state that uses the ruble as an official currency. The right to claim a savings money certificate is transferred only to citizens of the Russian Federation or another state that uses the ruble as an official payment unit.
In order not to lose the most stable source of credit resources, commercial banks are forced to carry out indexation on savings certificates under inflation conditions by raising the interest rate, which is an incentive for the population to purchase.
Certificates have significant advantages over term deposits issued by simple deposit agreements: due to the greater number of possible financial intermediaries in the distribution and circulation of certificates, the circle of potential investors is expanding; thanks to the secondary market, the certificate can be sold ahead of time by the owner to another person with some income for the time of storage and without changing the volume of the bank's resources, while early withdrawal by the owner of a term deposit means a loss of income for him, and for the bank the loss of part of the resources .
The disadvantages of certificates are: the increased costs of the bank associated with the issue of certificates, as well as the fact that income from them is subject to taxation, in contrast to demand accounts and time deposits. The latter feature is taken into account by banks, so the interest on certificates is usually higher than the interest on term deposits with similar terms and amounts.
So, drawing a conclusion from the above theoretical material, we can say that for commercial banks, deposits are the main and at the same time the most profitable type of resources. An increase in the share of this element in the resource base makes it possible to place a larger volume of attracted funds, thereby increasing the bank's liquidity.
The intensification of competition between banks and other financial structures for deposits of individuals and legal entities has led to the emergence of a huge variety of deposits, their prices and service methods. According to some foreign experts, there are currently more than 30 types of bank deposits in developed countries. At the same time, each of them has its own characteristics, which allows customers to choose the most appropriate and possible form of saving money and paying for goods and services that suits their interests.
It can be seen from the above that deposits among the attracted funds of the bank are an important source of resources. However, such a source of formation of banking resources as deposits also has some disadvantages. First of all, we are talking about the significant material and monetary costs of the bank when attracting funds to deposits, the limited availability of funds within a particular region. Nevertheless, the competition between banks in the market of credit resources forces them to take measures to develop services that help attract deposits.
1.3 Analysis of the Russian market of deposit services
The process of forming a deposit policy is closely interconnected with the bank's interest rate policy, since the deposit interest is an effective tool in the field of attracting resources. At the time of state regulation, the marginal rates of interest were established by law in accordance with the maturity of the deposit. Currently, banks can independently set competitive interest rates based on the discount rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (10.00% since September 30, 2009), as well as the state of the money market and based on their own deposit policy.
A feature of the household deposit market is the significant influence of interest rate levels on the formation of demand for deposits - that is, the interest rates on deposits set by banks largely determine the growth rate of their resource base. Moreover, for different groups of banks, this influence manifests itself to varying degrees. Such heterogeneity of the market can lead to a significant redistribution of market shares among banks, which may be accompanied by the emergence of new major players. Let's try to understand these processes.
An analysis of the cost of banking resources indicates that Russian credit institutions are actively using the factor of manipulating interest rates in their deposit policy in order to ensure the influx of new depositors. Of course, the level of interest rates is not the only factor that determines fluctuations in the deposit base, but from a practical point of view, the task of determining the impact of the cost of deposits on fluctuations in the client base "ceteris paribus" is very relevant.
The increase in deposit rates leads to an increase in the growth rate of the total deposit base of the bank. For example, if in 2006 the average level of interest rates in commercial banks was approximately 10% (at the same time, there was an increase in bank deposits at a rate equivalent to 40% per annum), then the deviation of the rates of attraction by banks to 11% on average provided them with an increase in the growth rate of deposits up to 50 %.
The dynamics of attracted deposits of the population in the banking system, from 2006 to the second half of 2008, had a positive trend. This was due to the growth in household incomes and an increase in the level of confidence in the banking system (Figure 8). Currently, the growth in the volume of attracted funds has slowed down due to the financial crisis. The highest rates in the market of bank deposits of individuals are demonstrated by credit institutions from the “other” group. These medium-sized banks are the most active in attracting new customers, and the size of interest payments becomes the main argument available to them when attracting new depositors (the reliability of these credit institutions is still not capable of significantly influencing their deposit policy by itself).

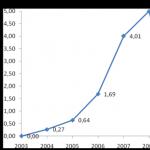
Figure 8. Dynamics of household deposits for the period (2006-2008)
The deposit insurance system that has appeared in Russia, in addition to obvious advantages, can also bring certain dangers - in the opinion of the population, there is a gradual smoothing in risk assessments of various banks that differ in real levels of financial stability. As a result, it is for these banks that the price factor is the main tool in the competitive struggle. It is no coincidence that in this group of banks the demand for deposits is most sensitive to changes in interest rates. And this explains the highest growth rates of household deposits in this group of banks.
The cost of the corresponding resources in the group of the largest Russian private banks slightly exceeds the levels of the cost of deposits in commercial banks. This group initially enjoyed higher trust among the population (compared to banks from the “junior” groups), which allowed them to provide a moderate cost of attracting deposits for quite a long time. However, in recent years, the competitive advantages of this group of banks have been declining in the eyes of the population, which, on the one hand, is explained by the emergence of a deposit insurance system, and, on the other hand, by the experience of the banking crisis in the summer of 2004, when several largest Russian banks were on the verge of losing solvency. As a result, the status of large banks is gradually leveling off in relation to smaller credit institutions. And, as a result, the price factor, as well as for banks from the "other" group, plays a significant role here - sensitivity to changes in interest rates. At the same time, high sensitivity combined with rather high rates does not guarantee them the same growth rates of their deposit base. This is due to the special "disloyalty" of their clientele, which, reasonably not seeing a significant difference in risks, preferred to transfer deposits to smaller credit institutions offering obviously higher interest rates.
The most significant is the cost of resources of the group of banks with the participation of foreign capital. Their deposit policy is based on high credit ratings of parent structures, which are unattainable for Russian commercial banks. This factor allows banks with the participation of foreign capital to attract funds from the population at low rates rather cheaply. At the same time, since the spring of 2005, the group of banks with foreign capital remains the only category of banks consistently increasing the cost of deposits. This effect appears to be due to two factors.
First, initially, the main clientele of banks with foreign capital were wealthy segments of the population, who value reliability in bank deposits and are ready to put up with low interest rates. However, a deliberately small group of depositors today can no longer provide a significant increase in the volume of attraction. This means that banks are forced to pay attention to other potential depositors who are more focused on earning interest income. Fortunately, the current low levels of deposit rates of banks with foreign capital allow them to be increased without a significant reduction in bank margins.
Secondly, the recent rise in the cost of borrowing in foreign markets has made the Russian deposit market really interesting for banks with foreign capital, and they are ready to actively fight for a place on it, especially in the current financial crisis.
If until recently the sensitivity of the growth rates of deposits for banks with the participation of foreign capital to the value of deposits was actually absent, now we can already state their readiness to attract new depositors.
If you look at the dynamics of foreign currency and ruble deposits, you can see that over the past five years, the growth rate of deposits of individuals in rubles has almost constantly outpaced the growth rate of foreign currency deposits, which was caused by the decline in popularity of the dollar.

Figure 9 Growth rates of ruble and foreign currency deposits
As of July 1, 2008, foreign currency deposits accounted for 13.6% of the total volume of deposits. Today, according to the Bank of Russia, the volume of foreign currency deposits is about 30% of the total.
Speaking about interest rates, the following should be noted: for certain types of deposit accounts, the amount of income is determined by the term of the deposit, the amount, the specifics of the operation of the account, the volume and nature of related services, and depends on the client's compliance with the conditions of the deposit.
The system of interest rates on deposits should be oriented to market conditions, with the indispensable consideration of the emerging hierarchy of reliability of comparable instruments. Thus, a bank that keeps rates at a lower level than competitors close to it in terms of reliability risks losing part of its clientele.
The accrual of interest on deposits by the bank is the main part of operating expenses. Therefore, the bank, on the one hand, is not interested in a high level of interest rates, and on the other hand, it is forced to maintain such a level of interest rates on deposits that would be attractive to customers. Trying to attract deposits, especially of large size and for a long period, commercial banks offer high interest rates to their customers, despite the growth in interest costs. However, the attraction of funds from the population by banks is not unlimited. As of January 01, 2009 the average interest rate on attracted funds is 12% per annum (according to the statistics of the Central Bank). If we trace the dynamics of % rates in commercial banks of the North-West over the past 3 years, we can conclude that the average interest rate on deposits increased by approximately + - (3-4)%. Interest rates on deposits have changed especially noticeably in the context of the crisis that has developed in the world. Only for the 1st quarter of 2009 they increased by approximately (3-5)% in almost all commercial banks.
Chapter 2 Deposit policy of a commercial bank (on the example of JSC "Bank" Petrovsky ")
2.1 Place of JSC "Bank" Petrovsky "in the market of banking services
Before analyzing a specific area of activity of any subject of the economy, it is necessary to give a brief description of it.
Bank Petrovsky was registered by the Central Bank of the RSFSR on November 12, 1990. In 1991, the first 5 branches in St. Petersburg, as well as the first out-of-town office, began work.
In 1992, a cooperation agreement was signed between the Bank and the Department of the Federal Postal Service. As early as next year, together with the Federal Penitentiary Service and the St. Petersburg branch of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, Petrovsky began introducing a technology for paying pensions from current pension accounts at the city's post offices. In 1997, "Petrovsky" began to introduce its pension technology in the Leningrad region.
In 1997, the Bank received the status of an authorized Bank of the Government of the Russian Federation category "C", as well as an authorized Bank of the Government of the Leningrad Region.
In 2000, the management of the Bank decided to rename the Bank into OJSC "Petrovsky People's Bank".
In 2002, due to the change of the Bank's shareholders, Petrovsky Narodny Bank was renamed into MDM-Bank St. Petersburg.
In May 2006, the controlling stake in the Bank was acquired by East European Financial Corporation. In accordance with the decision of the general meeting of shareholders of the Bank, a new name of the Bank was approved: Open Joint Stock Company "Bank of the Eastern European Financial Corporation" (abbreviated name - JSC "VEFK Bank").
On October 29, 2008, the Deposit Insurance Agency (DIA), based on the requirements of the Federal Law “On additional measures to strengthen the stability of the banking system in the period up to December 31, 2011”, assumed the functions of an interim administration to manage the EEFC Bank. In February 2009, agreements were reached on the participation of NOMOS-BANK and FC OTKRITIE as co-investors in the capital of VEFK Bank.
As part of the Bank's financial recovery measures, investors represented by NOMOS-BANK and OTKRITIE Financial Corporation bought back 25% of the additional issue of VEFC Bank shares. The remaining 50% of the additional issue was purchased by DIA.
In September 2009, the Bank returned to its original name - Petrovsky Bank.
JSC "Bank" Petrovsky "provides a wide range of services for both legal entities and individuals. The bank offers private individuals such services as deposits in rubles and foreign currency, money transfers, payment of pensions, transfers from ruble and foreign currency accounts, safe deposit, cash transactions, opening and maintenance of plastic cards. The list of services for organizations is quite extensive. Let's name those that are most popular: lending, opening and maintaining ruble and foreign currency accounts, payroll projects.
The priority direction of activity of Bank Petrovsky OJSC is work with the population in the area of attracting deposits. Depositors of Bank Petrovsky OJSC can choose the most convenient scheme for saving and increasing their savings. The Bank offers its customers a flexible system of deposits in rubles and foreign currency for a period of 1 month to 3 years; various types of deposits, allowing you to choose a deposit that meets the needs of the client. JSC Bank Petrovsky issues its own international plastic cards VISA INTERNATIONAL and MASTER CARD INTERNATIONAL . JSC "Bank" Petrovsky "has an extensive correspondent network, consisting of major banks in Russia and the CIS. Bank Petrovsky OJSC has a widely branched (second largest after Sberbank) branch network - 170 branches in St. Petersburg and branches in Russian cities. Purposeful work to improve banking services and expand their range has become the basis for a significant increase in the number of clients of Bank Petrovsky OJSC.
The change of shareholders and top management of VEFC Bank, which took place at the end of April 2009, as well as the Bank's obtaining the status of a credit institution with state participation in the capital, had a positive impact on the attitude towards the Bank on the part of private individuals. reverse the downward trend in the main indicators characterizing the volume of operations for servicing individuals, observed in the previous period. see Figure 10. At the same time, the volume of term deposits grew by 6.6%, balances on pension accounts in the Bank's additional offices - by 15.5%, balances on bank card accounts - by 14.1%.

Figure 10 Dynamics of deposits of individuals for the period from 10.08-09.2009
The bank's average monthly income from transactions with individuals (money transfers, utility bills, safe deposit, etc.) also increased significantly. If, for comparison, in February-March this year. they averaged 7.5 million rubles, then in June the Bank's income increased to 8.3 million, in July - to 8.6 million.
The number of money transfers carried out by the Bank, which, for example, in the spring of this year, was 15-16 thousand units per week, has now reached 20 thousand.
Separately, I would like to note a serious increase in the balances on the accounts of pensioners who receive pensions directly at the offices of Bank Petrovsky OJSC. As you know, pensioners who receive a pension at the Bank can be served both in post offices and in additional offices of the Bank. At the same time, the list of services provided to this category of clients in additional offices is wider than in post offices. This fact is also understood by the pensioners themselves, as of July 2009 the bank serves about 1.2 million pensioners. The balances on the accounts of pensioners for the first half of the year increased by 1 billion rubles (53%).
Speaking about legal entities, it should be noted that since May 2009, account balances have increased by 20% - up to 7.5 billion rubles. If at the beginning of the year corporate clients opened about 150 accounts per week in Bank Petrovsky OJSC, then by the end of September 2009, 250-270 new accounts are opened per week. The total number of accounts of legal entities is now 67 thousand units.
According to Expert magazine, Bank Petrovsky is ranked 41st in the rating of 100 largest banks in Russia in 2008 as of 01.01.2009. The Bank is among the 30 leading banks in attracting deposits from individuals in 2008 at number 26
2.2 Types of deposits of Bank Petrovsky OJSC
Household deposits are of great importance in the resource base of Bank Petrovsky OJSC. Thus, as of September 1, 2009, household deposits amounted to 80.0% of the total resources. This is quite natural, since Petrovsky constantly pays special attention to the deposits of the population.
Consider the current as of 01.09.2009. types of deposits and conditions for them. They can be divided into three main groups: term deposits, pension deposits and demand deposits.
Table No. 1 Types of deposits as of 01.10.2009
| Types of deposits | Deposit term, prolongation | The amount of the down payment and additional contributions | Note | Annual % |
| Poste restante | any | At least 10 rubles. Add. Contributions are unlimited | 0,15 | |
| Autumn |
over 1 year up to 3 years |
From 1000 rubles From 100 dollars From 100 euros |
4.35-14.70 | |
| Autumn-retirement |
over 1 year up to 3 years |
From 1000 rubles From 100 dollars From 100 euros |
Add. contributions / payments capitalization, prolongation are not provided | 4.55-14.90 |
| Petrovsky-classic |
over 1 year up to 3 years |
From 1000 rubles From 100 dollars From 100 euros. |
4.10-14.70 | |
| Petrovsky-classic with a monthly payment of % |
over 1 year up to 3 years |
From 1000 rubles From 100 dollars From 100 euros |
Add. contributions / payments are not provided. % payment monthly |
3.10-13.70 |
| Petrovsky-cumulative |
over 1 year up to 3 years |
From 1000 rubles From 300 dollars From 300 euros Contributions from 500 rubles, 50 dollars, euros |
Add. capitalization payments are not provided | 5.10-13.70 |
| Petrovsky-compound interest |
over 1 year up to 3 years |
From 1000 rubles From 100 dollars From 100 euros |
Add. contributions / payments, not provided | 3.60-14.20 |
| Petrovsky-multicurrency |
over 1 year up to 3 years |
From 30000 rub From 1000 dollars From 1000 euros Contributions are unlimited |
Add. capitalization payments, prolongation are not provided | 6.35-13.70 |
| Petrovsky-universal |
over 1 year up to 3 years |
From 10000 rub From 300 dollars From 300 euros Contributions from 1000 rubles, 50 dollars, euros |
capitalization is not provided | 4.60-13.95 |
| Petrovsky-VIP |
over 1 year up to 3 years |
From 300000 rub From 10000 dollars From 10000 euros |
Add. contributions / payments capitalization, not provided | 5.55-15.20 |
| Pension savings deposit | 2 years |
Contributions are unlimited |
No extension provided | 12.50 |
| Pensioner's current account | any | 5-7 |
Table No. 1 shows that the most expensive deposits for individual clients are the deposits of Autumn-pension, Autumn, Petrovsky-classic and Petrovsky-VIP. This is due to the conditions of these types of deposits, namely the absence of monthly capitalization of interest, or a large amount of the deposit, as, for example, in Petrovsky-VIP.
It can be seen that a special place in the line of deposits is occupied by deposits aimed at pensioners. Thus, we can conclude that Bank Petrovsky OJSC offers a wide range of deposits that are aimed at various market segments. At the same time, special attention is paid to pensioners, for whom a line of deposits is provided that allows them to take into account their interests. A special allocation of deposits for pensioners is due to the fact that they are an important segment of depositors for Bank Petrovsky OJSC.
If we consider the additional conditions for deposits, given for each deposit separately in Appendix No. 1, we can trace the following trend in the use of such a criterion as prolongation. If there is a prolongation of the deposit in the terms of the agreement, then there is a significantly lower interest rate than for deposits without prolongation.
Analyzing the contributions (deposits) of JSC Bank Petrovsky, you can pay attention to the following:
when setting interest rates, the bank always ties deposits (deposits) to the investment period. So, for example, the interest rate of the “On demand” deposit is 0.15%, and the interest rate of the “Pension savings deposit” for 2 years is 12.5%;
the deposit amount is also tied to the interest rate. So, for example, the Petrovsky-accumulative deposit for 1 year and 1 day) in the amount of 1 to 700 tr. accepted at 13.25% per annum, and the same deposits in the amount of 700 tr. and above already under 13.70%;
the interest rate on ruble deposits is not lower than the inflation rate, which saves deposits from depreciation;
proceeding from the fact that income in the form of interest received by taxpayers on deposits in banks is not subject to taxation if:
interest on ruble deposits is paid within the amounts calculated based on the current refinancing rate of the Bank of Russia (10%), increased by five percentage points ,
the established rate does not exceed 9 percent per annum for deposits in foreign currency;
it can be noted that all the proposed deposits are not subject to taxation (the exception is Petrovsky - VIP).
For legal entities Bank Petrovsky OJSC offers its clients various options for placing temporarily free funds for various periods:
· term deposits in Russian rubles and foreign currency;
· Promissory notes of Bank "Petrovsky" in Russian rubles and foreign currency.
The Bank offers legal entities a medium-term financial instrument - a bank deposit.
The deposit agreement certifies the amount of the deposit made to the Bank and the depositor's right to receive, after the expiration of the established period, the amount of the deposit and the interest stipulated in the agreement. Payment of interest on the deposit is made monthly or lump sum after the expiration of the contract. A fixed interest rate is set for the entire term of the deposit. The Bank cannot unilaterally reduce or increase the interest rate stipulated in the agreement. Interest rates are set depending on the terms of placement of funds. Accordingly, the rate depends on the amount and term of the deposit. If the depositor demands the return of the deposit amount before the expiration of the contract, interest is paid at a rate of 0.01% per annum.
2.3 Analysis of the deposit portfolio
The main goal of the deposit policy of Bank Petrovsky OJSC is to attract the optimal amount of funds (by terms and currencies) necessary and sufficient to operate in the financial markets, provided that the minimum level of costs is ensured.
Attracting resources is carried out in the course of specific operations provided for by the current banking licenses. At the same time, the main instruments used by Bank Petrovsky OJSC to attract resources are:
o opening and maintaining accounts of legal entities and individuals, involving the receipt of funds on these accounts;
o opening and maintaining accounts of other banks, involving the receipt of funds into these accounts.
The list of instruments for raising funds can be expanded in the course of further banking activities. In the course of conducting deposit operations, the Bank's divisions are guided by the legislation of the Russian Federation, the regulations of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, the Charter of the Bank, this Document and internal documents regulating the technical procedure and conditions for conducting specific types of banking operations. If we trace the dynamics over several years, we can note a steady increase in the balances on the accounts of legal entities (Figure 11):

Figure 11 Dynamics of account balances of legal entities of Bank Petrovsky OJSC
We will analyze the deposits of individuals using table No. 2:
Analysis of the deposit portfolio of JSC "Bank" Petrovsky "in 2008 (according to the maturity of investments)
| No. p / p | Name of the article of the PDS | Balance account | The value of MPS, thous. rub. | PDS structure, in % | Changes over the period (+/-) | |||
| on 1.01.0 8 G. | on 1.01.0 9 G. | on 1.01.0 8 G. | on 1.01.0 9 G. | in thousand rubles | V% | |||
Deposits (D), total including: |
Σ item 1 - 7 | 19270123.00 | 18033769.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | -7% | ||
| I. | Demand deposits (Dvostr), total | 410-423(01), 42309, 425-426 (01), 42609 | 290832.00 | 1 | 2 | 40013 | 15.9 | |
| II. | Term deposits (Ds), total | 17742937.00 | 99 | 98 | -6.8 | |||
| 1. | for up to 30 days | 410-423(02), 42310, 425-426 (02), 42610 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| 2. | for a period of 30-90 days | 410-423 (03), 42311, 425-426 (03), 42611 | 445687 | 1109708 | 2 | 6 | 148 | |
| 3. | for a period of 91-180 days | 410-423(04), 42312, 425-426 (04), 42612 | 2247860 | 3590845 | 12 | 20 | 1342985 | 59.7 |
| 4. | for a period of 181 days to 1 year | 410-423(05), 42313, 425-426 (05), 42613 | 5946184 | 5155936 | 31 | 29 | -790248 | -13.3 |
| 5. | for a period of 1 to 3 years | 410-423(06), 42314, 425-426 (06), 42614 | 10379573 | 7886448 | 54 | 43 | -2493125 | -24.1 |
| 6. | for a period of more than 3 years | 410-423(07), 42315, 425-426 (07), 42615 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
Such an analysis makes it possible to identify the features of the bank's deposit policy and to determine in general the approximate terms for placing the bank's resources. In particular, the results of the analysis allow us to draw a conclusion about the attraction of resources in terms of their cost (“expensive” / “cheap”): time deposits are much more expensive than balances on demand accounts.
Additionally, to formulate the final conclusion on the analysis of deposits by maturity, it is advisable to calculate the following indicators:
The coefficient of urgency of the structure of deposits (d in D):
d in D = Ds/D, where Ds is the volume of time deposits; D is the total volume of deposits.
As of 01.01.2008 98%
As of 01.01.2009 98%
A high rate of maturity of the structure of deposits characterizes the degree of constancy and stability of the resource base.
In general, the growth in the share of term deposits in the total amount of bank deposits should be assessed positively, because. time deposits as the most stable component of the deposit portfolio provides at an acceptable level and allows to increase the bank's liquidity and conduct operations for the placement of resources for longer periods.
The share of term deposits (Ds) in the total amount of liabilities (P): d = Ds/P.
As of 01.01.2008 38.5%
As of 01.01.2009 21.4%
Commitment Structure Ratio (KSO): KSO = Dvostr./Ds.
As of 01.01.2008 1.3%
As of 01.01.2009 0.1%
The indicator characterizes the stability of the bank's financial resources. The lower the value of the indicator, the lower the relative need of the bank for liquid assets, due to the structure of liabilities.
Figure 12 shows that the largest volume of attracted funds falls on deposits with a term of more than 181 days and more than a year.

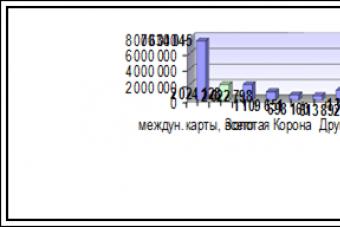
Figure 12 Structure of deposits of JSC "Bank "Petrovsky" by terms as of 01.01.2009
Starting from 2005 JSC Bank Petrovsky has been steadily increasing its deposit portfolio, as can be seen in Figure 13. 
Figure 13 Dynamics of balances on accounts of individuals
The banking crisis of October 2008 shook the stability of the bank, but today everything has stabilized
2.4 Organization of the formation and implementation of the deposit policy
The deposit policy of JSC Bank Petrovsky is closely connected with the credit and interest rate policy of the bank, being one of the elements of the banking policy as a whole.
The deposit policy is formed with the allocation of the following
Setting goals and defining objectives of the deposit policy;
Allocation of the relevant departments involved in the implementation of the deposit policy, the distribution of the powers of employees;
Development of the necessary procedures and technical procedures for conducting banking operations that ensure the attraction of resources;
Organization of control and management in the process of banking operations aimed at attracting resources.
When forming the deposit policy, the following specific principles are taken into account:
Principles for ensuring the optimal (taking into account the subsequent receipt of income from the allocation of resources) level of costs;
The principle of security of conducting deposit operations and maintaining the reliability of the bank.
Compliance with the above principles allows the Bank to form both strategic and tactical directions in the organization of the deposit process, thereby ensuring the efficiency and optimization of the deposit policy.
The deposit policy of JSC Bank Petrovsky is based on:
Subjects of deposit relations (in relation to individuals and legal entities);
Banking instruments used to attract resources;
Terms of attracting resources (short-term, medium-term and long-term deposit policy);
Purposes of attracting (for investing, lending, maintaining current liquidity);
Aggressiveness in matters of attracting resources and related pricing policy and the degree of risk of ongoing operations.
The deposit policy of JSC Bank Petrovsky provides for:
analysis of the deposit market;
o identifying target markets to minimize deposit risk;
o minimization of expenses in the process of attracting funds;
o optimization of deposit portfolio management in order to maintain the required level of the bank's liquidity and increase its stability.
JSC Bank Petrovsky, when conducting its deposit policy, takes into account the following factors:
Changes in tax legislation;
The current state and trends of the financial market, both in terms of attracting and allocating resources;
Changes made to the calculation of banking standards;
Change in the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation;
Limits, control figures set by the Bank itself for ongoing banking operations.
The implementation of the Bank's deposit policy is carried out in the course of specific banking operations, allowing to raise funds. At the same time, JSC "Bank" Petrovsky "conducts deposit operations, that is, attracts funds on the terms:
o recurrence;
o urgency;
o payment (when it is provided by the relevant agreements);
o publicity (regarding the conditions for raising funds).
The main principle of the Bank's work in the course of deposit operations is to ensure the amount of resources required for the normal functioning of the Bank, achieved at minimal cost for their purchase.
The main principle is achieved by diversifying the portfolio of attracted financial resources according to the sources of their attraction and structure, linking the volume and structure of these resources (by currency and maturity) to the volume and structure of assets.
An obligatory requirement in determining possible conditions for attracting resources is a preliminary analysis of possible directions for spending attracted resources with an assessment of financial results and structural changes as a result of proposed banking operations.
The main direction of the deposit policy of "Bank" Petrovsky "is the opening and maintenance of accounts of individuals.
The balances of funds on the accounts of individuals - clients of the bank make up a large part of the total volume of funds attracted by the bank. Nevertheless, the issue of intensifying work with individuals is supposed to be given increased attention.
The bank's policy in working with individuals is based primarily on working with a wide range of individuals, which is facilitated by a developed network of branches. Another block of clients are employees of organizations and enterprises that are the Bank's clients. The Bank opens and maintains accounts of individuals in rubles and foreign currency on the basis of existing agreements, which differ depending on the urgency of the accounts.
The pricing policy of the Bank in working with clients - individuals, provides for:
No fee for balances of funds held on current accounts of individuals.
Availability of a fee for balances of funds held on time (deposit) accounts of individuals, the amount of which is determined based on the basic conditions for raising funds approved by the Management Board of the Bank.
The Bank is taking measures aimed at increasing the share of term resources in the total amount of funds on the accounts of individuals, which is served by the Bank's interest rate policy, which provides for the creation of competitive conditions for attracting funds from individuals. This is how the bank conducts the bonus program "Premium Interest" for regular depositors.
The inflow of funds from individuals is directly or indirectly facilitated by additional services provided by the Bank to individuals. Among these services is the issuance and maintenance of plastic cards, money transfers, payment of utilities, rent of safe boxes.
Another important direction of the deposit policy of JSC "Bank" Petrovsky "is the opening and maintenance of accounts for legal entities.
The main source of formation of the Bank's resource base is the balance of funds on the accounts of legal entities - the Bank's clients.
The Bank's policy in dealing with legal entities is primarily based on working with the Bank's existing customers, as well as on attracting new ones.
Improving the sustainability of the Bank's resource base (in terms of volume and timing) should be facilitated by:
Business development by existing clients of the Bank;
Opening accounts with the Bank by organizations and enterprises - counterparties and partners of the existing customers of the Bank;
Accumulation of financial flows related to the implementation of programs and projects implemented with the participation of the Bank's clients.
The Bank opens and maintains accounts of legal entities in rubles and foreign currency on the basis of existing agreements. The pricing policy of the Bank in working with clients - legal entities, provides for the absence of payment for the balances of funds held on settlement accounts of legal entities, except for the cases of setting an individual fee for balances on the accounts of enterprises and organizations.
Given the increasing demands from the Central Bank of the Russian Federation regarding
increasing the level of liquidity, expressed in the need for daily compliance with banking standards, as well as striving to balance resources with assets by maturity, the Bank takes measures aimed at increasing the share of term resources in the total amount of funds on the accounts of legal entities. These activities involve personal work with specific clients, involving:
Tracking the movement of funds on the accounts of clients - legal entities, selecting, on the basis of the information received, the most promising clients in terms of forming an urgent resource base on the basis of the database of clients;
Creation of conditions for clients - legal entities, stimulating the transfer of part of the funds from current accounts to urgent accounts;
Timely informing clients - legal entities about the new terms of customer service.
As part of solving the tasks of expanding the circle of legal entities served by the Bank, increasing the Bank's resource base at the expense of funds accumulated on the accounts of legal entities, priority is given to creating conditions for customers that facilitate the inflow of financial resources to the Bank. Such conditions may include the Bank's competitive tariff policy compared to other banks, the Bank's flexibility in setting fees for borrowed funds, favorable service conditions for customers, including obtaining loans, the possibility of remote customer service through the Client-Bank system, etc. Further.
Chapter 3. Improving the deposit policy
3.1 Tools for improving the deposit policy of Bank Petrovsky OJSC
2008 was a difficult year for the banking system worldwide. Despite the assumptions and forecasts of a number of experts, the financial crisis also affected Bank Petrovsky OJSC. Despite the problematic situation in the banking market, OJSC Bank Petrovsky continued its development. According to the results of September 2009, the bank completely overcame all difficulties and achieved high financial results.
One of the problems that commercial banks are currently facing is the formation of a resource base. The resource base has a direct impact on the liquidity and solvency of a commercial bank. The very scale of a commercial bank's activity, and, consequently, the amount of income it receives, strictly depends on the size of the resources that the bank acquires in the market of various resources and, in particular, deposits. Hence there is a competitive struggle between banks for attracting resources.
The formation of a resource base, which includes not only attracting new clients, but also a constant change in the structure of sources for attracting resources, is an integral part of the flexible asset and liability management of a commercial bank. Effective liability management involves the implementation of a competent deposit policy. The specificity of this area of activity is that in terms of passive operations, the choice of a bank is usually limited to a certain group of clientele, to which it is attached much more strongly than to borrowers.
The limited resources associated with the development of banking competition leads to close attachment to certain clients. If the circle of these clients is narrow, then the bank's dependence on them is very high. Therefore, in our opinion, in order to strengthen the resource base, banks need a balanced deposit policy, which is based on maintaining the required level of diversification, ensuring the possibility of attracting funds from other sources and maintaining a balance with assets in terms of terms, volumes and interest rates.
In order to expand the resource potential of Bank Petrovsky OJSC, it is necessary to intensify its deposit policy. In this regard, one of the priority areas of the bank's work should be the gradual increase in the deposit portfolio through a competent deposit policy aimed, in particular, at expanding the list of deposits available to customers, introducing new types of services for their convenience.
The deposit policy of JSC Bank Petrovsky should take into account the needs of all social and age groups of citizens - working and retired people, youth and middle-aged people, and should also be designed for people with different income levels.
With each client, OJSC Bank Petrovsky should strive to establish long-term partnerships. To this end, the bank must anticipate the development of customer needs, develop and offer a full range of banking products and services.
Thus, Bank Petrovsky OJSC could offer a new type of deposit for accumulating funds for education or a gift to a child. The minimum initial deposit is 10,000 rubles. The deposit is opened for a year, with the accrual of 13% per annum in rubles and with the possibility of additional investment. If at the end of the term the deposit amount and the interest due remain for the next term on the same type of deposit, then the client will have the opportunity to receive a bonus of 0.5% to the interest rate in force at the time of prolongation for this type of deposit. It is possible to conduct promotions and give prizes to active investors.
In order to attract the younger generation of its clients, Bank Petrovsky could add new types of deposits to the list of deposits targeted at this group of the population, for example, offer a deposit for students. It is proposed to introduce the following conditions for this deposit: deposit term - 1 year (fourfold prolongation), opening only with a student card, a plastic card is opened for the deposit and interest is transferred to it monthly, an increase to the scholarship is obtained. In order to ensure the influx of depositors to this type of deposit, it is advisable, in our opinion, to introduce some incentives that are attractive to potential customers among the young population (for example, store discount cards).
For the greatest interest of clients and the inflow of deposits, Bank Petrovsky OJSC can offer payment of interest on deposits placed in advance in order to compensate for inflationary losses. In this case, the investor, when placing funds for a certain period, immediately receives the income due to him. However, if the agreement is terminated ahead of schedule, the bank will recalculate the interest on the deposit and the overpaid amounts will be deducted from the deposit amount. In addition to expanding the range of deposits, in order to improve the deposit policy, the bank is invited to master the issue of securities, namely, savings certificates. Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs will be able to purchase a certificate of deposit. The minimum amount of a deposit issued by a certificate of deposit is 100,000 rubles. The maximum period for which a certificate of deposit is issued is 2 years. A certificate of deposit is issued on the basis of a bank deposit agreement. Interest on the certificate is paid simultaneously with its redemption.
Payment for the certificate is carried out by the bank upon the date of claiming the amount on it on the basis of an application for payment and upon presentation of a certificate of deposit.
The deposit certificate can be presented for payment ahead of schedule. In case of early presentation of the certificate for payment, the bank pays the amount of the deposit and interest paid on the demand deposit, valid at the time of presentation of the certificate for payment.
Thus, when developing a deposit policy, a bank should be guided by certain criteria for its improvement, among which are the following:
- the relationship of deposit, credit and other operations of the bank to maintain its stability, reliability and financial stability;
– diversification of bank resources in order to minimize risk;
– segmentation of the deposit portfolio (by clients);
– differentiated approach to different customer groups;
– competitiveness of banking products and services.
These are some of the possible ways to improve the deposit policy of JSC "Bank" Petrovsky "and increase its role in ensuring its sustainability. In conclusion, we can say that each bank develops its own deposit policy, determining the types of deposits, their terms and interest on them, the conditions for conducting deposit operations, while relying on the specifics of its activities and taking into account the factor of competition from other banks and inflationary processes occurring in economy.
3.2 The deposit insurance system in the Russian Federation and its improvement
Attracting funds from legal entities and individuals, operations on deposit accounts are one of the main activities for banks. At the same time, bank failures result in depositors losing their money. The guarantee of safety of the bank deposit in such cases can be provided through the mechanism of deposit insurance.
One of the manifestations of the stabilization of the Russian economy is a pronounced upward trend in real incomes of the population, respectively, its savings potential. Monetary savings of citizens are an important reserve for increasing the resource base of the banking sector, which is so necessary to expand its investment opportunities. Therefore, the task of intensifying the process of mobilizing financial resources of individuals into deposits is of macroeconomic importance for our country.
According to leading domestic and foreign experts, the main factor hindering the successful solution of the problem under consideration is the low level of public confidence in commercial banks. To change this situation, the Government of the Russian Federation and the Bank of Russia adopted a whole range of measures. Among the most important of them, it is legitimate to include the introduction of a legislative framework for deposit insurance. This federal law provides the necessary legal framework for the centralized protection of the interests of depositors, establishes the organizational basis for the deposit insurance system, and regulates legal and financial relations arising in the course of its operation.
Independent experts and representatives of the banking community unanimously note its positive impact on the development of the savings business in modern Russia. At the same time, the analysis of the results of the functioning of the system made it possible to state the presence of a number of unresolved and controversial issues. They concern the conceptual apparatus, the general methodology of compulsory deposit insurance, its application mechanisms, and finally, the functions and powers of the Agency that manages this system.
The deposit insurance system is a set of measures aimed at protecting deposits and ensuring their guaranteed return in full (or in part) in the event of bankruptcy of a financial institution. The insurance system is based on the following principles:
Mandatory participation in the deposit insurance system;
Reducing the risks of adverse consequences for depositors in the event that banks fail to fulfill their obligations;
Transparency of the deposit insurance system;
The accumulative nature of the formation of the mandatory deposit insurance fund at the expense of regular contributions from banks participating in the deposit insurance system.
Nevertheless, the main factor determining the type of deposit protection system is the economic level of the country's development: the degree of development of the monetary system, the share of state ownership in the banking sector, as well as the possibility of a banking crisis, which is an important incentive to introduce a more effective deposit protection mechanism. .
The most important factor in the redistribution of funds between banks, of course, is the interest rate policy of banks. The introduction of any improved new guarantees will lead to a decrease in interest rates on deposits in commercial banks, and high interest rates will remain only in the most risky and aggressive banks that need additional funds, the stimulation of which is by no means among the tasks of creating a new system.
Amendments were made to the current federal law on deposit insurance in order to improve the efficiency of the deposit insurance system for individuals and increase public confidence in banks. Let us consider the improvement of the criteria and mechanisms for monitoring the compliance of banks with the requirements for participation in the deposit insurance system after the amendments made in 2008:
An inaccuracy has been eliminated, according to which the established requirements for banks participating in the deposit insurance system applied only to banks that, on the day this Federal Law came into force, had permission to attract funds from individuals as deposits and to open and maintain bank accounts of individuals. According to the new wording, not only banks that have the appropriate permission from the Bank of Russia, but also applicants for its issuance, must satisfy.
In addition, the requirements for banks participating in the deposit insurance system have been clarified. Previously, it was envisaged that a bank could become a participant in the deposit insurance system if it simultaneously met the following conditions:
Accounting and reporting of the bank are recognized by the Bank of Russia as reliable;
The Bank complies with the mandatory ratios established by the Bank of Russia;
The financial stability of the bank is recognized by the Bank of Russia as sufficient;
The bank is not subject to the measures provided for by banking legislation, and there are no grounds for their application (including the imposition of a ban on certain banking operations, the collection of fines from a credit institution, the implementation of measures to prevent bankruptcy).
Another requirement has been added: compliance by the bank with the established procedure for disclosing to an unlimited circle of persons information about persons that have a significant (direct or indirect) influence on decisions made by its management bodies. At the same time, the Bank of Russia is obliged to make a decision on the introduction of a ban on accepting deposits of funds from individuals if the bank does not meet the stipulated requirements within a certain period. Thus, in particular, it was established that the bank does not meet the requirements for participation in the deposit insurance system in cases where:
The bank's accounting and reporting are recognized by the Bank of Russia as unreliable for three consecutive months;
The Bank fails to comply with one and the same mandatory ratio from among those established by the Bank of Russia for six months in a row. Failure to comply with the mandatory ratio in the reporting month is its violation in the aggregate for six or more business days during this month;
In addition, the Bank of Russia has the right to make a decision to impose a ban on taking deposits from individuals in cases where:
1) the accounting and reporting of the bank are recognized by the Bank of Russia as unreliable;
2) the bank fails to comply with the same mandatory ratio from among those established by the Bank of Russia for two consecutive months;
3) the bank has been rated “unsatisfactory” for two months in a row for the same group of indicators (assessments of capital, assets, liquidity, as well as assessments of the quality of management of the bank, its operations and risks).
4) if the bank has an “unsatisfactory” rating for the same group of indicators (assessments of capital, assets and liquidity) for six reporting monthly dates in a row or for two reporting quarterly dates in a row;
5) if the bank has an “unsatisfactory” rating for a group of indicators for assessing the quality of bank management, its operations and risks, as well as with regard to the procedure for disclosing information to an unlimited circle of persons about persons that have a significant (direct or indirect) influence on decisions made by its management bodies , three consecutive months;
6) if the bank has an “unsatisfactory” rating for a group of indicators for assessing profitability for two reporting quarterly dates in a row.
Also, banks are obliged to keep records not only of the bank's obligations to depositors, but also of the bank's counterclaims to the depositor. Maintaining such records ensures the bank's readiness to form, upon the occurrence of an insured event, as well as on any day at the request of the Bank of Russia (within seven calendar days from the date of receipt of the specified request by the bank), a register of the bank's obligations to depositors. The register is formed in the manner and in the form established by the Bank of Russia at the suggestion of the Agency. The composition of deposits subject to mandatory insurance has been specified. Thus, this composition excludes funds placed on bank accounts (deposits) of lawyers, notaries and other persons, if such accounts are opened for professional activities.
The circle of persons entitled to receive compensation on deposits after the occurrence of an insured event was expanded, namely, the heirs of the depositor. The heir has the right to exercise the rights of the deceased contributor from the moment the heir is issued an appropriate certificate of the right to inheritance or another document confirming his right to the inheritance or the right to use the testator's funds.
In addition, a new rule has been introduced with respect to additional funds received on a deposit (to an account) after the Bank of Russia introduced a ban on attracting funds from individuals to deposits. Such funds (with the exception of interest accrued in accordance with the terms of the agreement) are not credited to the deposit (to the account), but are subject to either return to the persons who instructed to credit funds to the deposit (to the account), or, at the request of an individual, are transferred to an account of the same individual opened with another bank registered in the deposit insurance system.
According to the amendments made, the Agency was entrusted with the functions of a bankruptcy trustee (liquidator) in case of bankruptcy of credit institutions. In addition, it is envisaged that the Agency will be empowered to carry out transactions for the sale of property (collateral), which is security for the fulfillment of obligations of credit institutions - counterparties of the Bank of Russia.
From the foregoing, we can conclude that the main reason for improving the deposit insurance mechanism in the Russian Federation is the financial unreliability of most of the existing financial institutions and the enormous losses of the population from the collapse of the largest private banks during the unstable financial situation of the country's economy.
As is known, the most severe consequence of banking crises in various countries was a total crisis of public distrust in the banking system. It is quite obvious that no administrative measures can force the population to keep free money in banks. We need economic measures and the creation of adequate regulatory and legal support for the functioning of the system for protecting bank deposits. Under these conditions, the issue of creating a system to protect citizens' deposits from the risk of being lost comes to the fore in the implementation of measures to restore public confidence in banks. Political and economic instability are the result of:
Decrease in savings activity and increase in consumption at the expense of savings funds, with a drop in interest in income received on deposits in the form of interest;
Decreased activity of the population in investing in securities;
Transfer of funds from the ruble zone to the currency zone.
Therefore, in our opinion, the modern Russian state faces important tasks of improving the insurance system, concerning, firstly, stimulating economic growth and, secondly, increasing the level of protection of the rights and legitimate interests of a person and a citizen.
Thus, it is worth noting that for our country, in the conditions of general economic instability, inflation, a huge budget deficit, the creation of many banks, the reorganization of the banking system, etc. with all the acuteness the question arises of improving the insurance of banking activities, ensuring the interests of bank customers.
In conclusion of this issue, it must be said that the reliability of commercial banks is one of the decisive elements of their activities, and one of the important measures to ensure reliability is deposit insurance, which is used in all countries with highly developed banking systems. In this regard, the banking system needs to significantly increase the confidence of potential depositors in the full and timely return of funds entrusted to the bank. This will contribute to the solution of the important task of involving financial resources in the economy that the population currently has in the form of ruble and foreign currency cash worth many tens of billions of dollars.
Conclusion
Today, commercial banks are able to offer customers a variety of banking products and services. All banks in the Russian Federation are universal in their specifics. There is a certain basic set, without which the bank cannot exist and function normally. Among them, preference is given to attracting and placing temporarily free funds of clients in deposits.
Deposits are an important source of resources for commercial banks. Deposit accounts can be very diverse and basically their classification can be based on criteria such as sources of deposits, their intended purpose, degree of profitability, etc.
The attracted resources are important for banks, since it is through them that banks cover the largest share of their needs for funds, which averages 40% of the total resources of a commercial bank.
At the same time, one cannot but say that such a source of formation of banking resources as deposits has some disadvantages. We are talking about the significant material and monetary costs of the bank when attracting funds to deposits, limited free cash. In addition, the mobilization of funds for deposits depends to a large extent on the clients, and not on the bank itself. Therefore, the competition between banks in the market of credit resources forces them to take measures to develop services that help attract deposits. For these purposes, it is important for commercial banks to develop a deposit policy strategy based on their goals and objectives. Strengthening the deposit base is very important for banks. By increasing the total volume of deposits and expanding the circle of depositors of legal entities and individuals, it is possible to improve the organization of deposit operations and the system for stimulating the attraction of deposits.
In the course of writing the work, the activities of a specific subject of the banking system - Bank Petrovsky OJSC in the field of deposit operations were studied.
Analyzing the deposit market, it is possible to identify a growth trend in the share of deposits of legal entities and individuals in the total liabilities of the banking sector, their share has been steadily growing during 2005-2008.
As for the activities of Bank Petrovsky OJSC, both positive and negative trends can be noted here. The positive aspects in the work of the bank include the ever-expanding client base, capital and borrowed funds. However, in the structure of attracted funds, it is necessary to pay more attention to funds raised from legal entities, since it is deposits that are currently the most promising liabilities and a priority for banking growth.
As of January 1, 2009, deposits of legal entities accounted for approximately 24.2% of the total volume of deposits, which is three orders of magnitude less than deposits of individuals. This is due to the peculiarity of the deposit policy of JSC "Bank" Petrovsky ": not to involve in the service of the possible placement of funds from the client's current or current account in the bank into a term deposit, it is much more convenient and profitable for the funds to be free of charge on the current account, or, in the last resort case - monthly accrual of interest on average daily account balances. And if we take into account that there is such a thing as a comprehensive customer service (the presence of a current account, the Bank-Client system, a salary project, a business account and other services), which implies an increase in the interest rate by several points when using the term deposit service together with another service bank, we can conclude that the chances of a savings bank to attract this client are practically zero.
The volume of funds attracted in deposits from organizations has a positive trend over the past years. This is due to the growth in income of enterprises and the development of customer business.
The interest rate policy is an integral part of the formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank. This consists in observing a number of principles on which the optimal interest rate policy of the bank should be based. Among them, first of all, it is necessary to name the principle of differentiation of interest depending on the period of storage and the size of savings, the principle of "social" differentiation of interest on deposits, the principle of ensuring the profitability of banking activities and the principle of preserving and protecting the savings of depositors. When forming an effective interest and deposit policy of a bank, a combination of all these principles is required.
The policy in the field of attracting free cash in deposits for both legal entities and individuals in Bank Petrovsky OJSC, despite the uniform growth from year to year, should be constantly improved.
A study of the theoretical foundations of the deposit policy and an assessment of the current situation in the field of attracting funds in the conditions of the current financial crisis in deposits made it possible to develop a number of proposals and recommendations for improving the deposit policy.
Thus, in order to strengthen the deposit base and expand the resource potential, the bank is offered:
1) Expand the list of existing deposits, focusing on different segments of the population with different income levels. In this regard, a number of new contributions have been proposed.
2) Take measures to minimize the negative impact of unforeseen withdrawal of term deposits by the population.
3) To pay interest on placed deposits at a rate corresponding to the period of keeping funds in the account in order to compensate for inflationary losses for the client
The reliability of commercial banks is one of the decisive elements of their activity, and one of the important measures to ensure reliability is deposit insurance, which is used in all countries with highly developed banking systems. In this regard, the banking system needs to significantly increase the confidence of potential depositors in the full and timely return of funds entrusted to the bank.
For our country, in conditions of general economic instability, inflation, a huge budget deficit, the creation of many banks, the reorganization of the banking system, etc. with all the acuteness the question arises of improving the insurance of banking activities, ensuring the interests of bank customers.
Summing up, it should be noted that each bank develops its deposit policy on its own, determining the types of deposits, their terms and interest on them, the conditions for conducting deposit operations, while relying on the specifics of its activities and taking into account the factor of competition from other banks and inflationary processes occurring in economics.
Bibliography
1. "On banks and banking activities in the Russian Federation" Federal Law of the Russian Federation dated 02.12.1990 No. 395-1
2. Civil Code of the Russian Federation
3. "On the mandatory ratios of banks": Instruction of the Bank of Russia dated January 16, 2004 No. 110-I
4. "On the required reserves of credit institutions": Regulation of the Bank of Russia dated March 29, 2004 No. 255-P
5. “On the Procedure for Calculating Interest on Operations Associated with Raising and Placement of Funds and Recording These Operations in Accounts”: Bank of Russia Regulation No. 39-P dated June 26, 1998
6. "On Deposit and Savings Certificates of Credit Institutions": Regulations of the Bank of Russia dated 10.02.1992. No. 14-3-20 dated February 10, 1992 No. 14-3-20 as amended. letters of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated 12/18/92. #23
7. “On the Methodology for Calculating Equity (Capital) of Credit Institutions”: Letter of the Bank of Russia dated 16.12.1998. No. 363-T.
8. Federal Law No. 395-1-FZ of December 2, 1990 "On banks and banking activities" (as amended)
10. Federal Law No. 86-FZ of July 10, 2002 "On the Central Bank of the Russian Federation10 (Bank of Russia)" (as amended)
11. Federal Law No. 177-FZ of December 23, 2003 "On insurance of deposits of individuals in banks of the Russian Federation"
12. Federal Law No. 158-FZ of July 22, 2008 “On Amendments to Chapters 21, 23, 24, 25 and 26 of Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Certain Other Acts of the Legislation of the Russian Federation on Taxes and Fees”
13. Federal Law No. 48-FZ of March 11, 1997 “On a transferable and promissory note”
14. Regulation of the Bank of Russia No. 255-P dated March 20, 2004 "On the required reserves of credit institutions" (as amended)
15. Banking: Textbook / ed. G. N. Beloglazova, L. P. Krolivetskaya, 5th edition revised and enlarged, Moscow, “Finance and Statistics”, 2008.- 478p.
16. Banking operations / edited by Yu.I. Korobov.-M.: Master, 2007.-446s.
17. Banking operations: Textbook / edited by A. V. Pechnikov, O. M. Markov, E. B. Starodubtsev, Moscow, 2009.- 284p.
18. Banking operations: textbook / team of authors; under the editorship of O.I. Lavrushin.-M.: KNORUS, 2007.-384p.
19. Banking: Textbook. - 2nd ed., revised. and additional / Ed. O.I. Lavrushina.-M.: Finance and statistics, 2005. - 576 p.
20. Banking: textbook / edited by Doctor of Economics, Prof. G. G. Korobova.
21. Beloglazova G.N., Krolivetskaya L.P. Banking. Organization of the activities of a commercial bank: textbook.-M.: Higher education, 2008.- 422p.
22. Velieva I., Volkov S. "Time to collect money" // Expert No. 11 (650) dated 03/23/2009
23. Glushkova N.B. Banking: Textbook - M., Academic project, 2005.-210s.
24. Zharkovskaya E.P. Banking: a textbook for university students.- M., Omega-L, 2008.-480 p.
25. Sheremet A.D., Saifulin R.S.. Methods of financial analysis. - M., INFRA-Moscow, 2007.-376p.
26. Internet site of the DIA: http//www.asv.org.ru/guide (section "Contributor's Guide")
27. Internet site: http://www.rbcdaily.ru
28. Internet site: http://www.petrovskiybank.ru/
29. Internet site: http :// www . consultant . en
30. Internet site: http://bankrange.ru/
Application No. 1
AGREEMENT No. ______________
ABOUT DEPOSIT "DEMAND"
St. Petersburg "_________" _______________ 200___
1. SUBJECT OF THE CONTRACT
1.1. The subject of the agreement is the relationship of the parties regarding the acceptance of funds on deposit, the payment of interest and the return of the deposit on the terms and in the manner prescribed by this agreement.
2. PROCEDURE FOR CALCULATION AND PAYMENT OF INTEREST
2.1. The BANK opens an account for the DEPOSITOR __________________
2.2. For the use of funds, the BANK pays the DEPOSITOR __________________% per annum. Deposit term: on demand.
2.3. Interest on the deposit amount is accrued from the day following the day of its receipt by the BANK, until the day preceding its return to the DEPOSITOR, or its debiting from the DEpositor's account for other reasons. In this case, the actual number of calendar days in a year (365 or 366 days, respectively) is taken as the basis for calculation.
2.4. Interest accrued during the calendar year is added to the balance of the deposit, increasing its amount, on the last working day of the current year.
2.5. When paying in cash from a deposit in foreign currency, amounts less than the minimum denomination of banknotes of the corresponding currency are paid to the DEPOSTER in the currency of the Russian Federation at the rate established by the Central Bank of Russia on the date of payment.
3. RIGHTS AND OBLIGATIONS OF THE PARTIES
3.1. The INVESTOR has the right:
3.1.1. Make credit and debit transactions on the deposit, both in cash and non-cash. It is possible to replenish the deposit by third parties.
3.1.2. Unilaterally terminate the agreement and claim the amount of the deposit with the interest due.
3.1.3. Issue a power of attorney to a third party to dispose of the deposit and draw up a testamentary disposition of the rights to funds in the BANK.
3.2. INVESTOR is obliged:
3.2.1. Make a deposit in cash or by bank transfer in the amount of at least 10 (ten) rubles or the equivalent in foreign currency, not less than the minimum denomination of banknotes.
3.2.2. Do not use the "On Demand" deposit for making settlements related to entrepreneurial activities.
3.2.3. Reimburse the BANK for expenses arising from the execution by the BANK of the INVESTOR's instructions in accordance with the commission rates approved by the BANK.
3.2.4. Notify the BANK two working days in advance of the intention to claim from the deposit an amount exceeding 10,000 rubles or an equivalent in foreign currency as of the date of notification.
3.3.The BANK has the right:
3.3.1. During the term of the deposit, change the interest rate on the deposit. The new interest rate shall enter into force upon expiry of 10 days from the date of placement of the relevant notice on advertising stands in the BANK's premises.
3.3.2. Write off at the time of the operation from the DEPOSITOR'S account without acceptance the due fee for the BANK's services in accordance with the commission rates approved by the BANK.
3.4. The BANK is obliged:
3.4.1. Provide the DEPOSITOR with an account statement reflecting the movement of funds on the account when making income and expenditure transactions.
3.4.2. Observe the secrecy of the deposit in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
4. SPECIAL CONDITIONS
4.1. If the INVESTOR has a zero balance on the account within 12 (twelve) months from the date of the last transaction, the BANK has the right to consider this circumstance as a direct order of the INVESTOR to close the deposit account.
4.2. The savings book on the deposit is not issued.
CONTRACT TIME
5.1. This agreement comes into force from the moment of its conclusion and the deposit of funds and is valid until the account is closed at the request of the INVESTOR or until the circumstances specified in clause 4.1 occur. of this agreement.
5.2. This agreement is made in two copies, one for each of the parties, having the same legal force.
5. DETAILS, ADDRESSES AND SIGNATURES OF THE PARTIES
BANK : OJSC Bank Petrovsky:
191186 Saint-Petersburg, Nevsky pr., 26, c/c 30101810600000000809 at the Central Bank of the Bank of Russia for Saint-Petersburg, BIC 044030809,
TIN 7831000179, KPP 783501001, OKONKh 96120, OKPO 09801859, PSRN 1027800000568 SWIFT: PETR RU 2P
INVESTOR: FULL NAME ______________________ TIN
Date of Birth ___________________________
Postal code, address _____________________ Phone __________
Passport: series ________ number _______________ by whom and when issued _________________________________________________________________
Signature ___________________
Application No. 2
Deposit "PETROVSKY-UNIVERSAL"
The deposit accepts additional contributions in cash or by bank transfer. The frequency of making and the amount of additional contributions are not limited.
The deposit allows partial payments of amounts within 20% of the amount of funds in the account on the 1st day of the month in which the payment is made.
The deposit is subject to a 3-fold automatic prolongation of the deposit period without the personal presence of the depositor.
Interest on the deposit is paid on the date of return of the deposit of the main or extended term by adding it to the deposit amount. When claiming the deposit amount before the expiration of the main or extended term, interest for the period from the beginning of the term (main or extended) to the date of demand is charged at a rate of 0.05% per annum.
On the deposit, you can draw up a power of attorney and a testamentary disposition of the rights to the funds contributed by the depositor to the deposit.
Deposit "PETROVSKY - UNIVERSAL"
| 91-180 | 181-1 year | over 1 year up to 3 years | |
| amount, rub. | |||
| from 10,000 extra installment from 1 000 | 11,25 | 12,25 | 12,75 |
| from 500,000 additional contribution from 25 000 | 12,25 | 13,25 | 13,70 |
| from 1,000,000 additional contribution from 50 000 | 12,50 | 13,50 | 13,95 |
| amount, US dollars | |||
| from 300 extra installment from 50 | 5,00 | 6,00 | 6,15 |
| from 15,000 extra installment from 500 | 5,90 | 6,90 | 7,05 |
| 6,05 | 7,05 | 7,25 | |
| amount, euro | |||
| from 300 extra installment from 50 | 4,60 | 5,60 | 5,75 |
| from 15,000 extra installment from 500 | 5,50 | 6,50 | 6,65 |
| from 30,000 extra installment from 1 000 | 5,65 | 6,75 | 6,80 |
Deposit "PETROVSKY - CLASSIC"
With interest paid monthly or at the end of the deposit term
A term deposit agreement is concluded in writing by the depositor or his representative under a notarized power of attorney, which stipulates this right of the depositor's representative.
Deposits are accepted in rubles, US dollars or euros. The amount and term of the deposit can be any of the proposed setting ranges. The interest rate on the deposit depends on the amount and term of the deposit and is not subject to change during the main or extended terms.
Additional contributions to the contribution are not accepted. Payment of a part of the deposit with the preservation of the interest rate is not allowed. The deposit is subject to a 3-fold automatic prolongation of the term without the personal presence of the depositor with interest paid monthly.
Interest on the deposit is paid to the depositor's current account on the 1st day of each month and on the last day of the main or extended deposit term.
- with interest payment at the end of the deposit term
Interest on the deposit is paid on the date of return of the deposit of the main or extended term by adding it to the deposit amount.
When claiming the deposit amount before the expiration of the main or extended term, interest for the period from the beginning of the term (main or extended) to the date of demand is charged at a rate of 0.05% per annum. On the deposit, you can draw up a power of attorney and a testamentary disposition of the rights to the funds contributed by the depositor to the deposit.
Deposit "PETROVSKY-CLASSICAL"
| deposit term (inclusive), days | 31-90 | 91-180 | 181-1 year | over 1 year up to 3 years |
| interest rates on deposits (% per annum) with interest payment: | ||||
| rubles | at the end of the term | |||
| 1 000-100 000 | 9,20 | 12,75 | 13,75 | 14,25 |
| 100 000- 700 000 | 9,40 | 13,00 | 14,00 | 14,45 |
| from 700 000 | 9,60 | 13,25 | 14,25 | 14,70 |
| U.S. dollars | ||||
| 100-3 000 | 4,50 | 6,50 | 7,50 | 7,65 |
| 3 000-15 000 | 4,65 | 6,65 | 7,65 | 7,80 |
| from 15 000 | 4,80 | 6,80 | 7,80 | 7,95 |
| Euro | ||||
| 100-3 000 | 4,10 | 6,10 | 7,10 | 7,25 |
| 3 000-15 000 | 4,25 | 6,25 | 7,25 | 7,40 |
| from 15 000 | 4,40 | 6,40 | 7,50 | 7,55 |
| rubles | monthly | |||
| 1 000-100 000 | 8,20 | 11,75 | 12,75 | 13,25 |
| 100 000- 700 000 | 8,40 | 12,00 | 13,00 | 13,45 |
| from 700 000 | 8,60 | 12,25 | 13,25 | 13,70 |
| U.S. dollars | ||||
| 100-3 000 | 3,50 | 5,50 | 6,50 | 6,65 |
| 3 000-15 000 | 3,65 | 5,65 | 6,65 | 6,80 |
| from 15 000 | 3,80 | 5,80 | 6,80 | 6,95 |
| Euro | ||||
| 100-3 000 | 3,10 | 5,10 | 6,10 | 6,25 |
| 3 000-15 000 | 3,25 | 5,25 | 6,25 | 6,40 |
Attracted deposit funds (PDF) of the bank represent its "client" base in terms of the formation of the deposit base. In domestic banks, it is this component that occupies a significant part of the total funds raised. Thus, the analysis of the bank's deposit portfolio is a rather relevant topic in the situation of the global economic crisis, since the results of its implementation will allow taking timely measures to stabilize the activities of a particular bank and avoid default.
In this paper, the object of analysis will be the performance indicators of PrivatBank. The main areas of analysis of the bank's deposit portfolio can be represented as follows:
1) determination and analysis of the total value of the VAT, finding its share in the funds raised, assessment of the dynamics for the analyzed period.
As of 01.04.2008, the share of PDS in the total amount of attracted funds amounted to 78.299% (UAH 41,818.472 million). Comparing this figure with that of 01.04.2007, one can note an upward trend of 9.46% (by UAH 3,956.91 million).
The growth in the share of resources attracted from clients can be regarded as a positive development, as it contributes to the growth of the profitability of banking operations.
2) grouping and subsequent analysis of the PDS structure.
The analysis of MPS is carried out by groups characterizing the main sources of attracting bank resources. These groups are formed by the urgency of investments and by categories of investors.
To analyze the MPD in terms of the urgency of investments, it is advisable to form an analytical table 1.
Table 1.
Analysis of the deposit portfolio (by maturity of investments)
|
Article name |
Amount, in million UAH |
Structure, in % |
Deposits (D) total, including: |
Demand deposits |
Term deposits |
PDS/commitments |
Such an analysis of the PDS shows that term deposits make up the bulk of the deposit portfolio. However, there is a tendency to reduce its share in the total value of VAT: as of 01.04.2007, time deposits amounted to 66.815% in the total structure of deposits, and by 01.04.2007 they decreased by 2.205%. In terms of the cost of attracting resources, we can say that 65% of these resources are “expensive”.
In general, in absolute terms, there is an increase for the specified period by UAH 1,721.281 million. A positive moment in the composition of term deposits will be the growth of long-term resources, which will increase the terms of their placement. However, the amount of long-term assets should still be less than long-term liabilities. This is due to the fact that it is quite easy to increase the terms of loans issued and the average maturity of the loan portfolio. And to reduce the terms of placement of funds while reducing the terms of attracting resources is almost unrealistic. As a result, the bank may lose liquidity.
To formulate the final conclusion on the analysis of deposits by maturity, the following indicators are calculated (Table 2).
table 2
PDS usage indicators
|
Name of indicator |
· factor of urgency of structure of deposits (d in D). It is defined as the ratio of the volume of term deposits to the total volume of deposits.
The decrease in the share of term deposits in the total amount of the bank's deposits should be assessed negatively, since term deposits provide the bank's liquidity at an acceptable level and allow it to be increased, to carry out operations for the placement of resources for longer periods.
· share of term deposits in total liabilities d.
As can be seen from the calculations, an unfavorable situation has developed for the bank in terms of this coefficient, but there is a tendency to approach the recommended level. In the future, this will lead to an acceptable level.
· Liabilities Structure Ratio (LSC): the ratio of demand deposits to term deposits.
The calculated indicators of this ratio indicate that the relative need of the bank for liquid assets, due to the structure of liabilities, reaches a fairly high level. In addition, during the analyzed period, this need increased by 5.11%.
The analysis of PDS by depositors also makes it possible to identify the specifics of the bank's attraction policy (Table 3).
Table 3
The analysis showed that in the context of the category of depositors, the deposit portfolio of the bank is formed mainly at the expense of deposits of legal entities. The predominance of such deposits in the structure is a positive trend. For most banks, deposits of legal entities are cheaper than deposits of individuals. In addition, such attraction of funds is the least time-consuming type of banking operations.
It should be noted the growth of individuals' funds both in absolute value (by 1915.598 million hryvnia) and relative (by 13.12%), mainly due to the increase in their income.
Based on the results of the analysis, the following conclusion can be drawn. The growth of attracted funds is generally a positive trend, as it indicates the expansion of sources for active operations; attracting cheap resources by the bank; expanding the range of sources of these funds, including the use of term deposits. However, this situation can be accompanied by negative aspects. Here it is necessary to highlight the rise in the cost of attracted resources due to an increase in the volume of "expensive" resources, an increase in the volume of accounts payable, and an increase in the bank's outstanding obligations to its depositors and creditors.
Literature:
1. Sagitdinov M.Sh. On the issue of analyzing the activities of a commercial bank // Banking. - 2006, - No. 15
2. http://banker.ua
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Similar Documents
thesis, added 11/18/2009
Classification of deposit operations of commercial banks. Analysis of the formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank in the banking resource management system, ways of its optimization. Development of measures aimed at attracting deposit funds.
thesis, added 04/21/2011
Formation of deposit services of commercial banks. Analysis of the bank's marketing activities for deposit services. Opening and maintaining accounts of legal entities, attracting deposits from individuals. Issuance by the bank of its own debt obligations.
thesis, added 12/28/2015
Formation of the deposit policy of commercial banks in the banking resource management system. Analysis of the structure of deposits in the Russian Federation. Classification of deposit operations of commercial banks. Proposals for improving the deposit policy of UbrIR OJSC.
term paper, added 10/10/2011
Theoretical foundations for the formation of the deposit policy of commercial banks. Analysis of the state of the deposit services market. Development of proposals to improve the deposit policy of commercial banks. Deposit policy of OAO "Impexbank".
thesis, added 01/28/2004
Theoretical foundations for the formation and classification of the deposit policy of commercial banks. Analysis of the organization and accounting procedure for deposit operations on the example of JSC "Rosselkhozbank". Features and ways to improve the deposit insurance system in Russia.
thesis, added 02/28/2010
Theoretical foundations and essence of the deposit policy. Problems and prospects for the development of the resource base of banks in the Russian Federation. Elements of the deposit policy. The main stages of the formation of savings policy. Enlarged standard structure of the bank.
abstract, added 07/07/2014
The concept and place of deposits of the population in the resource base of the bank. Methodology for the analysis of the deposit portfolio. Contributions of the population: classification and characteristics. Problems and main prospects for attracting deposits by Russian banks of individuals' funds.
thesis, added 08/28/2014
Before starting to form the main directions of the deposit policy, it is necessary to analyze the composition and structure of the bank's deposit portfolio. Belarusbank was chosen as the analyzed bank, where, using the example of one of the branches, its activities to attract free cash in deposits will be considered. As you know, this bank is the legal successor of the former Savings Bank and it accumulates a significant part of the population's deposits. Therefore, most of the analysis is the consideration of deposits of the population.
First, let's consider the structure of household deposits in terms of the way they are withdrawn (see Tables 1 and 2).
These tables provide data on the ruble and foreign currency deposit portfolios of the bank on household deposits for three years. As shown, in 1997 ruble deposits were dominated by demand deposits, which accounted for 58.5% of the total amount of these deposits. The vast majority of these deposits are accounts to which the wages of the population are credited. The excess of demand deposits over time deposits by 17.3% indicates the low attractiveness of the latter, which is why the population left a significant part of the funds on current accounts.
As part of time deposits, the largest shares are occupied by deposits with terms of 6 months (12.97%) and 12 months and more (15.4%). This shows the propensity of the population to save for long periods of time. This was facilitated by acceptable interest rates, as well as relative stability in the economy. Attracting long-term resources by the bank helps to increase the stability of the resource base, increases the possibilities of long-term lending. Also of interest is the share of one-month deposits, which amounted to 7.23% of all ruble deposits of the population. They exceed deposits for a period of 3 months, which take only 5.57% of the attracted resources of the population. All this indicates that some depositors prefer to divert their funds only for a month, considering other, longer-term types of deposits unattractive, and possibly fearing changes in the economy.
It should be noted that there are savings certificates in the attracted funds. True, their share among deposits is very small (only 0.28%), which indicates the relative underdevelopment of this instrument, compared to traditional deposits. However, the very presence of certificates testifies to the bank's interest in raising funds using methods of various qualities.
The situation with the bank's foreign currency deposit portfolio on household accounts is somewhat different. Term deposits dominate here. Their share among all foreign currency deposits amounted to 57.8%, which indicates the tendency of the population to save money in foreign currency. As part of time deposits, more than a third is occupied by deposits for a period of 3 months, therefore, this is the most attractive type of currency savings. The high share of long-term deposits (18.5%) is also of interest. This indicates the ability of the population to divert significant foreign exchange funds for long periods, which allows them to issue long-term foreign currency loans or use them in other active operations. A slight lag in the share of deposits for a period of 6 months allows us to conclude that they are also relatively attractive. Indeed, otherwise their share would be much lower.
It is now necessary to consider changes in deposit portfolios as of 1998. The total growth of ruble deposits amounted to 32.8%. This was achieved due to the growth in the share of term deposits, which amounted to almost 54% of all ruble deposits of the population. The reason for what happened can be considered an increase in the attractiveness of these deposits due to higher interest rates, as well as relative stability in the economy. This is evidenced by the sharp decline in the share of term deposits for a period of one month. The population began to invest their money for longer periods. As before, the most attractive are deposits for a period of 12 months or more. The shares of deposits for 3 and 6 months have slightly decreased, but they are still used by the population, which is confirmed by their growth in absolute terms by 107 million and 88.8 million rubles, respectively.
The situation with the currency portfolio was different. The increase in deposits for the year amounted to 17.7%. The share of demand deposits has almost halved. This is explained by the fact that in 1997, through Belarusbank, lump-sum benefits were paid from the Mutual Understanding and Reconciliation Fund, as well as quarterly benefits to former soldiers of the Polish army from the Embassy of the Republic of Poland. In the reporting year, there were fewer clients receiving the above payments. Against the background of a decrease in the share of demand deposits, the share of term deposits increased significantly (to 76.6%). As with ruble deposits, the share of long-term attracted resources increased in their composition. Deposits with a maturity of 3 months decreased to 15.5%, while 6-month deposits increased to 23%, and annual deposits - to 37.5%.
This is very beneficial for the bank in terms of liquidity, however, at the same time, there is an increase in interest expenses on deposits.
It is impossible not to dwell on the situation with certificates. During the reporting period, their share fell to 0.01%. This signals the unattractiveness of this tool among customers and the need to review the conditions for their implementation and circulation.
At the beginning of 1999, the ruble deposit portfolio grew by almost 70%. There was also an increase in demand deposits by 4979.8 million rubles and their share in the ruble portfolio up to 48.8%. This can be explained by the increase in the minimum wage and, as a result, the increase in the amounts received on bank accounts as wages for employees of enterprises and organizations. In parallel, the amount of time deposits increased (growth by 4463.8). This also indicates an increase in the income of the population, which is reflected in savings. As part of time deposits, the share of deposits for a period of 1 month decreased to a minimum and amounted to only 0.53% of all ruble deposits. This is a vivid example of the loss of attractiveness of this type of deposits. To change the situation, it is necessary to change the conditions for this deposit, including the interest rate. Deposits for a period of 3 months also decreased (decreased by 4 million rubles). Consequently, they also lose their attractiveness and the population prefers other terms of investment. The population redistributed these funds into longer-term investments, as evidenced by a three-fold increase in the amount of deposits for up to 6 months and a 3.5-fold increase in deposits for 1 year and more. The share of certificates was one thousandth of a percent, which indicates the lack of demand for this product.
There were some other changes in the currency portfolio. The total increase in funds amounted to 15523.4 million rubles (an increase of 3.5 times). At the same time, balances on demand accounts continued to decline, despite the increase in the official foreign exchange rate. The reason for this was the decrease in the balances on the accounts of clients receiving quarterly payments from the Embassy of the Republic of Poland. Growth in time deposits amounted to 4.2 times, and it was achieved due to the growth of balances with accounts with a maturity of 12 months or more. It follows from this that the population is most satisfied with the conditions for keeping funds on these deposits, and also that they have opportunities for long-term savings in foreign currency.
Now consider the situation with the number of bank accounts opened by the population (see Table 3).
As of the beginning of 1997, 40,076 accounts were opened in the bank for the population. Of these, about 42.5 were demand deposits and approximately 57.5 were time deposits. It should be noted that in 1996 the current deposits of the population were consolidated, for which there was no movement for a long time. As of the beginning of 1996, 34,546 demand accounts were opened with the bank. And now they have been combined and only 16841 are left, which greatly facilitated the work of the service personnel. All foreign currency deposits accounted for only 0.7% of the total population's accounts, with demand deposits accounting for 0.5%. Therefore, the bank serves mainly ruble accounts. By the number of demand accounts, one can judge the work done by the bank to service these labor-intensive accounts. A high proportion of term deposits is achieved through compensatory accounts intended to cover the population's losses from the depreciation of their deposits in the early 90s. They occupy about three-fourths of all urgent accounts.
As of 1998, the total number of accounts decreased by 53. This was due to a decrease in the number of demand deposits in foreign currency (by 93), which is confirmed by the data in Table 2, and fixed-term ruble deposits (by 209). With regard to the latter, it should be noted that, according to Table 1, there was an increase in funds in these accounts by 1.5 times. Consequently, the population began to keep larger amounts of money. The growth in the number of ruble demand accounts indicates that additional customers have been attracted to the bank for servicing.
By 1999, the following situation had developed. The decrease in the total number of accounts continued, and they decreased by 1843 accounts. The reason for the decline was the decrease in the number of demand accounts. At the beginning of the year, special savings accounts were opened, to which the balances of deposits with amounts not exceeding 1,000 rubles were credited. Also, a continued decrease in the number of foreign currency demand accounts and fixed-term ruble deposits is noticeable. A slight increase in the number of fixed-term foreign currency deposits and a significant increase in funds for them indicates an increased amount of foreign currency funds invested by the population. The increase in the amount of funds contributed to ruble time deposits and demand deposits is evidenced by a decrease in their number and an increase in the amount of funds for them.
The dynamics of the number of accounts can be seen in the diagrams in appendices 1 and 2. As you can see, demand deposits, term deposits in general and term deposits for 12 months behave relatively stably. The reason for this is their large number, which hides minor changes in the deposit portfolio. The situation is different with time deposits for up to 12 months. As you can see, during the specified period there was a sharp drop in the number of deposits with a term of 1 month due to the loss of their attractiveness among the population. In parallel, there was an increase in the number of accounts with a term of 6 months, which is evidence of their growth in attractiveness.
Now let's analyze the structure of the deposit portfolio depending on the type of depositor, that is, the distinction will be made for deposits of legal entities and individuals (see Figure 2)
In the diagrams, one can notice an upward trend in account balances of both legal entities and individuals. For a more complete analysis, we will use the data from Table 4.
As we can see, as of the beginning of 1997, the deposits of the population significantly prevailed in the bank's deposit portfolio. Their share was 81.8%. Consequently, at that time this bank formed more than three-fourths of its credit resources at the expense of the free funds of the population. Half of all attracted funds are ruble accounts, which expands the possibilities of conducting active operations in rubles. The share of foreign currency deposits of the population is almost 30% of all bank resources. Against this background, the share of deposits of legal entities stands out insignificantly - only 18%, among which 30% are foreign currency funds. The total amount of attracted resources of the bank amounted to 19,088.46 million rubles.
As of the next reporting date, there was an increase in attracted resources by 14,062.9 million rubles (by 74%). In terms of types of depositors, it can be seen that the growth was mostly due to an increase in ruble funds of legal entities (5 times), which increased their share in the bank's resources to 36.7%. Such a high rate is ensured by the transfer of accounts of budgetary organizations to Belarusbank, as well as by attracting several new clients. A slight increase in foreign exchange balances in the accounts of enterprises indicates their weak spending, insufficient foreign economic activity. With regard to household deposits, it should be noted that their share has slightly decreased against the background of an increase in funds in the accounts of legal entities. However, in absolute terms, their ruble balances increased by 3360 million rubles (33%), foreign currency - by 943.4 (17.6%).
In 1999, the situation was as follows: the attracted resources of the bank increased by 48243.8 million rubles (2.5 times). The share of funds of legal entities increased to 44.9% in the total volume of resources, and both ruble funds (by 21129.2 million rubles) and foreign currency funds (by 2148.7 million rubles) increased. This indicates an increase in the funds circulating in the accounts. In the resources of the population, the largest increase was achieved by foreign currency accounts, which increased by 2.3 times. This happened due to the growth of the exchange rate and an increase in the propensity of the population to save in foreign currency. Ruble funds increased only 1.7 times.
Considering the changes in the shares of deposits in the deposit portfolio over the two analyzed periods, it can be assumed that deposits of legal entities will dominate in future periods.
Appendix 3 shows the dynamics of the bank's checkable deposits by category of depositors. As you can see, over the period indicated, checking accounts of individuals dominated, and their surge in the last quarter is explained by the fact that, in addition to loans, funds of compensatory government bonds began to be credited to these accounts.
Sav = Osr / V * D (1)
SSR- average term of deposit ruble storage in days;
osr- average daily balances in rubles;
IN- turnover on the issuance of deposits;
D- the number of days in the period.
This indicator reflects the dynamics of the stability of deposits, which is especially important when evaluating bank deposits as short-term lending resources. The result obtained shows the length of time during which the bank can use the funds attracted in deposits for active operations. Let us now calculate this indicator for the first quarters of 1997-98 (in billion rubles).
SSR(1997) = 11.612 / 117.7 * 90 = 10 (days),
including: on demand deposits of the population SSR(1997)=73.5 days,
on time deposits of the population SSR(1997) = 159.4 days
on legal deposits persons SSR(1997) = 1.8 days.
SSR(1998) = 44.386 / 263.23 * 90 = 15.2 days,
including: demand deposits of the population Ср (1998)= 55.2 days,
term deposits of the population SSR(1998) = 211 days,
legal deposits. persons SSR(1998) = 4.7 days.
As you can see, the average deposit ruble storage period for the reporting date was 15 days on average. This means that the funds invested in the entire deposit portfolio of the bank settle on the accounts for an average of 15 days, with the funds remaining for the longest time (211 days or 7 months); then come deposits of the population on demand (55 days or 1.8 months); and then the deposits of legal entities (almost 5 days). It can be seen from the calculations that the deposits of the population settle in bank accounts for longer periods, that is, they are more stable. This is due to the fact that most demand deposits of the population are intended to pay them wages and pensions and, therefore, are used once or twice a month. And according to the accounts of legal entities, the movement of funds is carried out several times a week, which is associated with their production activities. As a result, it turns out that the period of settling of funds on them is much less.
Compared to the same period of the previous year, there was an increase in the size of the indicator SSR, with the exception of funds held in demand deposits of the population. This indicates that people prefer not to keep large amounts of money in these accounts.
The second indicator is the level of settling of funds received in deposits. The following formula is used to calculate it:
Uo \u003d (Ok - He) / P * 100 (2)
Wo- the level of settling of funds received in deposits;
OK- balances of funds on deposits at the end of the period;
He- balances of funds on deposits at the beginning of the period;
P- receipts on deposits.
This indicator reflects the share of funds received in deposits that is not spent by the depositor and settles in the account. Based on it, banks analyze the results of the deposit policy and the possibility of conducting a credit policy. Let us calculate the level of settling of funds for the 1st quarter of 1997-98.
For the 1st quarter of 1997 we get the following numbers:
Wo(1997) = (16214,5-11653,7)/262451,9 *100 = 3,72 %
Including: on demand deposits of the population Wo(1997)= 23,2%,
on time deposits of the population Wo(1997) = 11,4%,
on deposits of legal entities Wo(1997) = 1.2%
For the 1st quarter of 1998 we get the following figures:
Wo(1998) = (31512,13-28788,5)/262451,9 * 100 = 1,04%
including: on demand deposits of the population Wo(1998) = 1,9%,
on time deposits of the population Wo(1998) = 27,6%
on deposits of legal entities Wo(1998) = 0,5%
As can be seen from the calculations, in 1997 the level of settling of funds received as deposits in the bank's deposit portfolio decreased 3.6 times and amounted to 1.04%. This means that almost 4 times less money was deposited in the accounts than at the beginning of the year. Increasing the indicator Wo occurred only with time deposits of individuals, because these accounts are intended for long-term storage of funds. This also confirms its high specific gravity in comparison with other contributions. On demand accounts of both the population and legal entities, there was a decrease in the value of the indicator Wo, and in terms of household deposits, the rate of decline was much higher. This indicates that depositors on demand accounts almost completely withdraw the amounts received by them: the population - for current consumption, enterprises and organizations - for the implementation of their economic activities.
Let's summarize. As it was seen, the bank has a fairly extensive deposit portfolio, and there are ruble and foreign currency deposits of the population and legal entities, as well as checking deposits. As of the last reporting date, in the context of borrowers, deposits of the population prevailed, however, they exceeded the deposits of legal entities by only 10%. In terms of the type of deposited currency, deposits in rubles dominate, their share is about 70% of the entire deposit portfolio. A significant share of ruble resources increases the bank's ability to lend to the population and business entities. Over the past year, cash balances on all deposits increased by 2.5 times. This is a positive factor, because as a result of the growth of the deposit base, the bank has an opportunity to expand its active operations. The bank also benefits from a high share of funds in accounts of legal entities, since these accounts pay a minimum interest. The next chapter will talk about the measures that banks can use to increase their borrowed resources.
One of the stages in the formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank is the organization of management and control in the process of deposit operations. This circumstance suggests an assessment of the deposit policy of a commercial bank.
In the economic literature, the issues of evaluating the deposit policy of a commercial bank are among the unexplored, requiring their theoretical understanding and development of practical techniques for evaluating and analyzing the results of a bank's activities in forming a deposit base, managing deposit resources and determining the effectiveness of their use, as well as developing basic recommendations for further improvement of the deposit policy in order to develop the bank.
In our opinion, each credit institution should develop and approve by the governing body a special document "Deposit Policy".
Appendix 2 of the Regulations contains a list of the main issues related to the implementation of internal control, on which the credit institution must adopt internal documents, including the "Deposit Policy" . Thus. The Bank of Russia, realizing the importance of the formation of the deposit base of commercial banks, actually obliges the latter to adopt a document defining the deposit policy.
For commercial banks that have developed and approved such a document, the author's methodology "Assessment of the deposit policy of a commercial bank" is proposed. This technique was based on the theoretical research of the author in the first chapter of the thesis on the concept of the deposit policy of the bank and the factors that determine it, as well as the procedure for the formation of the deposit policy of a commercial bank, presented in the second chapter.
When using this technique, the user may be
The methodology provides for assessing the deposit policy of a commercial bank by successively passing through a number of stages (Fig. 4). The content of each stage is presented in Table 2.1.
At the first stage - "Assessment of the organizational aspects of the deposit policy of a commercial bank" - the presence in the bank is assessed:
* a deposit policy document containing the goals and objectives of the deposit policy, the bank's strategy and means of its implementation;
* internal procedures and regulations accompanying the process of attracting funds to deposit accounts, namely: regulations on deposits of legal entities, regulations on deposits of individuals, instructions on the procedure for making deposit transactions with legal entities, instructions on the procedure for making deposit transactions with individuals;
* subdivisions and management bodies involved in the analysis of the deposit portfolio and management of deposit resources, exercising control and responsible for the implementation of relevant decisions;
* an information database, on the basis of which the bank's management and other managers (heads of departments) can evaluate the consequences of decisions made, their adequacy to the needs of the bank and market requirements.
Table 2.1
Characteristics of the individual stages of assessing the deposit policy of a commercial bank
|
Stage name |
Characteristic | |
|
1. Assessment of the organizational aspects of the deposit policy of a commercial bank | ||
|
2. Analysis of the deposit portfolio of a commercial bank | ||
|
3. Assessment of the sufficiency of deposit resources attracted by a commercial bank | ||
|
4. Determining the efficiency of using the deposit resources of a commercial bank | ||
|
5. Making a motivated judgment but evaluating the deposit policy of a commercial bank | ||
An assessment of the organizational aspects of the deposit policy being implemented by a commercial bank makes it possible to obtain information on the compliance of the developed deposit policy of the bank, presented in the form of a package of documents called the Deposit Policy Guide, with the actual situation in practice and the tasks being solved.
An assessment of the organizational aspects of the implemented deposit policy of a commercial bank is carried out annually under the guidance of the Deputy Chairman of the Board of the bank responsible for raising resources and liquidity with the appointment of persons (preferably included in the asset and liability management committee, specialists from the internal control department) responsible for collecting and summarizing information , as well as for providing a report on the results of the implemented deposit policy to the Chairman of the Board of the Bank (the Board of the Bank).
The assessment of the organizational aspects of the implemented deposit policy of a commercial bank is carried out on the basis of answers to the following questions developed by the author:
1. Does a commercial bank have a strategy approved by the Chairman of the Board (Board) in the field of the bank's deposit activities (hereinafter referred to as the Strategy) and does it correspond to the general strategic goals of the bank and its banking policy?
2. When developing the Strategy, did the credit institution evaluate its
Conducting SWOT - analysis and development of the Strategy?
3. Does the Strategy define banking products, operations, areas of activity in which the bank expects to gain advantages over competitors, as well as the sequence of implementation of the planned plans, taking into account the interconnection of strategic decisions regarding:
4. Does the document on the deposit policy of the bank define the methods by which the credit institution intends to achieve success (more efficient use of existing opportunities, capital growth, increase in the resource base, increase in the number of depositors, development of the territorial network, including through the creation of branches , additional offices, deposit cash desks (outside the cash desk), etc.)?
5. Does the document on the deposit policy of the bank take into account the specifics of the functioning of branches (additional offices) located outside the location of the head bank, which affect the marketing strategy?
6. Does the credit institution have a documented action plan defined by the deposit policy?
7. Does the credit institution regularly monitor the degree of achievement of the goals and objectives set in the deposit policy?
8. Are the plans developed by the credit institution to achieve the goals defined by the deposit policy being implemented?
9. Has the credit institution developed action plans in case of unforeseen circumstances that could provoke a loss of liquidity and solvency, have a significant negative impact on capital and/or financial performance?
10. Does the credit institution have divisions (officials) responsible for the analysis of the deposit portfolio and assessment of the bank's deposit policy?
11. Does the credit institution have the reports used by the organization on the state of the credit institution, the ratio of assets and liabilities, the risks taken?
12. Does the credit institution have internal documents on organizing the deposit process, managing the risks inherent in the deposit activities of the credit institution (deposit, interest, liquidity risk, operational), as well as the procedure for monitoring compliance on a daily basis with mandatory standards, internal restrictions on deposit operations?
13. Does the credit institution have formalized procedures for assessing the potential impact on the depository activity of the credit institution of a number of specified changes in risk factors that correspond to exceptional but probable events (massive outflow of depositors' funds)?
Positive answers to the above questions allow us to speak about the good organizational support of the implemented deposit policy.
Negative answers to some of the above questions are the basis for the bank's management (heads of departments) to take control over the elimination of identified shortcomings and / or consider the possibility of making adjustments to the bank's deposit policy.
The first stage ends with the execution of the results of the assessment of the organizational aspects of the deposit policy in the form of a document containing the shortcomings identified during the assessment, as well as the planned measures to eliminate these shortcomings, indicating specific deadlines and persons responsible for the implementation of the necessary actions.
When formulating the conclusion, special attention should be paid to finding out the reasons for the discrepancy between the actually used in practice intra-bank documents on the organization of the deposit process, performed by the bank's divisions, and the deposit policy developed by the bank.
The second stage of evaluating the deposit policy of a commercial bank is the analysis of the deposit portfolio of a commercial bank.
The successful functioning and development of the bank largely depends on after the adoption of all management decisions.
It should be noted that in the Russian practice of analyzing banking activities, there are no independent methods for analyzing a bank's deposit portfolio. There are methods for analyzing the resource base, which banks independently develop, and within their framework they can determine the directions for analyzing the deposit portfolio, taking into account the specifics of their activities and the characteristics of their operations.
How to analyze the deposit portfolio has not been studied in detail in the economic literature. So, M.A. Pomorina touches upon issues of operations. A number of authors show the need for an analysis of passive operations (the bank's resource base) and offer appropriate methods. As part of the analysis of the bank's resources, G.S. Panova and O.V. Kotin propose to analyze the deposit portfolio by the subjects of attraction and the urgency of investing funds by investors. Most of the authors, among them S.Yu. Buevich, O.G. Korolev, E.B. Shirinskaya, speaking about the analysis of passive or deposit operations, focuses solely on the stability and cost of funds raised (deposits), as well as the efficiency of resource use. However, given the variety of deposits and the specifics of economic relations that develop during deposit operations, in the study of banking activities in general and indicators that allow assessing the quality of funds raised (bank liabilities), in particular, the analysis of the deposit portfolio should occupy a special place. The need for such an analysis is confirmed by one of the main conclusions drawn from the analysis of the resource base and deposit operations of credit institutions of the Russian Federation carried out in the second chapter of the study - the share of deposits in the total volume of liabilities of the banking sector is increasing.
In theoretical terms, the author also relies on the conclusions of the first chapter of the study regarding the subject side of the implementation of the bank's deposit policy, i.e., the determination of the necessary combination of deposits of different types (the level of attracted deposits, the timing of their attraction, the cost of deposits) in conjunction with the management of mobilized resources, and in methodological plan - on previously conducted research by specialists in the field of banking regarding the assessment of the bank's resource base.
The methodology for analyzing the bank's deposit portfolio is the result of a search for the most appropriate way to assess the accuracy of the implemented strategic targets and objectives of the bank's deposit policy.
When developing a methodology for analyzing the deposit portfolio of a bank, the author proceeded from the following provisions:
The analysis of the bank's deposit portfolio is carried out in order to:
The analysis of the deposit portfolio, based on the basic characteristics of the deposit and deposit operations, is carried out in the following areas (Fig. 1):
Analysis in the above areas can be carried out only if the bank has a well-functioning system of analytical information.
Rice. 1. The main directions of the analysis of the deposit portfolio of a commercial bank